Product Description
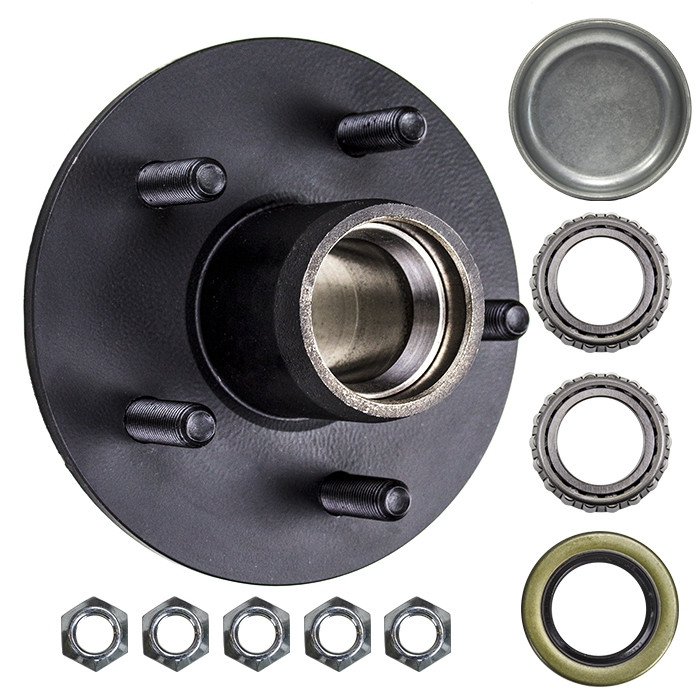
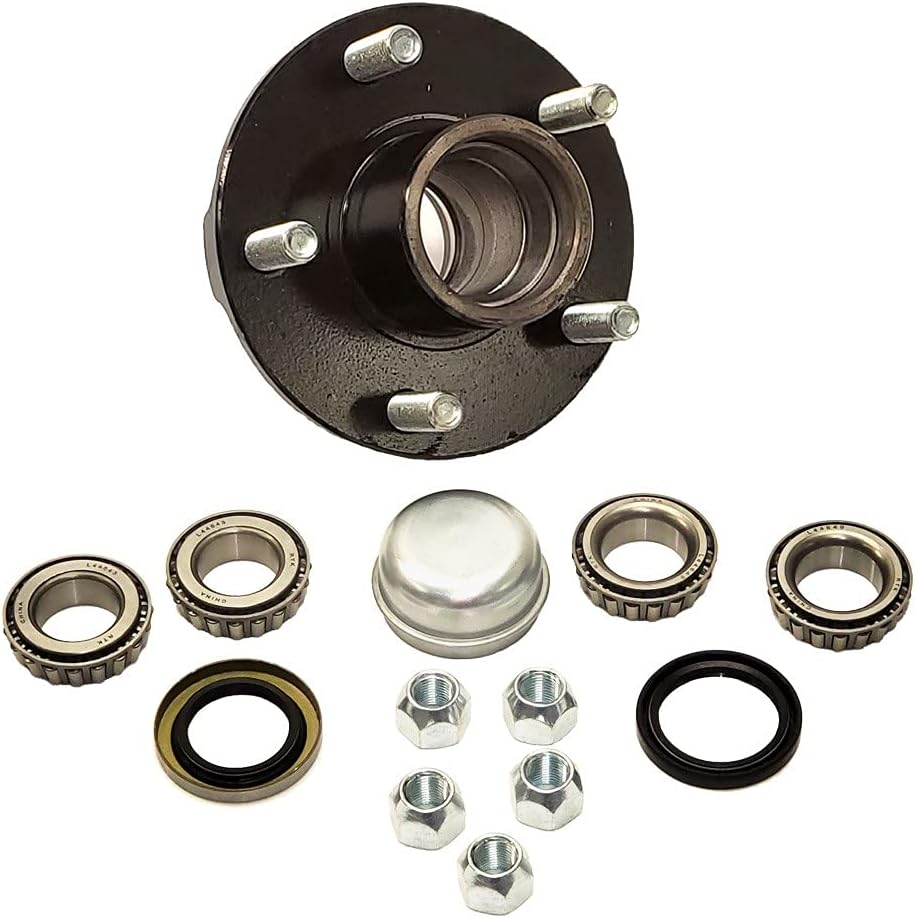
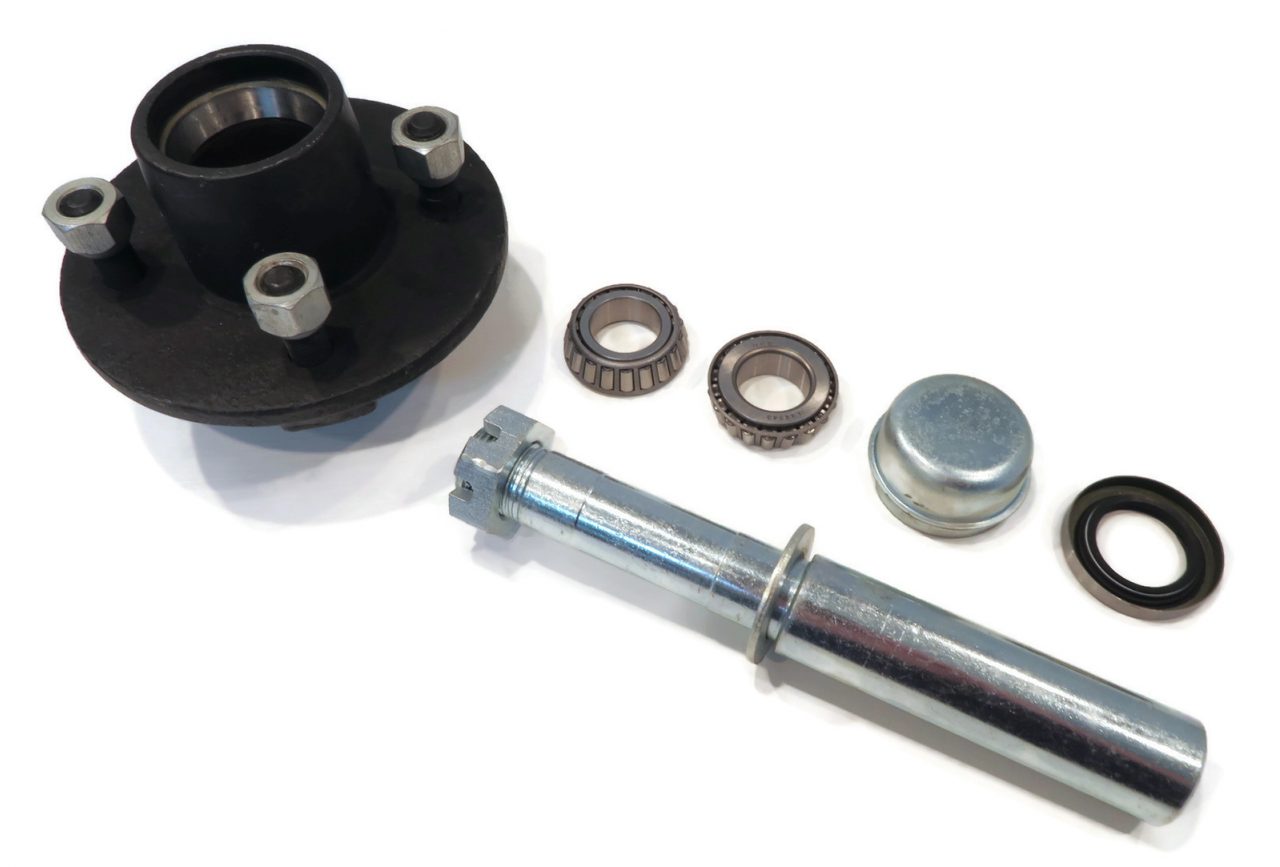
5×4.5 Idler Hubs with 3500# Bearing Kits Replace Trailer Axle fit Dexter ALKO
| Part NO | Capacity | Bolt Pattern | Wheel Stud | Bearing | Dust Cap |
| TH571 | 3500lbs | 5 x 4.5″ | 1/2″-20 UNF | L44649/10 ; L68149/11 | 1.98″ |
TWO – 5×4.5 Hubs w/ 3500# Bearing Kits
(4-1/4″ stud spacing)
5 x 4.5 Bolt Pattern with New Bearings
Part Number: SH2RV545-KITX2
This hub fits a standard 3500 pound axle, either spring type, or “torflex”. Bolt pattern is 5 bolt on a 4.5″ inch bolt circle. Studs are standard 1/2″-20 thread, spaced 4-1/4″ apart.
This kit includes:
2x 3500# Idler Hub, 5 x 4.5 Bolt Pattern
2x 1-1/16″ Bearing
PN: L44649
2x L44610 Race (Already Installed in Drum)
2x 1-3/8″ Bearing
PN: L68149
2x L68111 Race (Already Installed in Drum)
2x 1.71″ Seal
PN: 10-19
2x 1.98″ Dust Cap with Rubber Insert Plug
10x 1/2″-20 Matching Lug Nuts
These hubs will fit this axle:
Will fit most brands: Dexter, AL-KO, Quality, Lippert, etc. (If you are not sure, look at the axle spindle chart above, this hub fits spindle #84) I can ship more, if needed. I also have a few of other bolt patterns, see my other listings or just ask, and I will list them!
Hub Appearance may vary depending on what we have in stock
HangZhou CZPT Machinery Co., Ltd is a professional manufacturer of trailer parts in HangZhou, ZHangZhoug Province, China since 2016.
We can produce many trailer parts & accessories as follows: Towbars, axles, brake drums, hubs, brake disc, bearings, springs and springs and suspension kits, couplings, mudguards, U-Bolts, Jockey Wheels, keel rollers and brackets, wobble roller, wheel spacer, equalizers and all accessories related to trailers.
If you can send me the drawings or specifications of the trailer parts, mechanical parts and wheels, we can give you our price.
Q1: Do you have factory?
A: Yes, we have our own factory, own engineers, we can meet custom’s unique requirement.
Q2: Can I have a sample order?
A: Yes, welcome sample order to test and check quality. Mixed samples are acceptable.
Q3: It’s OK to print my logo on your product?
A: Yes, we can according to your exact requirement.
Q4:How do you ship the goods and how long does it take arrive?
A: We usually shipped by DHL, UPS, FedEx, it usually takes 3-5 days to arrive. Airline and sea shipping also optional.
Q5: What is your advantages?
A: We are professional supplier for more than 10 years, we always put the quality and price at the first place. At the same time, our products are exported to various countries, we have full experience to solve thorny problems.
If you want to know about our products and us, welcome to enquiry and email me.thanks
1-Welcome OEM
- You can use your own brands or ours, if you use our brand, our professional team will help you design the packing.
2-Our service
- You inquiry related to our products or prices will be replied in 24 hours.
- Well-trained and experienced staffs to answer all your enquirys in fluent English.
- Protection of your sales area, ideas of your design and all your private information.
- We have a QC team, every product will be checked by them before packed.
3-Welcome to visit
- When you come to our company visit us, we will arrange a car for picking up and help you book hotel. If you want to visit the local scenic spot, our colleague will accompany you.
4-Warranty
- Customer should be provide the video and the pictures for the problem products.
- Products returned within the warranty period must bear product number & date code.
5-After service
- In production and after delivery, we will track on time and tell you goods situation.
- When the goods arrived, if you find any design and quality questions, or difference from your samples, please feel free to contact us, we will find the question and solve it with you.
| Material: | Cast Iron |
|---|---|
| Type: | Wheel Hub |
| Drive Wheel: | RWD |
| Wheel Hub Diameter: | 16-20" |
| Finishing: | Black |
| Wheel Accessories: | Wheel Cover |
| Samples: |
US$ 35/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

What steps are involved in the proper removal and installation of an axle hub assembly?
Properly removing and installing an axle hub assembly requires a systematic approach and the use of appropriate tools. Here are the detailed steps involved in the process:
- Gather the necessary tools: Before starting the removal and installation process, gather the required tools and equipment. This may include a jack, jack stands, lug wrench, socket set, torque wrench, pry bar, hammer, and a suitable wheel bearing grease.
- Prepare the vehicle: Park the vehicle on a flat surface and engage the parking brake. If necessary, loosen the lug nuts on the wheel associated with the axle hub assembly, but do not remove them yet.
- Jack up the vehicle: Use a jack to lift the vehicle off the ground at a suitable jacking point. Place jack stands under the vehicle to provide additional support and ensure safety. Carefully lower the vehicle onto the jack stands.
- Remove the wheel: Completely remove the lug nuts and take off the wheel to access the axle hub assembly.
- Disconnect brake components: Depending on the specific vehicle, there may be brake components attached to the axle hub assembly. This can include brake calipers, brake pads, and brake rotors. Follow the appropriate procedure to disconnect these components, which may involve removing caliper bolts, brake pad retaining clips, or rotor retaining screws.
- Disconnect the axle: If the axle shaft is connected to the axle hub assembly, disconnect it by removing the retaining nut or bolts. This step may vary depending on the type of axle and vehicle.
- Remove the axle hub assembly: The axle hub assembly is typically secured to the steering knuckle or suspension component by bolts or studs. Use the appropriate tools to remove these fasteners and carefully detach the axle hub assembly from the vehicle. In some cases, the assembly may be tight and require the use of a pry bar or hammer to gently separate it from the mounting point.
- Clean and inspect: Once the axle hub assembly is removed, clean the mounting surface on the steering knuckle or suspension component. Inspect the mounting area for any damage or corrosion that may affect the installation of the new axle hub assembly. Also, inspect the axle shaft and surrounding components for any signs of damage or wear.
- Install the new axle hub assembly: Apply a thin layer of wheel bearing grease to the mounting surface of the steering knuckle or suspension component. Carefully align the new axle hub assembly with the mounting holes and slide it into place. Install the bolts or studs and tighten them according to the manufacturer’s specifications. If there are any retaining nuts or bolts for the axle shaft, reinstall them and torque them to the recommended values.
- Reconnect brake components: Reinstall any brake components that were disconnected, such as brake calipers, brake pads, and brake rotors. Make sure to follow the correct procedure and torque specifications for these components.
- Reinstall the wheel: Put the wheel back onto the vehicle and hand-tighten the lug nuts. Lower the vehicle from the jack stands using a jack, and then use a torque wrench to tighten the lug nuts to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specification.
- Test and verify: Once the axle hub assembly is installed and all components are properly reconnected, take the vehicle for a test drive. Pay attention to any unusual noises, vibrations, or handling issues. Verify that the axle hub assembly is functioning correctly and that there are no leaks or other problems.
It’s important to note that the specific steps and procedures may vary depending on the vehicle make and model. Always consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance if you are unsure about any aspect of the removal and installation process.
In summary, the proper removal and installation of an axle hub assembly involve gathering the necessary tools, preparing the vehicle, jacking up the vehicle, removing the wheel, disconnecting brake components and the axle, removing the old axle hub assembly, cleaning and inspecting, installing the new assembly, reconnecting brake components, reinstalling the wheel, and finally testing and verifying the functionality of the axle hub assembly.

