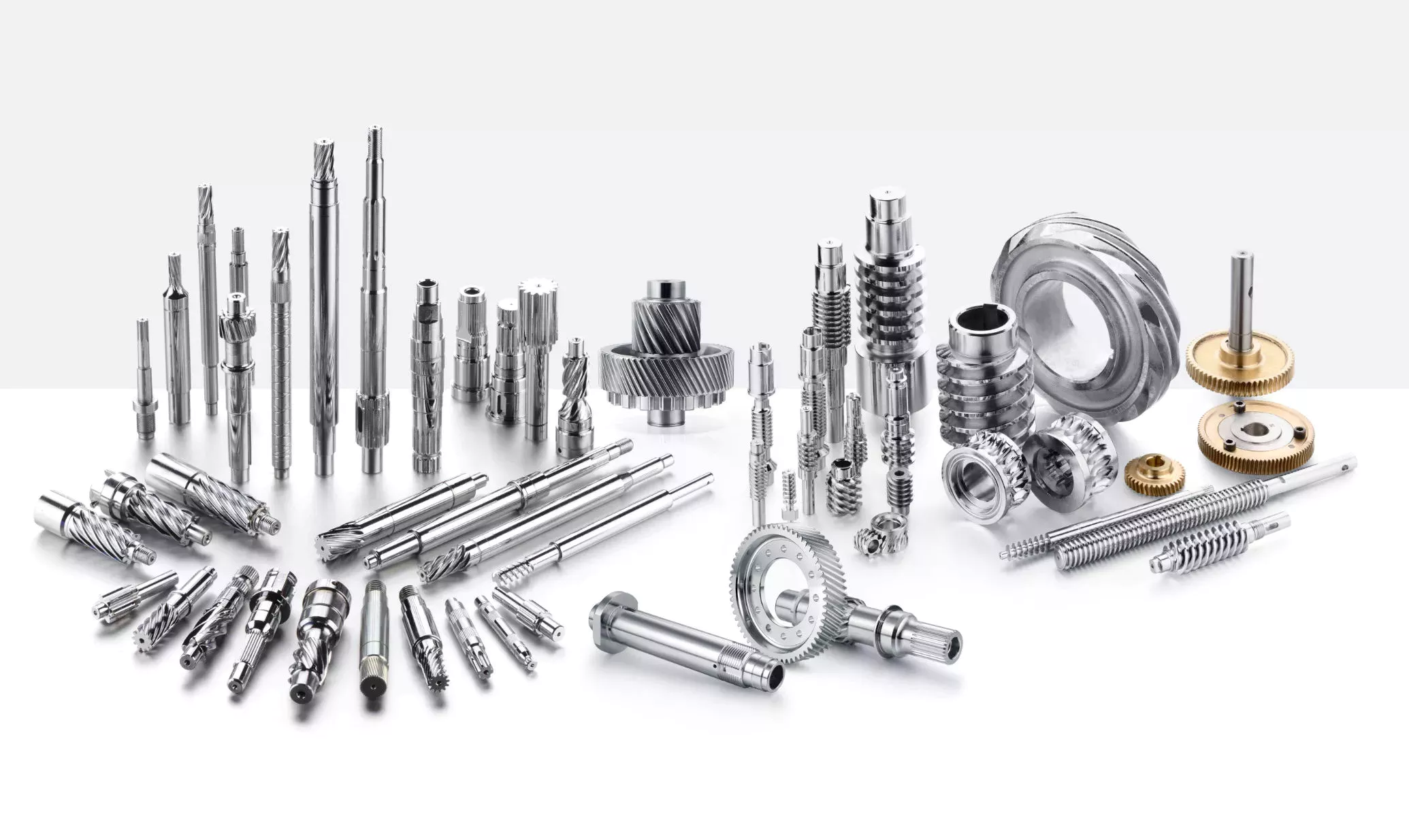
Product Description
Welcome to choose KORTON INDUSTRIAL LIMITED.;
NO 1.; our adwantages:;
1.; 14 years bearing products manufacturing and 4 years exporting experiences.;
2.; OEM order and non-standard bearing order can be accepted.;
3.; Our main bearing products include Deep groove ball bearings,; tapered roller bearings,; cylindrical rollerbearings,; spherical ball bearings,; spherical roller bearings,; angular contact bearings,; needle roller bearings,; thrust ball bearings,; spherical plain bearings,; spherical bearings,; automotive bearings pump bearings,; and many nonstandard bearings are also in our product range.;
4.; Sample available
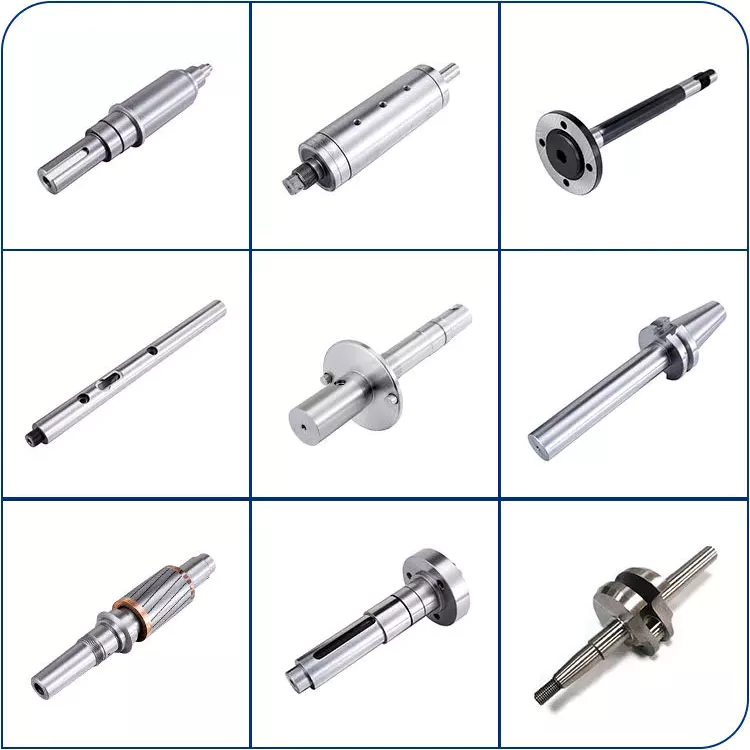
NO 2.; Description:; Needle Bearing
| 1 | Drawn Cup Needle Bearing | HK,; BK |
| 2 | Needle Bearing with Inner Ring | NA,; NKI |
| 3 | Needle Bearing without Inner Ring | NK,; RNA |
| 4 | Full Complement Needle Bearing | NAV |
| 5 | Radial Needle Roller and Cage Assemblies | K,; KK |
| 6 | Thrust Needle Roller and Cage Assemblies | AXK,; AS |
NO 3.; OEM all brand bearing
1.; deep groove ball bearing 6000,;6200,;6300,;6400,;61800,;61900,;Z,;RS,;ZZ,;2RS
2.; spherical roller bearing 22200,;22300,;23000,;24000,;23100,;24100,;CA,;CC,;E,;W33
3.; cylindrical roller bearing N,;NU,;NJ,;NN,;NUP,;E,;ECP,;ECM,;ECJ
4.; taper roller bearing 35710,;30300,;32200,;32300,;31300,;32000
5.; Aligning ball bearing 1200,;1300,;2200,;2300,;
6.; needle roller bearing NA,;NAV,;NK,;NKI,;RNA,;NK,;RNAV,;ZKLF,;ZKLN,;ZARF,;ZARN
7.; thrust ball bearing 51100,;51200,;51300,;51400,;E,;M
8.; angular contact ball bearing7000,;7100,;7200,;7300,;AC,;BECBM,;C
9.; spherical plain bearing GE,;GEG,;GEEW,;U,;UC,;UG,;GX,;GAC,;SA,;SABP
10.;Wheel hub bearing /ceramic bearing/plastic bearing/lazy susan bearing
NO 4.; Needle Bearing Specification:;
| Seals Types | OPEN |
| Vibration Level | Z1V1,;Z2V2,;Z3V3 |
| Clearance | C2,;C0,;C3,;C4,;C5 |
| Tolerance Codes | ABEC-1,;ABEC-3,;ABEC-5 |
| Materral | GCr15-China/AISI52100-USA/Din100Cr6-Germany |
| MOQ | 1Set at least |
| Delivery Time | 15-45 days after contract |
| Payment Terms | TT/PAPAL/WESTERN UNION |
| Pavkage | Tube package+outer carton+pallets;Single box+outer carton+pallets; Tube pavkge+middle box+outer carton+pallets; According to your requirement |
NO 5.; Needle Bearing Models and Size:;
| Bearing Designation | Boundary Dimensions | Basic Load Ratings | Limiting Speed | ||||
| HK | BK | Fw | D | C | Cr Dynamic | Cor Static | Oil |
| mm | mm | mm | Nm | Nm | |||
| HK0306TN | BK0306TN | 3 | 6.;5 | 6 | 1320 | 950 | 60000 |
| HK0408TN | BK0408TN | 4 | 8 | 8 | 1540 | 1070 | 40000 |
| HK0509 | BK0509 | 5 | 9 | 9 | 2200 | 1790 | 36000 |
| HK0608 | – | 6 | 10 | 8 | 1830 | 1550 | 32000 |
| HK0609 | BK0609 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 2650 | 2400 | 3000 |
| HK0708 | – | 7 | 11 | 8 | 2800 | 2150 | 27000 |
| HK0709 | BK0709 | 7 | 11 | 9 | 2800 | 2150 | 27000 |
| HK0808 | BK0808 | 8 | 12 | 8 | 2550 | 2400 | 21000 |
| HK571 | BK571 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 3700 | 3450 | 21000 |
| HK08×14×10 | – | 8 | 14 | 10 | 3800 | 3950 | 25000 |
| HK08×14×12 | – | 8 | 14 | 12 | 4100 | 4320 | 25000 |
| HK571 | BK571 | 9 | 13 | 10 | 4050 | 4250 | 25000 |
| HK571 | – | 9 | 13 | 12 | 5000 | 6000 | 25000 |
| HK1571 | BK1571 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 3900 | 4800 | 19000 |
| HK1012 | BK1012 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 5000 | 6300 | 19000 |
| HK1015 | – | 10 | 14 | 15 | 6700 | 7800 | 19000 |
| HK10×16×10 | – | 10 | 16 | 10 | 6800 | 8800 | 18000 |
| HK10×16×12 | – | 10 | 16 | 12 | 6800 | 8800 | 18000 |
| HK10×16×15 | – | 10 | 16 | 15 | 6800 | 8800 | 19000 |
| HK1210 | BK1210 | 12 | 16 | 10 | 4150 | 5800 | 19000 |
| HK1212 | BK1212 | 12 | 18 | 12 | 3800 | 5100 | 15000 |
| HK12×17×12 | – | 12 | 17 | 12 | 5100 | 7000 | 15000 |
| HK12×17×15 | – | 12 | 17 | 15 | 5100 | 7000 | 15000 |
| HK12×17×18 | – | 12 | 17 | 18 | 5100 | 7000 | 15000 |
| HK12×18×12 | BK12×18×12 | 12 | 18 | 12 | 550 | 6300 | 17000 |
| HK1312 | BK1312 | 13 | 19 | 12 | 6200 | 7100 | 17000 |
| HK13.;5×20×12 | – | 13.;5 | 20 | 12 | 6250 | 7590 | 16000 |
| HK1412 | – | 14 | 20 | 12 | 6800 | 7500 | 14000 |
| HK1416 | – | 14 | 20 | 16 | 7300 | 9000 | 14000 |
| HK15×20×12 | – | 15 | 20 | 12 | 5800 | 6000 | 14000 |
| HK15×20×16 | – | 15 | 20 | 16 | 6000 | 6200 | 14000 |
| HK15×20×20 | – | 15 | 20 | 20 | 6100 | 6400 | 14000 |
| HK1512 | BK1512 | 15 | 21 | 12 | 7000 | 8400 | 14000 |
| HK1514 | – | 15 | 21 | 14 | 8500 | 10400 | 13000 |
| HK1515 | – | 15 | 21 | 15 | 9100 | 11400 | 13000 |
| HK1516 | BK1516 | 15 | 21 | 16 | 9800 | 11400 | 14000 |
| HK1522 | – | 15 | 21 | 22 | 10400 | 16500 | 14000 |
| HK15×22×12 | – | 15 | 22 | 12 | 14300 | 18400 | 13000 |
| HK1612 | BK1612 | 16 | 22 | 12 | 7100 | 9200 | 14000 |
| HK1614 | – | 16 | 22 | 14 | 8800 | 9900 | 12000 |
| HK1616 | BK1616 | 16 | 22 | 16 | 15710 | 14300 | 14000 |
| HK1622 | – | 16 | 22 | 22 | 11100 | 17400 | 14000 |
| HK1712 | – | 17 | 23 | 12 | 6900 | 9300 | 13000 |
| HK1714 | – | 17 | 23 | 14 | 6800 | 15710 | 10000 |
| HK1716 | – | 17 | 23 | 16 | 8500 | 12500 | 10000 |
| HK1718 | – | 17 | 23 | 18 | 9500 | 10600 | 10000 |