Are there specific tools required for DIY axle hub replacement, and where can I find them?
When undertaking a DIY axle hub replacement, certain tools are needed to ensure a smooth and successful process. Here are some specific tools that are commonly required for DIY axle hub replacement and where you can find them:
- Jack and jack stands: These tools are essential for raising the vehicle off the ground and providing a stable support system. You can find jacks and jack stands at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Lug wrench or socket set: A lug wrench or a socket set with the appropriate size socket is necessary to loosen and tighten the lug nuts on the wheel. These tools are commonly available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Torque wrench: A torque wrench is required to tighten the lug nuts on the wheel and other fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Torque wrenches can be found at automotive supply stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Pry bar: A pry bar is useful for gently separating the axle hub assembly from the mounting point, especially if it is tightly secured. Pry bars are available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Hammer: A hammer can be used to tap or lightly strike the axle hub assembly or its components for removal or installation. Hammers are commonly available at hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Wheel bearing grease: High-quality wheel bearing grease is necessary for lubricating the axle hub assembly and ensuring smooth operation. Wheel bearing grease can be purchased at automotive supply stores, lubricant suppliers, and online retailers.
- Additional tools: Depending on the specific vehicle and axle hub assembly, you may require additional tools such as a socket set, wrenches, pliers, or specific specialty tools. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or online resources for the specific tools needed for your vehicle model.
To find these tools, you can visit local automotive supply stores, hardware stores, or tool stores in your area. They typically carry a wide range of automotive tools and equipment. Alternatively, you can explore online retailers that specialize in automotive tools and equipment, where you can conveniently browse and purchase the tools you need.
It’s important to ensure that the tools you acquire are of good quality and suitable for the task at hand. Investing in quality tools can make the DIY axle hub replacement process more efficient and help achieve better results. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines when using tools and equipment.
In summary, specific tools are required for DIY axle hub replacement, such as a jack and jack stands, lug wrench or socket set, torque wrench, pry bar, hammer, and wheel bearing grease. These tools can be found at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers. Acquiring quality tools and following proper safety guidelines will contribute to a successful DIY axle hub replacement.

Can axle hubs impact the alignment of a vehicle, and how is this corrected?
Axle hubs can indeed impact the alignment of a vehicle, and any alignment issues arising from the axle hubs should be corrected to ensure optimal vehicle handling, tire wear, and overall safety. Here’s a detailed explanation:
An axle hub is a critical component that connects the wheel assembly to the vehicle’s suspension. It houses the wheel bearings and provides the mounting point for the wheel. If an axle hub is damaged, worn, or improperly installed, it can lead to misalignment issues. Here are a few ways axle hubs can impact vehicle alignment:
- Bearing Wear: Axle hubs contain wheel bearings that allow the wheels to rotate smoothly. If the bearings are worn or damaged, they can introduce play or uneven movement in the wheel assembly. This can result in misalignment, causing the vehicle to pull to one side or affect the camber, toe, or caster angles.
- Improper Installation: If an axle hub is not installed correctly, it can introduce misalignment issues. For example, if the hub is not tightened to the specified torque or if the mounting surfaces are not properly cleaned, it can result in uneven pressure distribution and misalignment.
- Impact Damage: Axle hubs can get damaged due to accidents, hitting potholes, or other impacts. Any deformation or misalignment of the axle hub can affect the alignment of the wheel assembly.
To correct alignment issues caused by axle hubs, the following steps are typically taken:
- Inspection: A thorough inspection of the axle hubs is conducted to identify any damage, wear, or improper installation. This may involve removing the wheels and visually examining the axle hubs for signs of damage or wear.
- Replacement: If the axle hubs are found to be damaged, worn, or improperly installed, they need to be replaced. Replacement axle hubs should be sourced from reputable manufacturers or OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) suppliers to ensure proper fit and alignment.
- Wheel Alignment: After replacing the axle hubs, a wheel alignment procedure is necessary to correct any misalignment caused by the previous issues. This typically involves adjusting the camber, toe, and caster angles to the manufacturer’s specifications using specialized alignment equipment.
- Additional Repairs: In some cases, axle hub-related alignment issues may have caused additional damage to suspension components or steering linkage. These components should be inspected and repaired as needed to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
It’s important to note that correcting alignment issues caused by axle hubs generally requires the expertise of a qualified mechanic or alignment specialist. They have the necessary knowledge, experience, and equipment to accurately diagnose and rectify alignment problems associated with axle hubs.
In summary, axle hubs can impact the alignment of a vehicle. Issues such as bearing wear, improper installation, or impact damage can introduce misalignment. To correct these alignment issues, a thorough inspection of the axle hubs is conducted, followed by replacement if necessary. Afterward, a wheel alignment procedure is performed to adjust the angles to the manufacturer’s specifications. Professional assistance from a qualified mechanic or alignment specialist is recommended to ensure accurate diagnosis and proper correction of axle hub-related alignment issues.


editor by CX 2023-11-10
China factory Good Quality Car Part Auto Bearing Rear Axle Wheel Hub OEM 52750-C8000 713626880 R184.85 922433 for CZPT I20 axle alignment
Product Description
Quick view:
| Name | Wheel hub Bearing 52750-C8000 |
| Bearings Material | Steel GCr15, 65Mn, or 55 |
| Application car makes | Hyundai |
| Size | OD:132 mm |
| Weight | 2.6 kg |
| With ABS | with integrated wheel speed sensor |
| Bolt | 4 Bolts |
| Position | Rear Axle |
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized |
| Packing | Neutral, our brand packing or customized |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Manufacture place | ZHangZhoug, China |
| MOQ | 100 PCS |
| Warranty | 1 year or 40,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal, Alibaba |
OEM:
HYUNDAI: 52750-C8000
HYUNDAI: 52750C8000
Ref.:
F AG:
SNR: R184.85
SNR: R18485
ASHIKA: 44-20331
MOOG: HY-WB-12922
OPTIMAL: 922433
Application:
HYUNDAI i20 (GB, IB) 2014-
Other types(contact for more):
| BCA | S KF | TIMKEN | Car Model |
| 513215 | BR93571 | HA590071 | Chevy Malibu |
| 515000 | BR930116 | 515000 | Ford Aerostar |
| 515001 | BR930094 | 515001 | Chevy/GMC All K Series |
| 515002 | BR930035 | 515002 | Chevy/GMC K Series |
| 515003 | BR935712 | SP455710 | Ford Explorer Sport |
| 515004 | BR935718 | SP555711 | Ford Expedition |
| 515006 | BR935716 | 515006 | Dodge R1500/W150 |
| 515007 | BR935717 | HA599361 | Dodge Dakota |
| 515008 | BR935714 | SP455711 | Dodge Dakota |
| 515009 | BR935715 | SP455710 | Dodge Dakota |
| 515571 | BR93 0571 | SP555710 | Ford F150 |
| 515011 | BR930400 | HA597851 | Dodge D250 |
| 515012 | BR930405 | HA59571 | Dodge D250 |
| 515013 | BR930343 | SP455711 | Ford Ranger |
| 515015 | BR930406 | SP580302/580303 | Chevy/GMC 20/2500 |
| 515016 | SP580300 | Chevy/GMC 20/2500 | |
| 515017 | BR935718 | 515017 | Ford F150 |
| 515018 | HA591339 | Chevy/GMC | |
| 515571 | BR930420 | 515571 | Ford F350 |
| 515571 | BR930424 | 515571 | Ford F250 |
| 515571 | BR93571 | 515571 | Ford F150 |
| 515571 | BR93571 | SP555710 | Dodge R1500 |
| 515571 | BR93571 | 515571 | Ford F350/F450 Super Duty |
| 515026 | BR930341 | 515026 | Ford Ranger |
| 515571 | BR930342 | 515571 | Ford Ranger |
| 515571 | BR930423 | 515571 | Ford F150 |
| 515030 | BR93571 | 515030 | Ford F150 |
| 515031 | BR935716 | 515031 | Ford Expedition |
| 515032 | BR930361 | HA599528 | Dodge Dakota |
| 515033 | BR930360 | HA599406 | Dodge Dakota |
| 515037 | Chevy/GMC K3500 | ||
| 515038 | BR930305 | HA599863 | Dodge Ram |
| 515039 | BR930409 | SP555712 | Dodge Ram |
| 515041 | BR930406 | SP580302/580303 | Chevy/GMC K1500 |
| 515042 | BR93571 | SP555716 | Ford Expedition |
| 515048 | Chevy/GMC K1500 | ||
| 515049 | BR93571 | SP555711 | Dodge R1500 |
| 515050 | BR93 0571 | SP475711 | Ford Explorer |
| 515051 | BR930345 | SP455713 | Ford Ranger |
| 515052 | BR93571 | SP455712 | Ford Explorer Sport |
| 515054 | SP550306 | Chevy Silverado | |
| 515055 | Chevy/GMC K1500 | ||
| 515058 | BR93571 | SP58571 | Chevy Silverado |
| 515061 | BR930502 | HA590032 | Dodge D250 |
| 515063 | BR935713 | HA595713 | Dodge D250 |
| 515072 | BR935714 | HA55710 | Dodge R1500 |
| 515073 | BR935715 | Dodge R1500 | |
| 515084 | BR930611 | HA590001 | Dodge Ram 1500 |
| 518500 | BR930000 | 518500 | Chrysler LeBaron |
| 518501 | BR930001 | 518001 | Chrysler E Class |
| 518502 | BR930002 | 518502 | Chrysler E Class |
| 518503 | BR930153K | 518503 | Ford Escort |
| 518506 | BR935710K | 518506 | Toyota Camry |
| 518507 | BR930300K | 518507 | Chevy Prizm |
| 518510 | BR930263K | HA590263K | Ford Focus |
| 520000 | BR930151K | 520000 | Ford Taurus |
| 525710 | BR930152K | 525710 | Ford Taurus |
| 521000 | BR935719K | 521000 | Ford Explorer |
| 513011K | BR930091K | 513011K | B uick Century |
| 513016K | BR930571K | 513016K | B uick Century |
Company Profile
ZheJiang Mighty Machinery Co. Ltd is a professional manufacturer of auto bearings for more than 20 years. We provide a one-stop service for our customers. Our main products include wheel bearings & hub assembly, belt tensioners, clutch release bearings, and auto parts.
Relying on the professional and rich manufacturing experience and many substantial factories which stable cooperated for many years, Mighty suppliers customers high-quality products at very competitive prices.
Customer satisfaction is our First Priority, We adhere to the concept of ” Quality First, Customer First”. We will continue to provide high-quality products and the best services to our customers and build up CZPT long-time friendship partners.
Main Products:
Deep groove ball bearing
tapered roller bearing
spherical roller bearing
self-aligning bearing
rod end bearing
pillow blocks
linear motion bearing and CZPT rail
wheel bearing & hub unit
clutch release bearing & hydraulic clutch
belt tensioner & pulley
universal joint
Our Bearing Advantage:
1. Free Sample bearing
2.ISO certified
3. Bearing Small order accepted
4. In Stock bearing
5. OEM bearing service
6. Professional: Over 20 years manufacture bearing
7. Customized bearing, Customer’s bearing drawing or samples accepted
8. Competitive price
9. TT Payment, Paypal, Alibaba payment, Trade Assurance Order
Packages:
FAQ:
1. When are you going to deliver?
A: Sample: 5-15 business days after payment is confirmed.
Bulk order:15-60 workdays after deposit received…
2. What’s your delivery way?
A: By sea, by air, by train, express as your need.
3. What are your terms of delivery?
A: EXW, FOB, CFR, CIF, DAP, etc.
4. Can you support the sample order?
A: Yes, we can supply the sample if we have parts in stock, but the customer has to pay the sample payment(according to the value of the samples) and the shipping cost.
5. What are you going to do if there has a claim for the quality or quantity missing?
A: 1. For quality, during the warranty period, if any claim for it, we shall help the customer to find out what’s the exact problem. Using by mistake, installation problem, or poor quality? Once it’s due to the poor quality, we will arrange the new products to customers.
2. For missing quantities, there have 2 weeks for claiming the missing ones after receiving the goods. We shall help to find out where it is.
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0 |
| Certification: | ISO9001, TS16949 |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do I diagnose and address noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub?
Diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub requires a systematic approach to identify the root cause and take appropriate corrective measures. Here’s a detailed explanation of the diagnostic process and steps to address the problem:
1. Identify the Noise:
The first step is to identify the specific noise associated with the malfunctioning axle hub. Pay attention to the type and characteristics of the noise, such as grinding, growling, clicking, or humming. Note when the noise occurs, whether it’s during acceleration, deceleration, or while turning. This initial identification can help narrow down the possible causes.
2. Inspect the Axle Hub:
Visually inspect the axle hub for any signs of damage or wear. Look for cracks, corrosion, or loose components. Check if there is any leaking grease around the hub, as it can indicate bearing failure. A thorough inspection can provide valuable clues about the condition of the axle hub.
3. Perform a Road Test:
Take the vehicle for a road test to observe the noise and its behavior under different driving conditions. Pay attention to any changes in the noise when making turns, accelerating, or braking. Note whether the noise gets louder or changes in pitch. This can help in further narrowing down the issue.
4. Jack up the Vehicle:
If the noise persists and is suspected to be coming from the axle hub, jack up the vehicle and secure it with jack stands. Rotate the wheel associated with the suspected axle hub and listen for any abnormal noise or roughness. Try to wiggle the wheel by hand to check for excessive play or looseness, which can indicate a problem with the hub assembly.
5. Check Wheel Bearings:
A common cause of noise issues in axle hubs is worn-out or damaged wheel bearings. To check the wheel bearings, grasp the tire at the 12 o’clock and 6 o’clock positions and attempt to rock it back and forth. Excessive movement or play indicates a potential problem with the wheel bearings. Additionally, spin the wheel and listen for any grinding or rumbling noises, which can also be indicative of bearing issues.
6. Addressing the Issue:
If a malfunctioning axle hub is identified as the source of the noise, the following steps can be taken to address the problem:
- Replacement: If the axle hub is severely damaged or the bearings are worn out, replacing the entire hub assembly is often recommended. This ensures proper fitment, bearing integrity, and overall reliability. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or seek professional assistance for the correct replacement procedure.
- Bearing Replacement: In some cases, it may be possible to replace the wheel bearings within the axle hub if they are the sole source of the noise issue. This requires specialized tools and expertise, so it is advisable to consult a qualified mechanic for bearing replacement.
- Additional Repairs: Depending on the severity of the issue, it may be necessary to address other related components. This can include replacing damaged CV joints, inspecting and replacing worn brake components, or addressing any other issues identified during the diagnostic process.
7. Post-Repair Verification:
After addressing the noise issue by repairing or replacing the malfunctioning axle hub, take the vehicle for a test drive to verify that the noise is eliminated. Ensure that the vehicle operates smoothly, and there are no abnormal vibrations or noises coming from the axle hub during different driving conditions.
It’s important to note that diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub can be complex, and it may require the expertise of a qualified mechanic. If you’re uncomfortable performing the diagnostics and repairs yourself, it’s advisable to seek professional assistance to ensure an accurate diagnosis and proper resolution of the issue.
In summary, diagnosing and addressing noise issues associated with a malfunctioning axle hub involves identifying the noise, inspecting the hub, performing a road test, checking wheel bearings, and taking appropriate repair or replacement measures. Following a systematic approach and seeking professional help when needed can help resolve the noise issue and ensure the safe operation of the vehicle.