| HK17×25×14 | – | 17 | 25 | 14 | 13100 | 147000 | 10000 |
| HK17×25×18 | – | 17 | 25 | 18 | 9500 | 10600 | 11000 |
| HK1812 | – | 18 | 24 | 12 | 7100 | 9900 | 12000 |
| HK1816 | BK1816 | 18 | 24 | 16 | 10600 | 15300 | 12000 |
| HK2571 | – | 20 | 26 | 10 | 5900 | 7200 | 10000 |
| HK2014 | – | 20 | 26 | 14 | 9700 | 18100 | 9000 |
| HK2016 | BK2016 | 20 | 26 | 16 | 11700 | 29100 | 10000 |
| HK2018 | – | 20 | 26 | 18 | 7900 | 12800 | 9000 |
| HK2571 | – | 20 | 26 | 20 | 13700 | 24000 | 10000 |
| HK2030 | – | 20 | 26 | 30 | 21800 | 40000 | 15710 |
| HK20×27×20 | – | 20 | 27 | 20 | 26300 | 47800 | 9900 |
| HK2210 | – | 22 | 28 | 10 | 7200 | 9500 | 1571 |
| HK2212 | BK2212 | 22 | 28 | 12 | 8100 | 10400 | 1571 |
| HK22×29×30 | – | 22 | 29 | 30 | 19400 | 33100 | 9000 |
| HK2512 | BK2512 | 25 | 32 | 12 | 10000 | 14200 | 9000 |
| HK2525 | BK2525 | 25 | 32 | 25 | 22200 | 36700 | 9000 |
| HK2816 | BK2816 | 28 | 35 | 16 | 15400 | 22500 | 8700 |
| HK2820 | BK2820 | 28 | 35 | 20 | 18900 | 32000 | 8700 |
| HK3012 | BK3012 | 30 | 37 | 12 | 15710 | 16200 | 8100 |
| HK3571 | BK3571 | 30 | 37 | 20 | 19700 | 33500 | 8100 |
| HK3224 | – | 32 | 39 | 24 | 25500 | 5200 | 7300 |
| HK3516 | BK3516 | 35 | 42 | 16 | 15700 | 27500 | 7100 |
| HK4012 | BK4012 | 40 | 47 | 12 | 14000 | 24300 | 6300 |
| HK4512 | BK4512 | 45 | 52 | 12 | 12900 | 22500 | 5800 |
| HK5571 | BK5571 | 50 | 58 | 20 | 28000 | 60000 | 5300 |
| HK6012 | BK6012 | 60 | 68 | 12 | 12400 | 29000 | 4100 |
| Shaft Dia | Unit No.; | Dimensions (mm); | Basic Load Ratings | Limiting speed | Weight | ||||||
| mm | d | F | D | B | r min | S | C KN | C0 KN | r/min | g | |
| 10 | NA4900 | 10 | 14 | 22 | 13 | 0.;3 | 0.;5 | 8.;5 | 9.;2 | 20000 | 23 |
| 12 | NA4901 | 12 | 16 | 24 | 13 | 0.;3 | 0.;5 | 9.;4 | 10.;9 | 17000 | 26 |
| 15 | NA4902 | 15 | 20 | 28 | 13 | 0.;3 | 0.;5 | 10.;6 | 13.;6 | 14000 | 34 |
| 17 | NA4903 | 17 | 22 | 30 | 13 | 0.;3 | 0.;5 | 11 | 14.;6 | 12000 | 37 |
| 20 | NA4904 | 20 | 25 | 37 | 17 | 0.;3 | 0.;8 | 21 | 25.;5 | 10000 | 141 |
| 22 | NA49/22 | 22 | 28 | 39 | 17 | 0.;3 | 0.;8 | 22.;8 | 29.;5 | 9500 | 80 |
| 25 | NA4905 | 25 | 30 | 42 | 17 | 0.;3 | 0.;8 | 23.;6 | 31.;5 | 9500 | 88 |
| 28 | NA49/28 | 28 | 32 | 45 | 17 | 0.;3 | 0.;8 | 24.;4 | 33.;5 | 8500 | 97.;7 |
| 30 | NA4906 | 30 | 35 | 47 | 17 | 0.;3 | 0.;8 | 25 | 35.;5 | 8000 | 101 |
| 32 | NA49/32 | 32 | 40 | 52 | 20 | 0.;6 | 0.;8 | 30.;5 | 47.;5 | 7000 | 158 |
| 35 | NA4907 | 35 | 42 | 55 | 20 | 0.;6 | 0.;8 | 31.;5 | 50 | 7000 | 170 |
| 40 | NA4908 | 40 | 48 | 62 | 22 | 0.;6 | 1 | 43 | 67 | 6000 | 230 |
| 45 | NA4909 | 45 | 52 | 68 | 22 | 0.;6 | 1 | 45 | 73 | 8500 | 5500 |
| 50 | NA4910 | 50 | 58 | 72 | 22 | 0.;6 | 1 | 47 | 80 | 5000 | 274 |
| 55 | NA4911 | 55 | 63 | 80 | 25 | 1 | 1.;5 | 58 | 100 | 4700 | 393 |
| 60 | NA4912 | 60 | 68 | 85 | 25 | 1 | 1.;5 | 60 | 108 | 4300 | 426 |
| 65 | NA4913 | 65 | 72 | 90 | 25 | 1 | 1.;5 | 61 | 112 | 4100 | 456 |
| 70 | NA4914 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 30 | 1 | 1.;5 | 84 | 156 | 3800 | 728 |
| 75 | NA4915 | 75 | 85 | 105 | 30 | 1 | 1.;5 | 86 | 162 | 3600 | 775 |
| 80 | NA4916 | 80 | 90 | 110 | 30 | 1 | 1.;5 | 89 | 174 | 3400 | 878 |
| 85 | NA4917 | 85 | 100 | 120 | 35 | 1.;1 | 1 | 111 | 237 | 2800 | 1250 |
| 90 | NA4918 | 90 | 105 | 125 | 35 | 1.;1 | 1 | 114 | 250 | 3000 | 1312 |
| 95 | NA4919 | 95 | 110 | 130 | 3 | 1.;1 | 1 | 116 | 260 | 2800 | 1371 |
| 100 | NA4920 | 100 | 115 | 140 | 40 | 1.;1 | 2 | 128 | 270 | 2900 | 1900 |
| 110 | NA4922 | 110 | 125 | 150 | 40 | 1.;1 | 2 | 132 | 290 | 2600 | 2070 |
| 120 | NA4924 | 120 | 135 | 165 | 45 | 1.;1 | 2 | 181 | 390 | 2300 | 2860 |
| 130 | NA4926 | 130 | 150 | 180 | 50 | 1.;5 | 1.;5 | 203 | 470 | 2000 | 3900 |
| 140 | NA4928 | 140 | 160 | 190 | 50 | 1.;5 | 1.;5 | 209 | 500 | 1800 | 4150 |
| NO.; | NO.; | SIZE | ||||
| WITH INNER | WITHOUT INNER | mm | ||||
| d | Fw | D | C | r min | ||
| NA5902 | RNA5902 | 15 | 20 | 28 | 18 | 0.;3 |
| NA5903 | RNA5903 | 17 | 22 | 30 | 18 | 0.;3 |
| NA5904 | RNA5904 | 20 | 25 | 37 | 23 | 0.;3 |
| NA59/22 | RNA59/22 | 22 | 28 | 39 | 23 | 0.;3 |
| NA5905 | RNA5905 | 25 | 30 | 42 | 23 | 0.;3 |
| NA59/28 | RNA59/28 | 28 | 32 | 45 | 23 | 0.;3 |
| NA5906 | RNA5906 | 30 | 35 | 47 | 23 | 0.;3 |
| NA59/32 | RNA59/32 | 32 | 40 | 52 | 27 | 0.;6 |
| NA5907 | RNA5907 | 35 | 42 | 55 | 27 | 0.;6 |
| NA5908 | RNA5908 | 40 | 48 | 62 | 30 | 0.;6 |
| NA5909 | RNA5909 | 45 | 52 | 68 | 30 | 0.;6 |
| NA5910 | RNA5910 | 50 | 58 | 72 | 30 | 0.;6 |
| NA5911 | RNA5911 | 55 | 63 | 80 | 34 | 1 |
| NA5912 | RNA5912 | 60 | 68 | 85 | 34 | 1 |
| NA5913 | RNA5913 | 65 | 72 | 90 | 34 | 1 |
| NA5914 | RNA5914 | 70 | 80 | 100 | 40 | 1 |
| NA5915 | RNA5915 | 75 | 85 | 105 | 40 | 1 |
| NA5916 | RNA5916 | 80 | 90 | 110 | 40 | 1 |
| NA5917 | RNA5917 | 85 | 100 | 120 | 46 | 1.;1 |
| NA5918 | RNA5918 | 90 | 105 | 125 | 46 | 1.;1 |
| NA5919 | RNA5919 | 95 | 110 | 130 | 46 | 1.;1 |
| NA5920 | RNA5920 | 100 | 115 | 140 | 54 | 1.;1 |
| NA5922 | RNA5922 | 110 | 125 | 150 | 54 | 1.;1 |
| NA5924 | RNA5924 | 120 | 135 | 165 | 60 | 1.;1 |
| NA5926 | RNA5926 | 130 | 150 | 180 | 67 | 1.;5 |
| NA5928 | RNA5928 | 140 | 160 | 190 | 67 | 1.;5 |
| Bearing NO.; | Shaft Diameter (mm); | Dimension(mm); | Mass Approx (g); | ||