Where can I find a comprehensive guide for DIY replacement of an axle hub?
If you are looking for a comprehensive guide to assist you with the DIY (Do-It-Yourself) replacement of an axle hub, there are several reliable sources you can refer to. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Manufacturer’s Service Manual: The first and most authoritative source of information for any vehicle repair or maintenance task is the manufacturer’s service manual. The service manual provides detailed instructions, diagrams, and specifications specific to your vehicle’s make, model, and year. It covers all aspects of the vehicle, including axle hub replacement procedures. You can usually obtain the manufacturer’s service manual from the vehicle manufacturer’s official website or through authorized dealerships.
- Online Repair Guides: Many reputable automotive websites and forums offer comprehensive online repair guides. These guides often include step-by-step instructions, accompanied by photographs or illustrations, to help you through the process of replacing an axle hub. Some websites compile user-contributed guides, while others are created by automotive professionals. Popular sources for online repair guides include AutoZone, RepairPal, and iFixit.
- Video Tutorials: Video tutorials can be invaluable resources for visual learners. Websites like YouTube host a wide range of DIY automotive repair videos that cover various tasks, including axle hub replacement. Watching a video tutorial can provide a clear demonstration of the required steps, tools, and techniques involved in the process. You can search for specific video tutorials by using keywords such as “DIY axle hub replacement” along with your vehicle’s make and model.
- Automotive Forums: Online automotive forums are communities where enthusiasts and professionals share knowledge and experiences. Forums like Reddit’s r/MechanicAdvice, Automotive Forums, or specific forums dedicated to your vehicle’s make or model can be excellent sources of information. You can search or post questions specific to axle hub replacement, and experienced members may provide detailed guidance, tips, or even links to comprehensive guides they have found useful.
- Library Resources: Public libraries often have a selection of automotive repair manuals and guides available for borrowing. These printed resources can provide comprehensive instructions and illustrations for various repair tasks, including axle hub replacement. Look for repair manuals specific to your vehicle’s make, model, and year in the automotive section of your local library.
When using any guide or resource for DIY repairs, it’s important to exercise caution and ensure your own safety. Follow all recommended safety procedures, use the appropriate tools, and take necessary precautions. If you are unsure or uncomfortable with any aspect of the repair process, it is advisable to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or professional technician.
In summary, a comprehensive guide for DIY replacement of an axle hub can be found in various sources such as the manufacturer’s service manual, online repair guides, video tutorials, automotive forums, and library resources. These resources provide step-by-step instructions and guidance to help you successfully replace an axle hub. Remember to prioritize safety and seek professional help if needed.

Where can I access reliable resources for understanding the relationship between axles and hubs?
When seeking reliable resources to understand the relationship between axles and hubs, there are several avenues you can explore. Here’s a detailed explanation:
1. Manufacturer’s Documentation: The first place to look for information is the official documentation provided by the vehicle manufacturer. Consult the owner’s manual or technical service manuals for your specific vehicle model. These resources often contain detailed explanations, diagrams, and specifications regarding axles and hubs, including their relationship and functionality.
2. Automotive Repair and Service Manuals: Automotive repair and service manuals, such as those published by Haynes or Chilton, can be valuable sources of information. These manuals provide comprehensive guidance on various vehicle systems, including axles and hubs. They often include step-by-step instructions, diagrams, and troubleshooting tips to help you understand the relationship between axles and hubs.
3. Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to automotive enthusiasts or specific vehicle makes and models can be excellent resources. These platforms provide opportunities to interact with experienced individuals who may have in-depth knowledge about axles and hubs. Participating in discussions, asking questions, and sharing experiences can help you gain insights and a better understanding of the relationship between axles and hubs.
4. Professional Mechanics and Technicians: Consulting with professional mechanics or technicians who specialize in your specific vehicle make or have expertise in axles and hubs can provide valuable information. They can explain the relationship between axles and hubs, answer your questions, and provide practical insights based on their experience. Local service centers or authorized dealerships are good places to seek professional advice.
5. Educational Institutions: Technical schools, vocational programs, and community colleges often offer courses or resources related to automotive technology. Consider exploring their curriculum or reaching out to instructors who can provide educational materials or guidance on understanding axles and hubs.
6. Online Research and Publications: Conducting online research can lead you to various publications, articles, and websites that provide information on axles and hubs. However, it’s crucial to critically evaluate the credibility and reliability of the sources. Look for reputable websites, publications from trusted automotive organizations, or articles written by experts in the field.
Remember to cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy and reliability. It’s also important to stay up to date with the latest advancements and industry standards in the automotive field, as knowledge and technology can evolve over time.
In summary, to access reliable resources for understanding the relationship between axles and hubs, consider consulting manufacturer’s documentation, automotive repair manuals, online forums, professional mechanics, educational institutions, and conducting online research. By exploring these avenues, you can gain comprehensive knowledge and a better understanding of the relationship between axles and hubs.


editor by CX 2023-11-09
China factory Good Quality Auto Parts Rear Axle Car Wheel Hub for Peugeot 206 Hub Unit Bearing Vkba3659 OEM 3748.76 3748.79 boat trailer axle
Product Description
Basic information:
| Description | Good Quality Rear Axle Car Wheel Hub For PEUGEOT 206 Hub Unit Bearing VKBA3659 OEM 3748.76 3748.79 |
| Material | Chrome steel Gcr15 |
| Application | For CITROEN For PEUGEOT |
| Size | Rim Hole Number: 4 Flange Ø: 129 mm |
| Position | Rear wheel |
| With ABS | with integrated ABS sensor |
| Bolts | 4 holes |
| Weight | 1.85 kg |
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized |
| Packing | Neutral, SI, PPB brand packing or customized |
| OEM/ODM service | Yes |
| Manufacture place | ZHangZhoug, China |
| MOQ | 50 PCS |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Inspection | 100% |
| Warranty | 1 year or 40,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 TS16949 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal, Alibaba |
Detailed pictures:
Wheel bearing kits components:
Bearing 1
Nut 1
Sealing/Protective Cap 1
O.E.:
3748.76
3748.79
Ref.:
F-AG:
FEBI BILSTEIN: 31185
OPTIMAL: 657151
S-KF: VKBA 3659
SNR: R166.32
Application:
For CITROEN C3 I (FC_) (2002/02 – /)
For CITROEN C3 Pluriel (HB_) (2003/05 – /)
For CITROEN C2 (JM_) (2003/09 – /)
For CITROEN C3 II (2009/11 – /)
For CITROEN C2 ENTERPRISE (2009/04 – /)
For PEUGEOT 206 Hatchback (2A/C) (1998/08 – /)
For PEUGEOT 206 CC (2D) (2000/09 – /)
For PEUGEOT 206 SW (2E/K) (2002/07 – /)
For PEUGEOT 1007 (KM_) (2005/04 – /)
For PEUGEOT 206 Saloon (2007/03 – /)
How to extend the bearing’s life?
Don’t allow strong impact, such as hammer striking, transfer roller pressure
Use the accurate installation tool, avoid using cloth kind and short fibers
Lubricate the bearing to avoid rust with high-quality oil
General inspection, such as the surrounding temperature, vibrate, noise inspection
Keep bearing cleaning from dirt, dust, pollutant, and moisture.
The bearing should not be ultra cooled.
Front Wheel Bearing Hub Assembly Replacement, Wheel Bearing & Hub Assembly, Hub Bearing Assembly, front bearing hub replacement, hub and bearing replacement, wheel hub bearings, front wheel bearing hub assembly, front wheel bearing hub replacement, hub bearing assembly front, wheel hub assembly, bearing assembly, Front Wheel Bearing and Hub Assembly, Front Wheel Drive Hub and Bearing Assembly
Packing and Delivery:
Work shop:
Exhibitions:
FAQ:
Q1.What is your shipping logistic?
Re: DHL, TNT, FedEx express, by air/sea/train.
Q2:What’s the MOQ?
Re: For the wheel hub assembly. The MOQ is always 50 sets. If ordering together with other models, small quantities can be organized. But need more time due to the production schedule.
Q3. What are your goods of packing?
Re: Generally, our goods will be packed in Neutral white or brown boxes for the hub bearing unit. Our brand packing SI & CZPT are offered. If you have any other packing requests, we shall also handle them.
Q4. What is your sample policy?
Re: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock.
Q5. Do you have any certificates?
Re: Yes, we have the certificate of ISO9001:2015.
Q6:Any warranty of your products.
Re: Sure, We are offering a guarantee for 12 months or 40,000-50,000 km for the aftermarket.
Q7: How can I make an inquiry?
Re: You can contact us by email, telephone, WhatsApp, , etc.
Q8: How long can reply inquiry?
Re: Within 24 hours.
Q9: What’s the delivery time?
Re: Ready stock 10-15 days, production for 30 to 45 days.
Q10: How do you maintain our good business relationship?
Re: 1. Keep stable, reliable quality, competitive price to ensure our customer’s benefit;
2. Optimal lead time.
3. Keep customers updated about the new goods.
4. Make customers satisfaction as our main goal.
Q11: Can we visit the company & factory?
Re: Yes, welcome for your visit & business discussion.
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | Yes |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

Are there differences between front and rear axle hubs in terms of design and function?
Yes, there are differences between front and rear axle hubs in terms of design and function. Here’s a detailed explanation of these differences:
1. Design:
The design of front and rear axle hubs can vary based on the specific requirements of each axle position.
Front Axle Hubs: Front axle hubs are typically more complex in design compared to rear axle hubs. This is because front axle hubs are often responsible for connecting the wheels to the steering system and accommodating the front-wheel drive components. Front axle hubs may have provisions for attaching CV (constant velocity) joints, which are necessary for transmitting power from the engine to the front wheels in front-wheel drive or all-wheel drive vehicles. The design of front axle hubs may also incorporate features for connecting the brake rotor, allowing for the integration of the braking system.
Rear Axle Hubs: Rear axle hubs generally have a simpler design compared to front axle hubs. They are primarily responsible for connecting the wheels to the rear axle shafts and supporting the wheel bearings. Rear axle hubs may not require the same level of complexity as front axle hubs since they do not need to accommodate steering components or transmit power from the engine. However, rear axle hubs still play a critical role in supporting the weight of the vehicle, transmitting driving forces, and integrating with the brake system.
2. Function:
The function of front and rear axle hubs differs based on the specific demands placed on each axle position.
Front Axle Hubs: Front axle hubs have the following primary functions:
- Connect the wheel to the steering system, allowing for controlled steering and maneuverability.
- Support the wheel bearings to facilitate smooth wheel rotation and weight distribution.
- Integrate with the front-wheel drive components, such as CV joints, to transmit power from the engine to the front wheels.
- Provide a mounting point for the brake rotor or drum, allowing for the integration of the braking system.
Rear Axle Hubs: Rear axle hubs have the following primary functions:
- Connect the wheel to the rear axle shaft, facilitating power transmission and driving forces.
- Support the wheel bearings to enable smooth wheel rotation and weight distribution.
- Integrate with the brake system, providing a mounting point for the brake rotor or drum for braking performance.
3. Load Distribution:
Front and rear axle hubs also differ in terms of load distribution.
Front Axle Hubs: Front axle hubs bear the weight of the engine, transmission, and other front-end components. They also handle a significant portion of the vehicle’s braking forces during deceleration. As a result, front axle hubs need to be designed to handle higher loads and provide sufficient strength and durability.
Rear Axle Hubs: Rear axle hubs primarily bear the weight of the vehicle’s rear end and support the differential and rear axle shafts. The braking forces on the rear axle hubs are typically lower compared to the front axle hubs. However, they still need to be robust enough to handle the forces generated during acceleration, deceleration, and cornering.
In summary, there are differences between front and rear axle hubs in terms of design and function. Front axle hubs are typically more complex and accommodate steering components and front-wheel drive systems, while rear axle hubs have a simpler design focused on supporting the rear axle and integrating with the brake system. Understanding these differences is important for proper maintenance and repair of the axle hubs in a vehicle.

Are there specific tools required for DIY axle hub replacement, and where can I find them?
When undertaking a DIY axle hub replacement, certain tools are needed to ensure a smooth and successful process. Here are some specific tools that are commonly required for DIY axle hub replacement and where you can find them:
- Jack and jack stands: These tools are essential for raising the vehicle off the ground and providing a stable support system. You can find jacks and jack stands at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Lug wrench or socket set: A lug wrench or a socket set with the appropriate size socket is necessary to loosen and tighten the lug nuts on the wheel. These tools are commonly available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Torque wrench: A torque wrench is required to tighten the lug nuts on the wheel and other fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Torque wrenches can be found at automotive supply stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Pry bar: A pry bar is useful for gently separating the axle hub assembly from the mounting point, especially if it is tightly secured. Pry bars are available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Hammer: A hammer can be used to tap or lightly strike the axle hub assembly or its components for removal or installation. Hammers are commonly available at hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Wheel bearing grease: High-quality wheel bearing grease is necessary for lubricating the axle hub assembly and ensuring smooth operation. Wheel bearing grease can be purchased at automotive supply stores, lubricant suppliers, and online retailers.
- Additional tools: Depending on the specific vehicle and axle hub assembly, you may require additional tools such as a socket set, wrenches, pliers, or specific specialty tools. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or online resources for the specific tools needed for your vehicle model.
To find these tools, you can visit local automotive supply stores, hardware stores, or tool stores in your area. They typically carry a wide range of automotive tools and equipment. Alternatively, you can explore online retailers that specialize in automotive tools and equipment, where you can conveniently browse and purchase the tools you need.
It’s important to ensure that the tools you acquire are of good quality and suitable for the task at hand. Investing in quality tools can make the DIY axle hub replacement process more efficient and help achieve better results. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines when using tools and equipment.
In summary, specific tools are required for DIY axle hub replacement, such as a jack and jack stands, lug wrench or socket set, torque wrench, pry bar, hammer, and wheel bearing grease. These tools can be found at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers. Acquiring quality tools and following proper safety guidelines will contribute to a successful DIY axle hub replacement.

What are the torque specifications for securing an axle hub to the vehicle?
The torque specifications for securing an axle hub to the vehicle may vary depending on the specific make, model, and year of the vehicle. It is crucial to consult the manufacturer’s service manual or appropriate technical resources for the accurate torque specifications for your particular vehicle. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Manufacturer’s Service Manual: The manufacturer’s service manual is the most reliable and authoritative source for torque specifications. It provides detailed information specific to your vehicle, including the recommended torque values for various components, such as the axle hub. The service manual may specify different torque values for different vehicle models or configurations. You can usually obtain the manufacturer’s service manual from the vehicle manufacturer’s official website or through authorized dealerships.
- Technical Resources: In addition to the manufacturer’s service manual, there are other technical resources available that provide torque specifications. These resources may include specialized automotive repair guides, online databases, or torque specification charts. Reputable automotive websites, professional repair manuals, or automotive forums dedicated to your vehicle’s make or model can be valuable sources for finding accurate torque specifications.
- Online Databases: Some websites offer online databases or torque specification tools that allow you to search for specific torque values based on your vehicle’s make, model, and year. These databases compile torque specifications from various sources and provide a convenient way to access the required information. However, it’s important to verify the accuracy and reliability of the source before relying on the provided torque values.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: In certain cases, the manufacturer may provide torque specifications on the packaging or documentation that accompanies the replacement axle hub. If you are using an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) or aftermarket axle hub, it is advisable to check any provided documentation for torque recommendations specific to that particular product.
Regardless of the source you use to obtain torque specifications, it is essential to follow the recommended values precisely. Torque specifications are specified to ensure proper tightening and secure attachment of the axle hub to the vehicle. Over-tightening or under-tightening can lead to issues such as damage to components, improper seating, or premature wear. It is recommended to use a reliable torque wrench to achieve the specified torque values accurately.
In summary, the torque specifications for securing an axle hub to the vehicle depend on the specific make, model, and year of the vehicle. The manufacturer’s service manual, technical resources, online databases, and manufacturer recommendations are valuable sources to obtain accurate torque specifications. It is crucial to follow the recommended torque values precisely to ensure proper installation and avoid potential issues.


editor by CX 2023-10-30
China Hot Selling Competitive Price Fuwa Axle 13ton with Best Price axle bearing
Solution Description
| Merchandise | Size (mm) | Wheel Foundation(mm) | Width of the Trailer(mm) | Loading Excess weight(kg) |
| CJAR330 | 1500 | 1370 | 1550 | 780 |
| CJAR520 | 1700 | 1570 | 1750 | a thousand |
| CJAR580 | 2000 | 1870 | 2100 | 1700 |
HangZhouU Equipment Co., Ltd. is situated in the hometown of civilized trailers at property and overseas. It is a modern day
comprehensive organization integrating style, analysis and advancement, production and product sales. Because its establishment,
the company has usually adhered to the enterprise philosophy of customer initial and CZPT cooperation, and has won the
help and have faith in of a large variety of new and old clients. The business now mostly produces and sells: axles
(American, German), suspension (American, German), outriggers (linkage, single-action), air reservoirs, rope tensioners
, fifty,90 traction pin traction saddles, brake air The products are exported to Southeast Asia, Africa, South America, Europe
and other nations around the world and locations. We sincerely welcome close friends from all walks of life to go over cooperation and seek
common improvement.
|
US $200 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Axle Number: | 2 |
| Application: | Trailer |
| Certification: | ASTM, CE, ISO |
| Material: | Steel |
| Type: | Axle Bearing |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item | Length (mm) | Wheel Base(mm) | Width of the Trailer(mm) | Loading Weight(kg) |
| CJAR330 | 1500 | 1370 | 1550 | 780 |
| CJAR520 | 1700 | 1570 | 1750 | 1000 |
| CJAR580 | 2000 | 1870 | 2100 | 1700 |
|
US $200 / Piece | |
1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| Condition: | New |
|---|---|
| Axle Number: | 2 |
| Application: | Trailer |
| Certification: | ASTM, CE, ISO |
| Material: | Steel |
| Type: | Axle Bearing |
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Item | Length (mm) | Wheel Base(mm) | Width of the Trailer(mm) | Loading Weight(kg) |
| CJAR330 | 1500 | 1370 | 1550 | 780 |
| CJAR520 | 1700 | 1570 | 1750 | 1000 |
| CJAR580 | 2000 | 1870 | 2100 | 1700 |
What Is an Axle?
An axle is the central shaft of a rotating wheel or gear. It can be fixed to the wheels and vehicle or may rotate freely. In many cases, the axle also includes a bearing. It is a critical part of your vehicle because it is responsible for the steering and acceleration of your vehicle. Several different types of axles are available.
Types of axles
Axles are used in various kinds of vehicles. Each type of axle carries a different load. The first kind is called the floating axle, while the second type is called the fixed axle. Both types are commonly used in light-duty vehicles and medium-duty trucks. In addition, there are different types of semi-floating axles. These axles are mainly used in trucks, light-duty pickups, and big SUVs.
A live axle transmits power from an engine to the wheels, while a dead axle does not convey power. A dead axle is also known as a lazy axle. A number of vehicles are fitted with dead axles. These axles are usually installed in front of the driving axle. However, a pusher axle is also a dead axle.
Besides being important for vehicle movement, axles are also important for suspension. These parts transfer the driving torque from the driveshaft to the wheels, which maintains the position of the wheels. They are made of durable steel, and are very hard to bend except in cases of severe impact. There are different types of axles based on their purpose: driving axles transfer engine torque to the wheels and dead axles serve as suspension components.
Floating axles have two deep groove ball bearings at each end, and are often called full floating axles. They are usually mounted in SUVs, and are more durable than regular car axles. They are also relatively inexpensive, and can support large loads. The full floating axle is usually used in heavy-duty trucks, midsize trucks, and four-wheel-drive vehicles.
Another type of axle is called a lift axle. These axles are used in Multi-Axle Vehicles, which have more than four axles. As a result, the vehicle has a greater weight capacity than a normal car. A five-axle truck has a gross vehicle weight of forty-two tons, while its kerb weight is twelve tons. Unloaded, it is therefore equal to 30 tons.
Front axles: The front axles of cars are primarily responsible for steering and processing road shocks. The front axle is made of steel that is 0.4-3% carbon steel and one-to-three percent nickel steel. Its circular or elliptical ends and I-section center help it withstand bending loads during braking. The rear axles are the drive shafts and transmit power from the differential to the rear wheels.
Rear axles are inexpensive. They connect the rear differential and can be purchased for about $150, depending on the make and model of the car. They can be found in many modern vehicles, and are commonly found in front-drive vehicles. These modern vehicles also have axle CV shafts, which are more unique than traditional axles.
In addition to tyres, the axles are responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. An axle can break due to improper maintenance or a car accident, and can affect the performance of a vehicle. A damaged axle will cause it to transfer power slowly. It might also make a clunking or sputtering noise.
Cost of replacing an axle
Replacing an axle can be a costly task. A car’s axles should last between 35k and 100k miles. However, they can be damaged by hard hits or collisions. Depending on the extent of damage, the car may require a new axle or repair. The cost of an axle repair or replacement depends on several factors, including where the car was hit, the type of car and labor charges.
The cost of replacing an axle can range from around $200 to $900, depending on your vehicle and the type of work involved. Parts can be purchased for under $100 each, but you’ll also need to factor in labor, which can cost up to $200 or more. If you’re replacing both the rear and front axles, the cost will be higher than for just one axle replacement.
Axle repair is a complicated procedure, and the cost varies based on the make and model of your vehicle. A replacement axle will allow wheels to rotate freely. Depending on the severity of the problem, a front axle repair can run between $500 and $800. A rear axle repair will run you about $700.
Although an axle replacement may seem like an expensive and time-consuming task, the process will be less expensive than repairing the whole assembly. Professional mechanics can also replace one axle at a time. If you have a warranty on your car, this can cover the cost of the repair. This is a good way to save money and time while getting your car back on the road.
One of the most common causes of axle failure is the leakage of grease. When grease leaks, the CV joint is left dry, and dirt will get in. Without lubrication, this leads to increased wear, and increases the cost of axle replacement. For this reason, most mechanics will recommend replacing the entire half-shaft instead of just the axle, thereby reducing the cost and the labor time.
Depending on the severity of the damage, replacing an axle can take several hours. Aside from the repair, an alignment may be needed afterward. Most garages include this service with axle work. Depending on the type of alignment, it could cost from $20 to $150+. A complete diagnosis of the vehicle can take up to three hours to complete.
In some cases, a broken axle is completely irreparable. It will damage the rest of the vehicle and may lead to other problems. In such cases, it’s best to take it to a mechanic for repair as soon as possible. In most cases, an axle replacement should be needed just once during the life of the car.
Axles are available in pairs or individually. You can also find them at a junkyard. Installing a new axle is not difficult if you have the proper tools. An impact wrench can help make the job go faster. However, it’s important to have a flat surface for the work and wear safety gear.
Insurance coverage for repairing an axle
Car insurance may cover the costs of repairing an axle if it’s damaged in an accident, but if the damage occurred because of normal wear and tear, it may not be covered. Similarly, your insurance policy may not cover damage to tires or rims, and it might not cover the costs of a new axle, depending on the condition of the axle.
Your car’s axle is an important part of the vehicle, transferring power from the engine to the wheels. They are built to be durable, but they can bend or break due to a variety of factors, including running over a curb, hitting potholes at high speed, and auto collisions. In such cases, your car may not be able to drive, and a replacement axle may be expensive.
Some of the symptoms of an axle problem are shuddering or clicking sounds when shifting gears. Occasionally, a car may even completely stop. This can lead to an accident or even a loss of control. It’s best to fix an axle before it damages your car in an accident. In some cases, repairing the axle can cost only a few hundred dollars.
You should have your vehicle inspected for signs of wear and tear before repairing an axle. It’s crucial to take your vehicle to a mechanic immediately after an accident, as delayed repairs can lead to further suspension issues. Ideally, your vehicle’s axle should last four to five years or fifty thousand miles, although these numbers can vary. The life of an axle depends on a variety of factors, including the type of driving you do and how often you drive. Driving over rocky or icy surfaces can wear out the protective rubber boot. The rubber can also dry out and crack over time.
While the axle itself is a sturdy component, the parts connected to it are more susceptible to wear and tear. Associated components such as axle bearings are critical to the axle, as they help control the speed of the wheels when they turn. They also help maintain the integrity of the vehicle’s structural system.
Repairing an axle can be expensive, depending on the vehicle’s make and model. Depending on the severity of the problem, the costs of an axle repair can range from $500 to more than $1,000. The cost of an axle repair may also include other necessary repairs. If the damage is caused by normal use, your insurance provider may pay for the costs.
When your vehicle is in need of an axle replacement, it’s a good idea to contact a vehicle repair shop. A vehicle repair shop will give you the best possible estimate of the cost and time to repair the axle.