| Current Code | Fw | D | C | ||
| K3X5X7TN | 3 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 0.;3 |
| K3X5X9TN | 3 | 3 | 5 | 9 | 0.;4 |
| K3X6X7TN | 3 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 0.;4 |
| K4X7X7TN | 4 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 0.;5 |
| K4X7X10TN | 4 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 0.;7 |
| K5X8X8TN | 5 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 0.;7 |
| K5X8X10TN | 5 | 5 | 8 | 10 | 0.;9 |
| K6X9X8TN | 6 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 0.;8 |
| K6X9X10TN | 6 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 1 |
| K6X10X13TN | 6 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 1.;3 |
| K7X10X8TN | 7 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 0.;9 |
| K7X10X10TN | 7 | 7 | 10 | 10 | 1.;1 |
| K8X11X8TN | 8 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 1.;1 |
| K8X11X10TN | 8 | 8 | 11 | 10 | 1.;7 |
| K8X11X13TN | 8 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 1.;8 |
| K8X12X10TN | 8 | 8 | 12 | 10 | 1.;3 |
| K9X12X10TN | 9 | 9 | 12 | 10 | 1.;5 |
| K9X12X13TN | 9 | 9 | 12 | 13 | 1.;9 |
| K10X13X10TN | 10 | 10 | 13 | 10 | 1.;6 |
| K10X13X13TN | 10 | 10 | 13 | 13 | 2.;1 |
| K10X13X16TN | 10 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 2.;2 |
| K10X14X10TN | 10 | 10 | 14 | 10 | 2.;9 |
| K10X14X13TN | 10 | 10 | 14 | 13 | 4.;3 |
| K10X16X12TN | 10 | 10 | 16 | 12 | 3.;7 |
| K12X15X9TN | 12 | 12 | 15 | 9 | 2.;7 |
| K12X15X10TN | 12 | 12 | 15 | 10 | 1.;9 |
| K12X15X13TN | 12 | 12 | 15 | 13 | 2.;4 |
| K12X16X8TN | 12 | 12 | 16 | 8 | 2.;9 |
| K12X16X10TN | 12 | 12 | 16 | 10 | 3.;4 |
| K12X16X13TN | 12 | 12 | 16 | 13 | 3.;8 |
| K12X17X13TN | 12 | 12 | 17 | 13 | 4.;4 |
| K12X18X12TN | 12 | 12 | 18 | 12 | 5 |
| K12X15X20TN | 12 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 3.;8 |
| K14X17X10 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 10 | 4 |
| K14X17X17 | 14 | 14 | 17 | 17 | 6.;8 |
| K14X18X10 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 10 | 4.;8 |
| K14X18X13 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 13 | 6.;3 |
| K14X18X14 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 14 | 6.;8 |
| K14X18X15 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 15 | 7.;3 |
| K14X18X17 | 14 | 14 | 18 | 17 | 8.;1 |
| K14X20X12 | 14 | 14 | 20 | 12 | 8.;6 |
| K15X18X14 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 14 | 5.;3 |
| K15X18X17 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 17 | 6.;4 |
| K15X19X10 | 15 | 15 | 19 | 10 | 5.;1 |
Why Choose Us:;