editor by czh 2022-12-17
China Bearing Kit Vkba3575 Front Wheel Axle Size 40X75X37mm OEM C2s8276 for Jaguar and Ford axle dump
Product Description
Basic information:
| Description | Front wheel bearing C2S8276 |
| Material | Chrome steel Gcr15 |
| Application | For CZPT and JAGUAR |
| Size | Inner: 40mm Outer: 75mm Width: 37mm |
| Position | Front axle left and right |
| With ABS | Yes |
| Weight | 0.75 kg |
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized |
| Packing | Neutral, SI, PPB brand packing or customized |
| OEM/ODM service | Yes |
| Manufacture place | ZHangZhoug, China |
| MOQ | 50 PCS |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Inspection | 100% |
| Warranty | 1 year or 40,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 TS16949 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal, Alibaba |
Detailed pictures:
O.E.:
For FORD: 1 133 571
For FORD: 1S7W-1215-AA
For FORD: 4103363
For FORD: 4563516
For JAGUAR: C2S8276
Ref.:
For FAG:
For FAG:
For FEBI BILSTEIN: 19705
For FEBI BILSTEIN: 19706
For OPTIMAL: 301183
For SKF: VKBA 3575
For SNR: R152.23
Application:
For CZPT Cougar Coupe (EC) (131 – 205 PS, 08.1998 – 12.2001 MY)
For FORD Mondeo Mk3 Hatchback (B5Y) (90 – 226 PS, 10.2000 – 03.2007 MY)
For FORD Mondeo Mk3 Estate (BWY) (90 – 226 PS, 10.2000 – 03.2007 MY) For FORD Mondeo Mk3 Saloon (B4Y) (90 – 226 PS, 10.2000 – 03.2007 MY) For CZPT X-Type Estate (X400) (130 – 230 PS, 11.2003 – 12.2009 MY) For CZPT X-Type Saloon (X400) (130 – 230 PS, 06.2001 – 11.2009 MY) For CZPT XF Saloon (X250) (340 PS, 10.2012 – 04.2015 MY)
Other types(contact us for more):
| S-KF Ref. | Application |
| VKBA 3494 | S-KODA |
| VKBA 3495 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3496 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3497 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3498 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3499 | BMW |
| VKBA 3500 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3501 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3502 | ALFA ROMEO,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A |
| VKBA 3503 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3504 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3506 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3508 | IVEc |
| VKBA 3510 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3511 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3512 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3513 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3514 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3517 | FORD |
| VKBA 3518 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3519 | AUDI,SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3520 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3521 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3522 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3523 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3524 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3525 | DACIA, NISSAN,R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3526 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3527 | LAND-ROVER |
| VKBA 3528 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3530 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3531 | FORD |
| VKBA 3532 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3534 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3535 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3536 | AUDI, SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3538 | CITROËN,FIAT,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3539 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3540 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3541 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3542 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3543 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3544 | LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A |
| VKBA 3545 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3546 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3548 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3549 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3550 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3551 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3552 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3553 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3554 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3555 | O-PEL,SAAB,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3556 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3557 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3558 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3559 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3560 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3561 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3562 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3564 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3565 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3567 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3568 | S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3569 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3570 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3571 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3572 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3574 | BMW |
| VKBA 3575 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3576 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3577 | FIAT,FORD,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A |
| VKBA 3578 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A |
| VKBA 3580 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3581 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3583 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3584 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3585 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3586 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3587 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3588 | FORD |
| VKBA 3589 | FORD |
| VKBA 3590 | FORD |
| VKBA 3592 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3594 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3595 | CITROËN, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3596 | DACIA,NISSAN, R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3597 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3598 | FIAT,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A,O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3599 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A,O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3600 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3601 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3602 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3603 | LAND-ROVER,MG, ROVER |
| VKBA 3604 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3605 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3606 | AUDI,SEAT |
| VKBA 3607 | AUDI,SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3608 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3609 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3610 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3611 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3612 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3613 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3614 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
Our Company:
SI&PPB bearing has a plant area of 50,000 square meters, assets of RMB180 million, 500 employees, and 150 professional and technical personnel. The company uses high-quality GCR15 as its raw materials and uses Austenite heat treatment to ensure the service life of the products.
“The factory produces series models of mechanical clutch release bearings, belt tension wheel units, wheel bearings, and wheel bearing repair kits.
Partial products are produced by professional outsourcing factories, and the company’s testing center provides professional testing to ensure that the products meet the drawings or customer’s requirements.”
A wide range of applications:
• agriculture and forestry equipment
• automotive and industrial gearboxes
• automotive and truck electric components, such as alternators
• electric motors
• fluid machinery
• material handling
• power tools and household appliances
• textile machinery
• 2 Wheeler.
FAQ:
Q1.What is your shipping logistic?
Re: DHL, TNT, FedEx express, by air/sea/train.
Q2:What’s the MOQ?
Re: For the wheel hub bearing repair kit. The MOQ is always 50 sets. If ordering together with other models, a small quantities can be organized. But need more time due to the production schedule.
Q3. What are your goods of packing?
Re: Generally, our goods will be packed in Neutral white or brown boxes for the hub bearing unit. Our brand packing SI & CZPT are offered. If you have any other packing requests, we shall also handle them.
Q4. What is your sample policy?
Re: We can supply the sample if we have ready parts in stock.
Q5. Do you have any certificates?
Re: Yes, we have the certificate of ISO9001:2015.
Q6:Any warranty of your products.
Re: Sure, We are offering a guaranty for 12 months or 40,000-50,000 km for the aftermarket.
|
US $4.5-30 / Piece | |
50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0 |
| Certification: | ISO9001, TS16949 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Description | Front wheel bearing C2S8276 |
| Material | Chrome steel Gcr15 |
| Application | For Ford and JAGUAR |
| Size | Inner: 40mm Outer: 75mm Width: 37mm |
| Position | Front axle left and right |
| With ABS | Yes |
| Weight | 0.75 kg |
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized |
| Packing | Neutral, SI, PPB brand packing or customized |
| OEM/ODM service | Yes |
| Manufacture place | Zhejiang, China |
| MOQ | 50 PCS |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Inspection | 100% |
| Warranty | 1 year or 40,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 TS16949 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal, Alibaba |
###
| S-KF Ref. | Application |
| VKBA 3494 | S-KODA |
| VKBA 3495 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3496 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3497 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3498 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3499 | BMW |
| VKBA 3500 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3501 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3502 | ALFA ROMEO,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3503 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3504 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3506 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3508 | IVEc |
| VKBA 3510 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3511 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3512 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3513 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3514 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3517 | FORD |
| VKBA 3518 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3519 | AUDI,SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3520 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3521 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3522 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3523 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3524 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3525 | DACIA, NISSAN,R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3526 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3527 | LAND-ROVER |
| VKBA 3528 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3530 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3531 | FORD |
| VKBA 3532 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3534 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3535 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3536 | AUDI, SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3538 | CITROËN,FIAT,LANCIA,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3539 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LANCIA, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3540 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LANCIA, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3541 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3542 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3543 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3544 | LANCIA |
| VKBA 3545 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3546 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3548 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3549 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3550 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3551 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3552 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3553 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3554 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3555 | O-PEL,SAAB,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3556 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3557 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3558 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3559 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3560 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3561 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3562 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3564 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3565 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3567 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3568 | S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3569 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3570 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3571 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3572 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3574 | BMW |
| VKBA 3575 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3576 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3577 | FIAT,FORD,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3578 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3580 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3581 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3583 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3584 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3585 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3586 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3587 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3588 | FORD |
| VKBA 3589 | FORD |
| VKBA 3590 | FORD |
| VKBA 3592 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3594 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3595 | CITROËN, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3596 | DACIA,NISSAN, R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3597 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3598 | FIAT,LANCIA,O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3599 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LANCIA,O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3600 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3601 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3602 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3603 | LAND-ROVER,MG, ROVER |
| VKBA 3604 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3605 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3606 | AUDI,SEAT |
| VKBA 3607 | AUDI,SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3608 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3609 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3610 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3611 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3612 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3613 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3614 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
|
US $4.5-30 / Piece | |
50 Pieces (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Yes |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 12 Month |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0 |
| Certification: | ISO9001, TS16949 |
###
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) |
|---|
###
| Customization: |
Available
|
|---|
###
| Description | Front wheel bearing C2S8276 |
| Material | Chrome steel Gcr15 |
| Application | For Ford and JAGUAR |
| Size | Inner: 40mm Outer: 75mm Width: 37mm |
| Position | Front axle left and right |
| With ABS | Yes |
| Weight | 0.75 kg |
| Brand | SI, PPB, or customized |
| Packing | Neutral, SI, PPB brand packing or customized |
| OEM/ODM service | Yes |
| Manufacture place | Zhejiang, China |
| MOQ | 50 PCS |
| OEM replacement | Yes |
| Inspection | 100% |
| Warranty | 1 year or 40,000-50,000 KMS |
| Certificate | ISO9001:2015 TS16949 |
| Payment | T/T, PayPal, Alibaba |
###
| S-KF Ref. | Application |
| VKBA 3494 | S-KODA |
| VKBA 3495 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3496 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3497 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3498 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3499 | BMW |
| VKBA 3500 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3501 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3502 | ALFA ROMEO,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3503 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3504 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3506 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3508 | IVEc |
| VKBA 3510 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3511 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3512 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3513 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3514 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3517 | FORD |
| VKBA 3518 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3519 | AUDI,SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3520 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3521 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3522 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3523 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3524 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3525 | DACIA, NISSAN,R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3526 | V-OLVO |
| VKBA 3527 | LAND-ROVER |
| VKBA 3528 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3530 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3531 | FORD |
| VKBA 3532 | FORD, MAZDA |
| VKBA 3534 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3535 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3536 | AUDI, SEAT, VW |
| VKBA 3538 | CITROËN,FIAT,LANCIA,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3539 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LANCIA, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3540 | ALFA ROMEO,CITROËN,FIAT,FORD,LANCIA, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3541 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3542 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3543 | SAAB |
| VKBA 3544 | LANCIA |
| VKBA 3545 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3546 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3548 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3549 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3550 | AUDI,VW |
| VKBA 3551 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3552 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3553 | IVEC |
| VKBA 3554 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3555 | O-PEL,SAAB,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3556 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3557 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3558 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3559 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3560 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3561 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3562 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3564 | P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3565 | MERCEDES-BENZ |
| VKBA 3567 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3568 | S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3569 | AUDI,SEAT,S-KODA,VW |
| VKBA 3570 | SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3571 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3572 | O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3574 | BMW |
| VKBA 3575 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3576 | FORD,JAGUAR |
| VKBA 3577 | FIAT,FORD,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3578 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LANCIA |
| VKBA 3580 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3581 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3583 | FIAT |
| VKBA 3584 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3585 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3586 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3587 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3588 | FORD |
| VKBA 3589 | FORD |
| VKBA 3590 | FORD |
| VKBA 3592 | CITROËN,P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3594 | CITROËN |
| VKBA 3595 | CITROËN, P-EUGEOT |
| VKBA 3596 | DACIA,NISSAN, R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3597 | ALFA ROMEO |
| VKBA 3598 | FIAT,LANCIA,O-PEL,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3599 | ALFA ROMEO,FIAT,LANCIA,O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3600 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3601 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3602 | O-PEL, VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3603 | LAND-ROVER,MG, ROVER |
| VKBA 3604 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3605 | AUDI |
| VKBA 3606 | AUDI,SEAT |
| VKBA 3607 | AUDI,SEAT,VW |
| VKBA 3608 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3609 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3610 | MG,ROVER |
| VKBA 3611 | ROVER |
| VKBA 3612 | R-ENAULT |
| VKBA 3613 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
| VKBA 3614 | O-PEL,R-ENAULT,VAUXHALL |
What Is an Axle?
An axle is the central shaft of a vehicle that rotates a wheel or gear. It may be fixed to the wheels or to the vehicle itself, and can rotate with the wheels and gears. It may include bearings and mounting points. If the axle is fixed to the vehicle, it may have a steering or drive shaft attached.
Rear axle
The rear axle is a crucial part of your vehicle. If it fails to function correctly, it can cause major issues when driving at high speeds. This assembly can be a complicated component, and it is crucial that you find a mechanic who knows how to fix it. Rear axles require periodic gear oil replacement and bearing adjustments.
The rear axle is the final leg of the drivetrain, transferring rotational power from the driveshaft to the rear wheels. While the design of the rear axle varies between vehicles, all axles are designed to follow similar principles. Rear axles may have a single drive shaft or two. The drive shafts are mounted at either end of the axle.
The rear axle ratio is important because it affects how much fuel the truck uses. The lower the ratio, the more fuel-efficient the vehicle is. Higher numbers, like 4:10, are better for towing, but they will decrease fuel economy. When choosing a rear axle ratio, be sure to consider how much weight you’ll be hauling.
The rear axle is the most complicated part of the vehicle. It has many components and may not be easily visible. However, a properly functioning rear axle is essential for maximizing safety and performance. If you have a problem, you should contact a professional for a quick and easy fix. Even minor issues can make a significant difference in how your car or truck functions. A professional will ensure that your vehicle’s rear axle will be up to OEM standards.
Semi-floating axle
A semi-floating axle is the next step up from a stub axle. Semi-floating axles have a bearing that supports the shaft, which then floats inside the axle casing. These axles are best suited for midsize trucks. They are also lighter than full-floating axles and can be manufactured at a lower cost.
This design is most commonly found on rear-wheel-drive passenger cars and lighter trucks. The semi-floating design also allows for a wider diameter axle shaft, and it can increase axle capacity by increasing the diameter of the axle shaft. It also has a wider offset to accommodate larger tires. It can accommodate any offset, although this is usually only useful in off-road environments.
Semi-floating axles are often made with a tapered end. This helps keep the axel from twisting while providing traction. The rear hub of a semi-floating axle is usually connected to the axel via a big, strong nut. This nut also provides friction on the axel shaft.
A full-floating axle is common in 3/4-ton and 1/2-ton trucks. It is important to note, however, that almost all factory full-floating rear ends use eight-lug wheels. However, this rule is not strictly enforced and some companies, like Czpt, specialize in semi-floating axles and custom axles.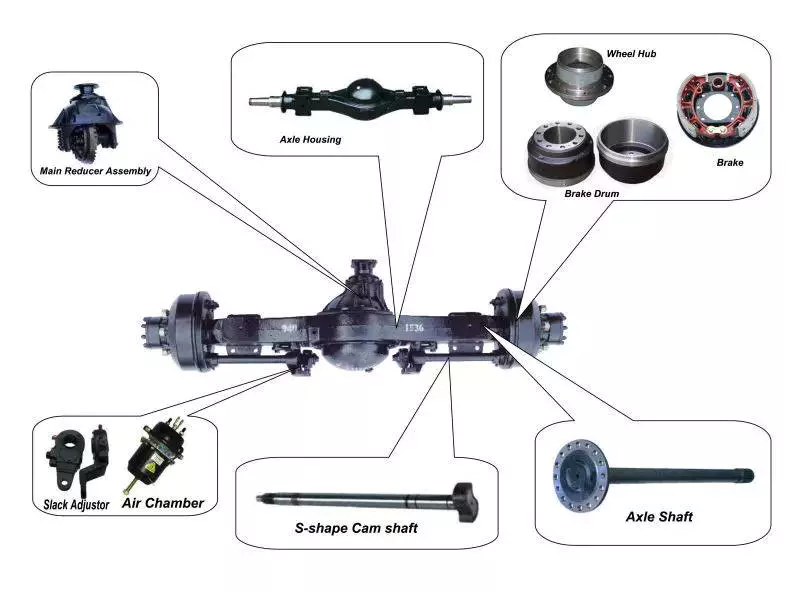
Drive shaft
A drive shaft is an important part of your vehicle’s drivetrain, which helps to transfer torque from the transmission to the drive wheels. You’ll need to know how it functions in order to properly maintain your car. Fortunately, there are a variety of different parts you can use to upgrade your drive shaft.
In order to improve the performance of your vehicle’s drivetrain, you can replace your existing drive shaft with an upgraded one. These are available in various lengths, so that you can find the right length and fit for your vehicle. Some shafts can even be customized to fit the exact length of your axle.
Generally, short axle shafts are made of solid steel. The longer ones are made of aluminum or carbon fiber. To ensure a smooth and safe ride, they are dynamically balanced to eliminate vibrations. Some models are fitted with giubo joints and universal joints to absorb shock. You can also add flex discs to improve your suspension and dampen the bucking sensation of a drive shaft.
You can tell if your drive shaft needs replacement if you hear a clicking noise while driving. This noise is often audible when the vehicle is turning sharply. You should take your vehicle to a mechanic as soon as you hear this noise, or it could lead to a costly repair. In addition to a clicking noise, your car may also be exhibiting a shuddering or vibrating sensation. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, you should take your car in for a checkup by an ASE certified technician. If you ignore these warnings, your car’s drive shaft could separate, causing you a lot of damage.
The drive shaft is attached to the axle flange by a drive shaft bolt. This is an important part of the drivetrain because it’s the only point where the drive shaft will connect to the axle. If the bolt is too long, it could be vulnerable to damage if the washers don’t fit tightly. The drive shaft socket yoke can also be easily damaged when you loosen the bolt.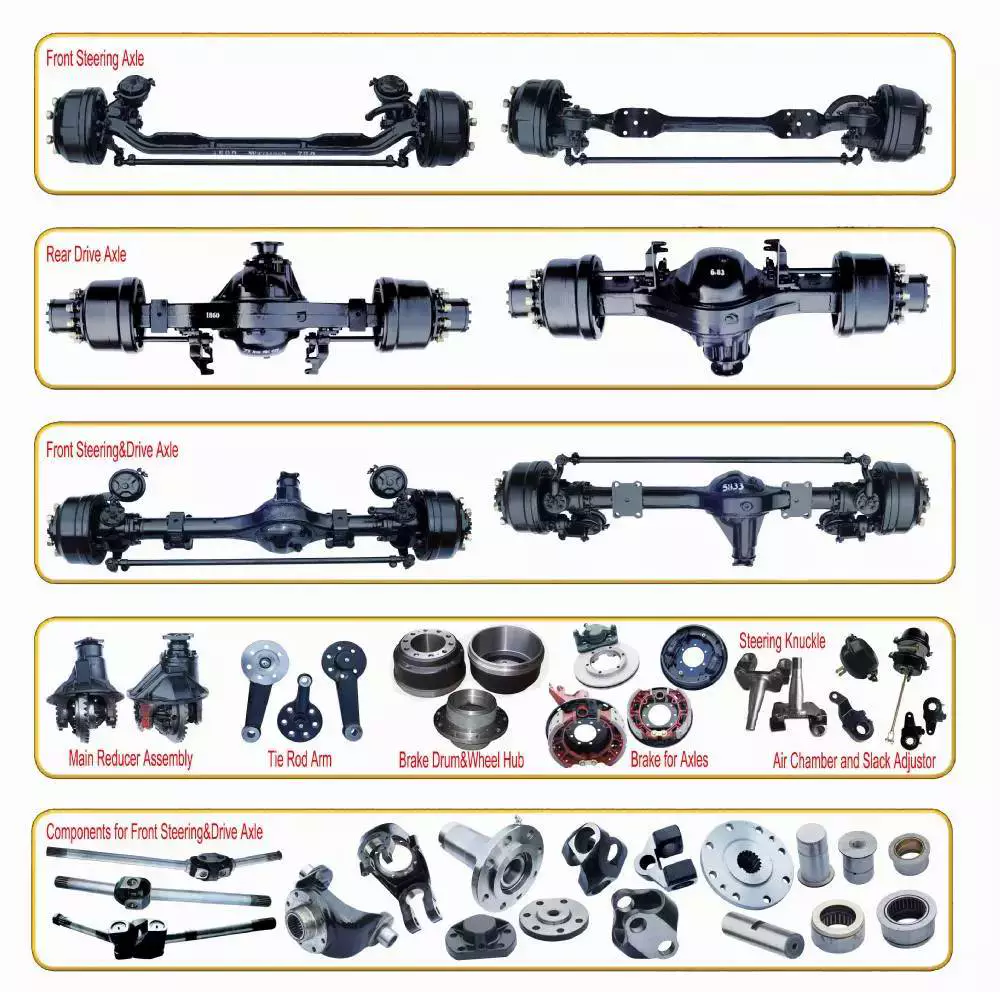
U-joint
When you replace a u-joint on an axle, you need to take a few things into consideration. One of these considerations is the type of grease you’re going to use. Some of these greases are better than others, and you should always check for a quality grease before you install a new one. A good grease can help to reduce the friction and improve the temperature resistance of the part.
It’s also important to check the u-joint itself. This is the joint between the axle shaft and the wheel. If it’s not functioning properly, it could cause further problems. You should inspect the u-joint every time you change the oil in your vehicle. You can test its lubrication by pressing on the tire with a pry bar or axle stands. You can also try turning the steering wheel fully to test if the joint is loose.
A u-joint failure can leave your car inoperable, which can make driving a risky proposition. If the drive shaft loosens and falls to the ground, you could lose control of your car and risk being stranded. In some severe cases, the front of the driveshaft can even drop to the ground and lift the rear of the car, pushing the car sideways. It’s vital to check u-joints regularly, as failure of the u-joint can cause costly and frustrating car repairs.
When you notice a bad universal joint, you should consider getting it replaced immediately. The most common symptom of a bad u-joint is a clunking sound during acceleration and deceleration. You may also hear vibrations when the u-joint becomes worn and you drive the car. If you notice these symptoms, contact a qualified technician to perform a proper diagnosis.

editor by czh 2022-11-24
China best Original Good Quality Car Truck Bus Vehicle Front Axle Rear Axle Hub005-64 Auto Wheel Hub Bearing near me factory
Product Description
CORES Auto bearing:
1. Material: Bearing steel or chrome steel
2. Features:
A. auto wheel hub bearings are adopted with international superior raw material and high-class grease from USA Shell grease.
B. The series auto wheel hub bearings are in the nature of frame structure, light weight, large rated burden, strong resistant capability, CZPT stability, good dustproof performance and etc.
C. Auto wheel hub bearing can be endured bidirectional axial load and major radial load and sealed bearings are unnecessary to add lubricant additives upon assembly.
3. Application: Auto wheel bearing are mainly used on Ford, Chrysler, Benz, BMW, Audi, FIAT, Seat, Isuzu, Polo, Renault, Peugeot, Toyota, Nissan, Santana and etc.
4. Size: We principally provides automotive wheel hub bearings for open formula, single or double shield from 25mm to 43mm on inner diameter.
5. Packing: Carton and pallet
| Wheel Hub Bearings | ||||||||||||||
| Bearing N0. | Dimensions(mm) | Net Weight | Seal | Use in automotive | ||||||||||
| CORES Bearing | d | D | B | C | (Kg) | |||||||||
| DAC124 | 546467 576467 | BAHB445539 | FC12571 GB4571 FC12784S03 | IR-2220 | C525 L29 | |||||||||
| DAC2552 | HB-3080C/SBR | 513116 | ||||||||||||
| DAC306E1 AU 0571 -4LL | BAH/SBR | IR-8622 | ||||||||||||
| DAC3564 | GB12807S03 GB40706 | IR-8066 | 770309571 | |||||||||||
| DAC37725717 | 527631 | BA2B 633571CB | ||||||||||||
| DAC3772571 | 562398A | BAHB633531B BAHBC 439622C 540360 | 4TCRI-0868 De571 | BA2B 309692 BA2B 35716 BAHB 35711 BAHB 311315BD | 39BWD02 39BWD03CA69 | IR-8052 IR-8111 | ||||||||
| DAC3968 BAHB 311396B BAHB | BAHB311443B | GB12320 S02 | IR-8095 | Fw130 | ||||||||||
| DAC40720637 | 51 | |||||||||||||
| DAC4074A | GB12399 S01 | IR-8530 | 328723 | |||||||||||
| DAC4571033 | 55580 539166 | 40BWD08AC55 | 51D 521771 | BA2B633457 BAHB311424A BAHB309245 BAHB603694A BAHB633196 BAHB633791 | GB12571 | IR-8061 IR-8509 | 513102 513112 LR571 | |||||||
| DAC4276 | BA2B35718 BA2B309609 | IR-8515 | 513154 | |||||||||||
| DAC4282 | BA2B446047 BAHB446097 GB4571 | GB12163S04 GB12875 GB4571 | IR-8086 IR-8642 | 513073 | ||||||||||
| DAC4282 | ||||||||||||||
| DAC458A | BAHB633960 | |||||||||||||
| DAC45870041 | ||||||||||||||
| DAC48860042/40 | 48BWD02 | |||||||||||||
| DAC48890044/42 | DAC4889WS | 48BWD01 | 510050 | |||||||||||
| DAC49880046 | 572506E | 49BWD01B | ||||||||||||
| DAC49840048 | DAC498448WCS47 | DU4984-7 | BTHB329129DE | FC40120S01 | JXC25469DB | |||||||||
| DAC50900034 | 528514 | BAHB633007C | ||||||||||||
| DAC49900045 | ||||||||||||||
Calculating the Deflection of a Worm Shaft
In this article, we’ll discuss how to calculate the deflection of a worm gear’s worm shaft. We’ll also discuss the characteristics of a worm gear, including its tooth forces. And we’ll cover the important characteristics of a worm gear. Read on to learn more! Here are some things to consider before purchasing a worm gear. We hope you enjoy learning! After reading this article, you’ll be well-equipped to choose a worm gear to match your needs.
Calculation of worm shaft deflection
The main goal of the calculations is to determine the deflection of a worm. Worms are used to turn gears and mechanical devices. This type of transmission uses a worm. The worm diameter and the number of teeth are inputted into the calculation gradually. Then, a table with proper solutions is shown on the screen. After completing the table, you can then move on to the main calculation. You can change the strength parameters as well.
The maximum worm shaft deflection is calculated using the finite element method (FEM). The model has many parameters, including the size of the elements and boundary conditions. The results from these simulations are compared to the corresponding analytical values to calculate the maximum deflection. The result is a table that displays the maximum worm shaft deflection. The tables can be downloaded below. You can also find more information about the different deflection formulas and their applications.
The calculation method used by DIN EN 10084 is based on the hardened cemented worm of 16MnCr5. Then, you can use DIN EN 10084 (CuSn12Ni2-C-GZ) and DIN EN 1982 (CuAl10Fe5Ne5-C-GZ). Then, you can enter the worm face width, either manually or using the auto-suggest option.
Common methods for the calculation of worm shaft deflection provide a good approximation of deflection but do not account for geometric modifications on the worm. While Norgauer’s 2021 approach addresses these issues, it fails to account for the helical winding of the worm teeth and overestimates the stiffening effect of gearing. More sophisticated approaches are required for the efficient design of thin worm shafts.
Worm gears have a low noise and vibration compared to other types of mechanical devices. However, worm gears are often limited by the amount of wear that occurs on the softer worm wheel. Worm shaft deflection is a significant influencing factor for noise and wear. The calculation method for worm gear deflection is available in ISO/TR 14521, DIN 3996, and AGMA 6022.
The worm gear can be designed with a precise transmission ratio. The calculation involves dividing the transmission ratio between more stages in a gearbox. Power transmission input parameters affect the gearing properties, as well as the material of the worm/gear. To achieve a better efficiency, the worm/gear material should match the conditions that are to be experienced. The worm gear can be a self-locking transmission.
The worm gearbox contains several machine elements. The main contributors to the total power loss are the axial loads and bearing losses on the worm shaft. Hence, different bearing configurations are studied. One type includes locating/non-locating bearing arrangements. The other is tapered roller bearings. The worm gear drives are considered when locating versus non-locating bearings. The analysis of worm gear drives is also an investigation of the X-arrangement and four-point contact bearings.
Influence of tooth forces on bending stiffness of a worm gear
The bending stiffness of a worm gear is dependent on tooth forces. Tooth forces increase as the power density increases, but this also leads to increased worm shaft deflection. The resulting deflection can affect efficiency, wear load capacity, and NVH behavior. Continuous improvements in bronze materials, lubricants, and manufacturing quality have enabled worm gear manufacturers to produce increasingly high power densities.
Standardized calculation methods take into account the supporting effect of the toothing on the worm shaft. However, overhung worm gears are not included in the calculation. In addition, the toothing area is not taken into account unless the shaft is designed next to the worm gear. Similarly, the root diameter is treated as the equivalent bending diameter, but this ignores the supporting effect of the worm toothing.
A generalized formula is provided to estimate the STE contribution to vibratory excitation. The results are applicable to any gear with a meshing pattern. It is recommended that engineers test different meshing methods to obtain more accurate results. One way to test tooth-meshing surfaces is to use a finite element stress and mesh subprogram. This software will measure tooth-bending stresses under dynamic loads.
The effect of tooth-brushing and lubricant on bending stiffness can be achieved by increasing the pressure angle of the worm pair. This can reduce tooth bending stresses in the worm gear. A further method is to add a load-loaded tooth-contact analysis (CCTA). This is also used to analyze mismatched ZC1 worm drive. The results obtained with the technique have been widely applied to various types of gearing.
In this study, we found that the ring gear’s bending stiffness is highly influenced by the teeth. The chamfered root of the ring gear is larger than the slot width. Thus, the ring gear’s bending stiffness varies with its tooth width, which increases with the ring wall thickness. Furthermore, a variation in the ring wall thickness of the worm gear causes a greater deviation from the design specification.
To understand the impact of the teeth on the bending stiffness of a worm gear, it is important to know the root shape. Involute teeth are susceptible to bending stress and can break under extreme conditions. A tooth-breakage analysis can control this by determining the root shape and the bending stiffness. The optimization of the root shape directly on the final gear minimizes the bending stress in the involute teeth.
The influence of tooth forces on the bending stiffness of a worm gear was investigated using the CZPT Spiral Bevel Gear Test Facility. In this study, multiple teeth of a spiral bevel pinion were instrumented with strain gages and tested at speeds ranging from static to 14400 RPM. The tests were performed with power levels as high as 540 kW. The results obtained were compared with the analysis of a three-dimensional finite element model.
Characteristics of worm gears
Worm gears are unique types of gears. They feature a variety of characteristics and applications. This article will examine the characteristics and benefits of worm gears. Then, we’ll examine the common applications of worm gears. Let’s take a look! Before we dive in to worm gears, let’s review their capabilities. Hopefully, you’ll see how versatile these gears are.
A worm gear can achieve massive reduction ratios with little effort. By adding circumference to the wheel, the worm can greatly increase its torque and decrease its speed. Conventional gearsets require multiple reductions to achieve the same reduction ratio. Worm gears have fewer moving parts, so there are fewer places for failure. However, they can’t reverse the direction of power. This is because the friction between the worm and wheel makes it impossible to move the worm backwards.
Worm gears are widely used in elevators, hoists, and lifts. They are particularly useful in applications where stopping speed is critical. They can be incorporated with smaller brakes to ensure safety, but shouldn’t be relied upon as a primary braking system. Generally, they are self-locking, so they are a good choice for many applications. They also have many benefits, including increased efficiency and safety.
Worm gears are designed to achieve a specific reduction ratio. They are typically arranged between the input and output shafts of a motor and a load. The 2 shafts are often positioned at an angle that ensures proper alignment. Worm gear gears have a center spacing of a frame size. The center spacing of the gear and worm shaft determines the axial pitch. For instance, if the gearsets are set at a radial distance, a smaller outer diameter is necessary.
Worm gears’ sliding contact reduces efficiency. But it also ensures quiet operation. The sliding action limits the efficiency of worm gears to 30% to 50%. A few techniques are introduced herein to minimize friction and to produce good entrance and exit gaps. You’ll soon see why they’re such a versatile choice for your needs! So, if you’re considering purchasing a worm gear, make sure you read this article to learn more about its characteristics!
An embodiment of a worm gear is described in FIGS. 19 and 20. An alternate embodiment of the system uses a single motor and a single worm 153. The worm 153 turns a gear which drives an arm 152. The arm 152, in turn, moves the lens/mirr assembly 10 by varying the elevation angle. The motor control unit 114 then tracks the elevation angle of the lens/mirr assembly 10 in relation to the reference position.
The worm wheel and worm are both made of metal. However, the brass worm and wheel are made of brass, which is a yellow metal. Their lubricant selections are more flexible, but they’re limited by additive restrictions due to their yellow metal. Plastic on metal worm gears are generally found in light load applications. The lubricant used depends on the type of plastic, as many types of plastics react to hydrocarbons found in regular lubricant. For this reason, you need a non-reactive lubricant.