We are an industrial and trading company.;We have our own brand:; SFNB .;If you interested in our product,;I can take you to visit our factory.;
Our factory have advanced testing equipment,;before the every product leave the factory,;we will be testing.;We can send samples to you,;you can test the quality,;and if you accept the sample quality,;we can promise:; the follow-up orders’ quality will be the same as samples.;
About ordinary standard type of bearing ,;We have rich inventory,;not have MOQ,;if your need a product is Non-standard size,;need customize,;we will according the product size to determine the MOQ.;
Our company can accept OEM,;you can send sample to me,;we can manufacturing products the same as sample.;Meanwhile,;we also can accept some well-known brands of OEM,;
If the amount of money is less,;you can pay it by Paypal.;Of course you can payment by TT or Western Union etc.;
Calculating the Deflection of a Worm Shaft
In this article, we’ll discuss how to calculate the deflection of a worm gear’s worm shaft. We’ll also discuss the characteristics of a worm gear, including its tooth forces. And we’ll cover the important characteristics of a worm gear. Read on to learn more! Here are some things to consider before purchasing a worm gear. We hope you enjoy learning! After reading this article, you’ll be well-equipped to choose a worm gear to match your needs.
Calculation of worm shaft deflection
The main goal of the calculations is to determine the deflection of a worm. Worms are used to turn gears and mechanical devices. This type of transmission uses a worm. The worm diameter and the number of teeth are inputted into the calculation gradually. Then, a table with proper solutions is shown on the screen. After completing the table, you can then move on to the main calculation. You can change the strength parameters as well.
The maximum worm shaft deflection is calculated using the finite element method (FEM). The model has many parameters, including the size of the elements and boundary conditions. The results from these simulations are compared to the corresponding analytical values to calculate the maximum deflection. The result is a table that displays the maximum worm shaft deflection. The tables can be downloaded below. You can also find more information about the different deflection formulas and their applications.
The calculation method used by DIN EN 10084 is based on the hardened cemented worm of 16MnCr5. Then, you can use DIN EN 10084 (CuSn12Ni2-C-GZ) and DIN EN 1982 (CuAl10Fe5Ne5-C-GZ). Then, you can enter the worm face width, either manually or using the auto-suggest option.