China best 90369-38003 Front Axle Bearing Taper Roller Wheel Bearing for CZPT Camry Mr2 with high quality
Product Description
| OEM | 90369-38003 |
| Item Name | Bearing |
| MOQ | 100PCS |
| Warranty | 6 months |
| Price term | EXW HangZhou |
| Delivery time | According to your order |
| Size | OEM Standard Size |
The Four Basic Components of a Screw Shaft
There are 4 basic components of a screw shaft: the Head, the Thread angle, and the Threaded shank. These components determine the length, shape, and quality of a screw. Understanding how these components work together can make purchasing screws easier. This article will cover these important factors and more. Once you know these, you can select the right type of screw for your project. If you need help choosing the correct type of screw, contact a qualified screw dealer.
Thread angle
The angle of a thread on a screw shaft is the difference between the 2 sides of the thread. Threads that are unified have a 60 degree angle. Screws have 2 parts: a major diameter, also known as the screw’s outside diameter, and a minor diameter, or the screw’s root diameter. A screw or nut has a major diameter and a minor diameter. Each has its own angle, but they all have 1 thing in common – the angle of thread is measured perpendicularly to the screw’s axis.
The pitch of a screw depends on the helix angle of the thread. In a single-start screw, the lead is equal to the pitch, and the thread angle of a multiple-start screw is based on the number of starts. Alternatively, you can use a square-threaded screw. Its square thread minimizes the contact surface between the nut and the screw, which improves efficiency and performance. A square thread requires fewer motors to transfer the same load, making it a good choice for heavy-duty applications.
A screw thread has 4 components. First, there is the pitch. This is the distance between the top and bottom surface of a nut. This is the distance the thread travels in a full revolution of the screw. Next, there is the pitch surface, which is the imaginary cylinder formed by the average of the crest and root height of each tooth. Next, there is the pitch angle, which is the angle between the pitch surface and the gear axis.
Head
There are 3 types of head for screws: flat, round, and hexagonal. They are used in industrial applications and have a flat outer face and a conical interior. Some varieties have a tamper-resistant pin in the head. These are usually used in the fabrication of bicycle parts. Some are lightweight, and can be easily carried from 1 place to another. This article will explain what each type of head is used for, and how to choose the right 1 for your screw.
The major diameter is the largest diameter of the thread. This is the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. The minor diameter is the smaller diameter and is the distance between the major and minor diameters. The minor diameter is half the major diameter. The major diameter is the upper surface of the thread. The minor diameter corresponds to the lower extreme of the thread. The thread angle is proportional to the distance between the major and minor diameters.
Lead screws are a more affordable option. They are easier to manufacture and less expensive than ball screws. They are also more efficient in vertical applications and low-speed operations. Some types of lead screws are also self-locking, and have a high coefficient of friction. Lead screws also have fewer parts. These types of screw shafts are available in various sizes and shapes. If you’re wondering which type of head of screw shaft to buy, this article is for you.
Threaded shank
Wood screws are made up of 2 parts: the head and the shank. The shank is not threaded all the way up. It is only partially threaded and contains the drive. This makes them less likely to overheat. Heads on wood screws include Oval, Round, Hex, Modified Truss, and Flat. Some of these are considered the “top” of the screw.
Screws come in many sizes and thread pitches. An M8 screw has a 1.25-mm thread pitch. The pitch indicates the distance between 2 identical threads. A pitch of 1 is greater than the other. The other is smaller and coarse. In most cases, the pitch of a screw is indicated by the letter M followed by the diameter in millimetres. Unless otherwise stated, the pitch of a screw is greater than its diameter.
Generally, the shank diameter is smaller than the head diameter. A nut with a drilled shank is commonly used. Moreover, a cotter pin nut is similar to a castle nut. Internal threads are usually created using a special tap for very hard metals. This tap must be followed by a regular tap. Slotted machine screws are usually sold packaged with nuts. Lastly, studs are often used in automotive and machine applications.
In general, screws with a metric thread are more difficult to install and remove. Fortunately, there are many different types of screw threads, which make replacing screws a breeze. In addition to these different sizes, many of these screws have safety wire holes to keep them from falling. These are just some of the differences between threaded screw and non-threaded. There are many different types of screw threads, and choosing the right 1 will depend on your needs and your budget.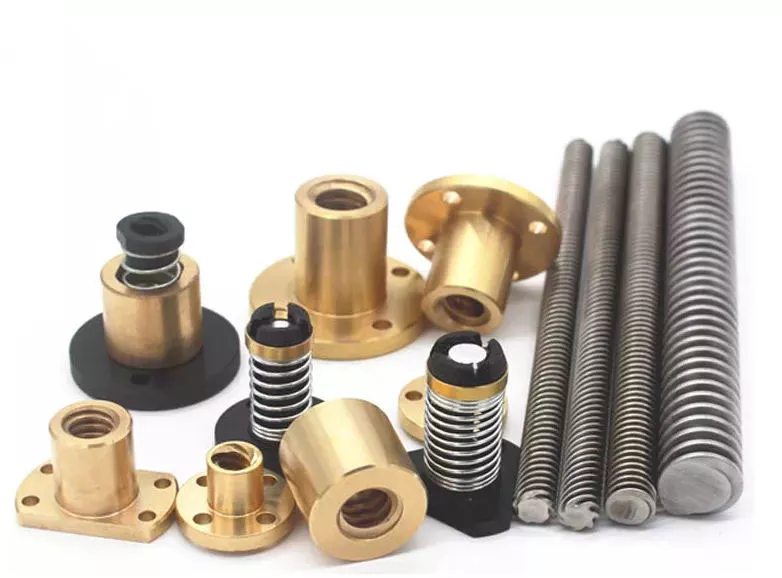
Point
There are 3 types of screw heads with points: cone, oval, and half-dog. Each point is designed for a particular application, which determines its shape and tip. For screw applications, cone, oval, and half-dog points are common. Full dog points are not common, and they are available in a limited number of sizes and lengths. According to ASTM standards, point penetration contributes as much as 15% of the total holding power of the screw, but a cone-shaped point may be more preferred in some circumstances.
There are several types of set screws, each with its own advantage. Flat-head screws reduce indentation and frequent adjustment. Dog-point screws help maintain a secure grip by securing the collar to the screw shaft. Cup-point set screws, on the other hand, provide a slip-resistant connection. The diameter of a cup-point screw is usually half of its shaft diameter. If the screw is too small, it may slack and cause the screw collar to slip.
The UNF series has a larger area for tensile stress than coarse threads and is less prone to stripping. It’s used for external threads, limited engagement, and thinner walls. When using a UNF, always use a standard tap before a specialized tap. For example, a screw with a UNF point is the same size as a type C screw but with a shorter length.
Spacer
A spacer is an insulating material that sits between 2 parts and centers the shaft of a screw or other fastener. Spacers come in different sizes and shapes. Some of them are made of Teflon, which is thin and has a low coefficient of friction. Other materials used for spacers include steel, which is durable and works well in many applications. Plastic spacers are available in various thicknesses, ranging from 4.6 to 8 mm. They’re suitable for mounting gears and other items that require less contact surface.
These devices are used for precision fastening applications and are essential fastener accessories. They create clearance gaps between the 2 joined surfaces or components and enable the screw or bolt to be torqued correctly. Here’s a quick guide to help you choose the right spacer for the job. There are many different spacers available, and you should never be without one. All you need is a little research and common sense. And once you’re satisfied with your purchase, you can make a more informed decision.
A spacer is a component that allows the components to be spaced appropriately along a screw shaft. This tool is used to keep space between 2 objects, such as the spinning wheel and an adjacent metal structure. It also helps ensure that a competition game piece doesn’t rub against an adjacent metal structure. In addition to its common use, spacers can be used in many different situations. The next time you need a spacer, remember to check that the hole in your screw is threaded.
Nut
A nut is a simple device used to secure a screw shaft. The nut is fixed on each end of the screw shaft and rotates along its length. The nut is rotated by a motor, usually a stepper motor, which uses beam coupling to accommodate misalignments in the high-speed movement of the screw. Nuts are used to secure screw shafts to machined parts, and also to mount bearings on adapter sleeves and withdrawal sleeves.
There are several types of nut for screw shafts. Some have radial anti-backlash properties, which prevent unwanted radial clearances. In addition, they are designed to compensate for thread wear. Several nut styles are available, including anti-backlash radial nuts, which have a spring that pushes down on the nut’s flexible fingers. Axial anti-backlash nuts also provide thread-locking properties.
To install a ball nut, you must first align the tangs of the ball and nut. Then, you must place the adjusting nut on the shaft and tighten it against the spacer and spring washer. Then, you need to lubricate the threads, the ball grooves, and the spring washers. Once you’ve installed the nut, you can now install the ball screw assembly.
A nut for screw shaft can be made with either a ball or a socket. These types differ from hex nuts in that they don’t need end support bearings, and are rigidly mounted at the ends. These screws can also have internal cooling mechanisms to improve rigidity. In this way, they are easier to tension than rotating screws. You can also buy hollow stationary screws for rotator nut assemblies. This type is great for applications requiring high heat and wide temperature changes, but you should be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions.