Common methods for the calculation of worm shaft deflection provide a good approximation of deflection but do not account for geometric modifications on the worm. While Norgauer’s 2021 approach addresses these issues, it fails to account for the helical winding of the worm teeth and overestimates the stiffening effect of gearing. More sophisticated approaches are required for the efficient design of thin worm shafts.
Worm gears have a low noise and vibration compared to other types of mechanical devices. However, worm gears are often limited by the amount of wear that occurs on the softer worm wheel. Worm shaft deflection is a significant influencing factor for noise and wear. The calculation method for worm gear deflection is available in ISO/TR 14521, DIN 3996, and AGMA 6022.
The worm gear can be designed with a precise transmission ratio. The calculation involves dividing the transmission ratio between more stages in a gearbox. Power transmission input parameters affect the gearing properties, as well as the material of the worm/gear. To achieve a better efficiency, the worm/gear material should match the conditions that are to be experienced. The worm gear can be a self-locking transmission.
The worm gearbox contains several machine elements. The main contributors to the total power loss are the axial loads and bearing losses on the worm shaft. Hence, different bearing configurations are studied. One type includes locating/non-locating bearing arrangements. The other is tapered roller bearings. The worm gear drives are considered when locating versus non-locating bearings. The analysis of worm gear drives is also an investigation of the X-arrangement and four-point contact bearings.
Influence of tooth forces on bending stiffness of a worm gear
The bending stiffness of a worm gear is dependent on tooth forces. Tooth forces increase as the power density increases, but this also leads to increased worm shaft deflection. The resulting deflection can affect efficiency, wear load capacity, and NVH behavior. Continuous improvements in bronze materials, lubricants, and manufacturing quality have enabled worm gear manufacturers to produce increasingly high power densities.
Standardized calculation methods take into account the supporting effect of the toothing on the worm shaft. However, overhung worm gears are not included in the calculation. In addition, the toothing area is not taken into account unless the shaft is designed next to the worm gear. Similarly, the root diameter is treated as the equivalent bending diameter, but this ignores the supporting effect of the worm toothing.
A generalized formula is provided to estimate the STE contribution to vibratory excitation. The results are applicable to any gear with a meshing pattern. It is recommended that engineers test different meshing methods to obtain more accurate results. One way to test tooth-meshing surfaces is to use a finite element stress and mesh subprogram. This software will measure tooth-bending stresses under dynamic loads.
The effect of tooth-brushing and lubricant on bending stiffness can be achieved by increasing the pressure angle of the worm pair. This can reduce tooth bending stresses in the worm gear. A further method is to add a load-loaded tooth-contact analysis (CCTA). This is also used to analyze mismatched ZC1 worm drive. The results obtained with the technique have been widely applied to various types of gearing.
In this study, we found that the ring gear’s bending stiffness is highly influenced by the teeth. The chamfered root of the ring gear is larger than the slot width. Thus, the ring gear’s bending stiffness varies with its tooth width, which increases with the ring wall thickness. Furthermore, a variation in the ring wall thickness of the worm gear causes a greater deviation from the design specification.
To understand the impact of the teeth on the bending stiffness of a worm gear, it is important to know the root shape. Involute teeth are susceptible to bending stress and can break under extreme conditions. A tooth-breakage analysis can control this by determining the root shape and the bending stiffness. The optimization of the root shape directly on the final gear minimizes the bending stress in the involute teeth.
The influence of tooth forces on the bending stiffness of a worm gear was investigated using the CZPT Spiral Bevel Gear Test Facility. In this study, multiple teeth of a spiral bevel pinion were instrumented with strain gages and tested at speeds ranging from static to 14400 RPM. The tests were performed with power levels as high as 540 kW. The results obtained were compared with the analysis of a three-dimensional finite element model.
Characteristics of worm gears
Worm gears are unique types of gears. They feature a variety of characteristics and applications. This article will examine the characteristics and benefits of worm gears. Then, we’ll examine the common applications of worm gears. Let’s take a look! Before we dive in to worm gears, let’s review their capabilities. Hopefully, you’ll see how versatile these gears are.
A worm gear can achieve massive reduction ratios with little effort. By adding circumference to the wheel, the worm can greatly increase its torque and decrease its speed. Conventional gearsets require multiple reductions to achieve the same reduction ratio. Worm gears have fewer moving parts, so there are fewer places for failure. However, they can’t reverse the direction of power. This is because the friction between the worm and wheel makes it impossible to move the worm backwards.
Worm gears are widely used in elevators, hoists, and lifts. They are particularly useful in applications where stopping speed is critical. They can be incorporated with smaller brakes to ensure safety, but shouldn’t be relied upon as a primary braking system. Generally, they are self-locking, so they are a good choice for many applications. They also have many benefits, including increased efficiency and safety.
Worm gears are designed to achieve a specific reduction ratio. They are typically arranged between the input and output shafts of a motor and a load. The 2 shafts are often positioned at an angle that ensures proper alignment. Worm gear gears have a center spacing of a frame size. The center spacing of the gear and worm shaft determines the axial pitch. For instance, if the gearsets are set at a radial distance, a smaller outer diameter is necessary.
Worm gears’ sliding contact reduces efficiency. But it also ensures quiet operation. The sliding action limits the efficiency of worm gears to 30% to 50%. A few techniques are introduced herein to minimize friction and to produce good entrance and exit gaps. You’ll soon see why they’re such a versatile choice for your needs! So, if you’re considering purchasing a worm gear, make sure you read this article to learn more about its characteristics!
An embodiment of a worm gear is described in FIGS. 19 and 20. An alternate embodiment of the system uses a single motor and a single worm 153. The worm 153 turns a gear which drives an arm 152. The arm 152, in turn, moves the lens/mirr assembly 10 by varying the elevation angle. The motor control unit 114 then tracks the elevation angle of the lens/mirr assembly 10 in relation to the reference position.
The worm wheel and worm are both made of metal. However, the brass worm and wheel are made of brass, which is a yellow metal. Their lubricant selections are more flexible, but they’re limited by additive restrictions due to their yellow metal. Plastic on metal worm gears are generally found in light load applications. The lubricant used depends on the type of plastic, as many types of plastics react to hydrocarbons found in regular lubricant. For this reason, you need a non-reactive lubricant.