China Standard Axle Front Wheel Bearing Japan Auto Rear Wheel Bearing Hub for CZPT Vitsz Hiace Altis Mits Dac25520043 Dac2050043/45 Dac25550043 Auto Bearing with high quality
Product Description
Product Description
Axle Front Wheel Bearing Japan Auto Rear Wheel Bearing Hub for CZPT Vitsz Hiace Altis Mits Dac2552
DAC20420030/29 DAC2 0571 16 DAC2 0571 16 DAC2552037 DAC25520040 DAC25520042 DAC25520043 DAC2050043/45 DAC25550043 DAC2550045 DAC25565716/29 DAC25560032 DAC25605716/29 DAC2562571/17 DAC25720043 DAC27520045/43 DAC27520050 DAC2760050 DAC28580042 DAC28610042 DAC39530037 DAC3 0571 042 DAC3060037 DAC3060037 DAC30600337-4RS DAC3060037/43 DAC30630042 DAC3063030042 DAC30640042 DAC30650571 DAC30670571 DAC30680045 DAC32700038 DAC32720045 DAC32720345 DAC34620037 DAC34640034 DAC34640037 DAC34640037 DAC34660037 DAC356180040 DAC35620040 DAC35640037 DAC35650035 DAC35650037 DAC35660032 DAC35660033 DAC35660037 DAC35680037 DAC35680037 DAC35680045 DAC35685713/30 DAC35725718 DAC35720033 DAC35720033 DAC3572571 DAC35725713/31 DAC35720034 DAC3572571 DAC35720045 DAC35740030 DAC35760054 DAC35770042 DAC36680033 DAC36720033/28 DAC36720034 DAC36720042 DAC3676571/27 DAC3772033 DAC37720037 DAC37725717 DAC3772571 DAC37740045 DAC38650050 DAC38680037 DAC3870037 DAC381700037 DAC38700038 DAC38710033/30 DAC38710039 DAC38720034 DAC38720036/33 DAC38725716/33 DAC38720040 DAC38730040 DAC38740036/33 DAC38740036/33 DAC38745716/33 DAC38740050 DAC38740450 DAC38800036/33 DAC39680037 DAC39680037 DAC39680037 DAC39680637 DAC3968571 DAC39720037 DAC39720037 DAC39720637 DAC39740036/34 DAC39740039 DAC39740 0571 RS DAC39/41750037 DAC40720037 DAC40720637 DAC4571055 DAC40740036/34 DAC40740036 DAC40740040 DAC40740042 DAC4571037 DAC4571033/28 DAC407641/38 DAC40800036/34 DAC408000302 DAC40800034 DAC408000381 DAC40800036 DAC40800045/44 DAC40840040 DAC457180032/17 DAC41680040/35 DAC42720038 DAC42720038/35 DAC42750037 DAC42750037 DAC42760033 DAC42760038/33 DAC42760038/35 DAC42760039 DAC42760040/37 DAC42780038 DAC42780041/38 DAC428000302 DAC42800036/34 DAC42800037 DAC42800042 DAC42800342 DAC42800045 DAC42820036 DAC42820036 DAC42820037 DAC42840036 DAC42840039 DAC4284030039 DAC43760043 DAC43790041/38 DAC43790041 DAC43790045 DAC43800038 DAC43800050/45 DAC43820045 DAC43 DAC44825037 DAC44840042/40 DAC45800045 DAC45830045 DAC45840039 DAC45840041/39 DAC45840042/40 DAC45840045 DAC458500302 DAC45850041 DAC45880039 DAC47810053 DAC47850045 DAC48890044/42 DAC49840043 DAC49840048 DAC49840050 DAC49880046 5908BD 5908B DU5496-5 DAC55900060 DAC56880040/35 DAC559052/40 DAC559054/39
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Our Advantages
Our Advantages:
1. World-Class Bearing: We provide our customers with all types of indigenous bearing with world-class quality.
2. OEM or Non-Stand Bearings: Any requirement for Nonstandard bearings is Easily Fulfilled by us due to its vast knowledge and links in the industry.
3. Genuine products With Excellent Quality: The company has always proved the 100% quality products it provides with genuine intent.
4. After Sales Service and Technical Assistance: The company provides after-sales service and technical assistance as per the customer’s requirements and needs.
5. Quick Delivery: The company provides just-in-time delivery with its streamlined supply chain.
SAMPLES
1. Samples quantity: 1-10 PCS are available.
2. Free samples: It depends on the Model No., material and quantity. Some of the bearings samples need client to pay samples charge and shipping cost.
3. It’s better to start your order with Trade Assurance to get full protection for your samples order.
CUSTOMIZED
The customized LOGO or drawing is acceptable for us.
MOQ
1. MOQ: 10 PCS standard bearings.
2. MOQ: 1000 PCS customized your brand bearings.
OEM POLICY
1. We can printing your brand (logo, artwork)on the shield or laser engraving your brand on the shield.
2. We can custom your packaging according to your design
3. All copyright own by clients and we promised don’t disclose any info.
FAQ
1.What is the minimum order quantity for this product?
Can be negotiated, we will try our best to meet customer needs.Our company is mainly based on wholesale sales, most customers’orders are more than 1 ton.
2.What is your latest delivery time?
Most orders will be shipped within 7-15 days of payment being received.
3.Does your company have quality assurance?
Yes, for 1 years.
4.What is the competitiveness of your company’s products compared to other companies?
High precision, high speed, low noise.
5.What are the advantages of your company’s services compared to other companies?
Answer questions online 24 hours a day, reply in a timely manner, and provide various documents required by customers for customs clearance or sales. 100% after-sales service.
6.Which payment method does your company support?
Do our best to meet customer needs, negotiable.
7.How to contact us quickly?
Please send us an inquiry or message and leave your other contact information, such as phone number, account or account, we will contact you as soon as possible and provide the detailed information you need.
Please feel free to contact us, if you have any other question
Screws and Screw Shafts
A screw is a mechanical device that holds objects together. Screws are usually forged or machined. They are also used in screw jacks and press-fitted vises. Their self-locking properties make them a popular choice in many different industries. Here are some of the benefits of screws and how they work. Also read about their self-locking properties. The following information will help you choose the right screw for your application.
Machined screw shaft
A machined screw shaft can be made of various materials, depending on the application. Screw shafts can be made from stainless steel, brass, bronze, titanium, or iron. Most manufacturers use high-precision CNC machines or lathes to manufacture these products. These products come in many sizes and shapes, and they have varying applications. Different materials are used for different sizes and shapes. Here are some examples of what you can use these screws for:
Screws are widely used in many applications. One of the most common uses is in holding objects together. This type of fastener is used in screw jacks, vises, and screw presses. The thread pitch of a screw can vary. Generally, a smaller pitch results in greater mechanical advantage. Hence, a machined screw shaft should be sized appropriately. This ensures that your product will last for a long time.
A machined screw shaft should be compatible with various threading systems. In general, the ASME system is used for threaded parts. The threaded hole occupies most of the shaft. The thread of the bolt occupy either part of the shaft, or the entire one. There are also alternatives to bolts, including riveting, rolling pins, and pinned shafts. These alternatives are not widely used today, but they are useful for certain niche applications.
If you are using a ball screw, you can choose to anneal the screw shaft. To anneal the screw shaft, use a water-soaked rag as a heat barrier. You can choose from 2 different options, depending on your application. One option is to cover the screw shaft with a dust-proof enclosure. Alternatively, you can install a protective heat barrier over the screw shaft. You can also choose to cover the screw shaft with a dust-proof machine.
If you need a smaller size, you can choose a smaller screw. It may be smaller than a quarter of an inch, but it may still be compatible with another part. The smaller ones, however, will often have a corresponding mating part. These parts are typically denominated by their ANSI numerical size designation, which does not indicate threads-per-inch. There is an industry standard for screw sizes that is a little easier to understand.
Ball screw nut
When choosing a Ball screw nut for a screw shaft, it is important to consider the critical speed of the machine. This value excites the natural frequency of a screw and determines how fast it can be turned. In other words, it varies with the screw diameter and unsupported length. It also depends on the screw shaft’s diameter and end fixity. Depending on the application, the nut can be run at a maximum speed of about 80% of its theoretical critical speed.
The inner return of a ball nut is a cross-over deflector that forces the balls to climb over the crest of the screw. In 1 revolution of the screw, a ball will cross over the nut crest to return to the screw. Similarly, the outer circuit is a circular shape. Both flanges have 1 contact point on the ball shaft, and the nut is connected to the screw shaft by a screw.
The accuracy of ball screws depends on several factors, including the manufacturing precision of the ball grooves, the compactness of the assembly, and the set-up precision of the nut. Depending on the application, the lead accuracy of a ball screw nut may vary significantly. To improve lead accuracy, preloading, and lubrication are important. Ewellix ball screw assembly specialists can help you determine the best option for your application.
A ball screw nut should be preloaded prior to installation in order to achieve the expected service life. The smallest amount of preload required can reduce a ball screw’s calculated life by as much as 90 percent. Using a lubricant of a standard grade is recommended. Some lubricants contain additives. Using grease or oil in place of oil can prolong the life of the screw.
A ball screw nut is a type of threaded nut that is used in a number of different applications. It works similar to a ball bearing in that it contains hardened steel balls that move along a series of inclined races. When choosing a ball screw nut, engineers should consider the following factors: speed, life span, mounting, and lubrication. In addition, there are other considerations, such as the environment in which the screw is used.
Self-locking property of screw shaft
A self-locking screw is 1 that is capable of rotating without the use of a lock washer or bolt. This property is dependent on a number of factors, but 1 of them is the pitch angle of the thread. A screw with a small pitch angle is less likely to self-lock, while a large pitch angle is more likely to spontaneously rotate. The limiting angle of a self-locking thread can be calculated by calculating the torque Mkdw at which the screw is first released.
The pitch angle of the screw’s threads and its coefficient of friction determine the self-locking function of the screw. Other factors that affect its self-locking function include environmental conditions, high or low temperature, and vibration. Self-locking screws are often used in single-line applications and are limited by the size of their pitch. Therefore, the self-locking property of the screw shaft depends on the specific application.
The self-locking feature of a screw is an important factor. If a screw is not in a state of motion, it can be a dangerous or unusable machine. The self-locking property of a screw is critical in many applications, from corkscrews to threaded pipe joints. Screws are also used as power linkages, although their use is rarely necessary for high-power operations. In the archimedes’ screw, for example, the blades of the screw rotate around an axis. A screw conveyor uses a rotating helical chamber to move materials. A micrometer uses a precision-calibrated screw to measure length.
Self-locking screws are commonly used in lead screw technology. Their pitch and coefficient of friction are important factors in determining the self-locking property of screws. This property is advantageous in many applications because it eliminates the need for a costly brake. Its self-locking property means that the screw will be secure without requiring a special kind of force or torque. There are many other factors that contribute to the self-locking property of a screw, but this is the most common factor.
Screws with right-hand threads have threads that angle up to the right. The opposite is true for left-hand screws. While turning a screw counter-clockwise will loosen it, a right-handed person will use a right-handed thumb-up to turn it. Similarly, a left-handed person will use their thumb to turn a screw counter-clockwise. And vice versa.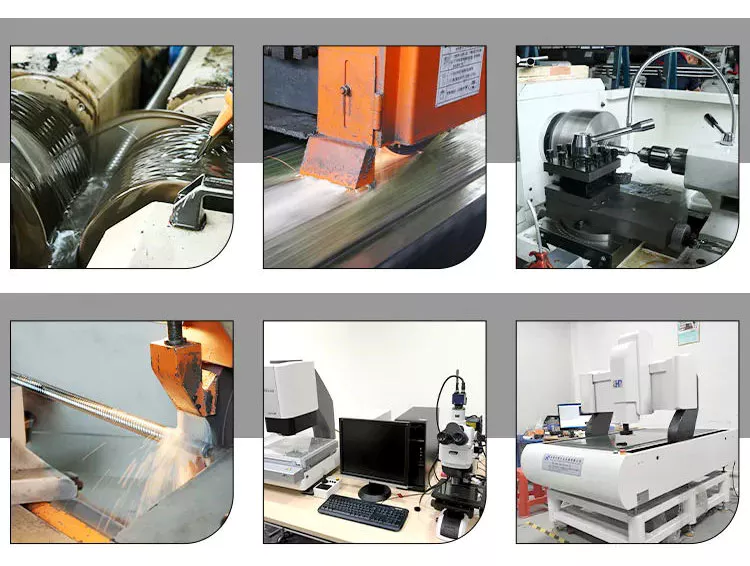
Materials used to manufacture screw shaft
Many materials are commonly used to manufacture screw shafts. The most common are steel, stainless steel, brass, bronze, and titanium. These materials have advantages and disadvantages that make them good candidates for screw production. Some screw types are also made of copper to fight corrosion and ensure durability over time. Other materials include nylon, Teflon, and aluminum. Brass screws are lightweight and have aesthetic appeal. The choice of material for a screw shaft depends on the use it will be made for.
Shafts are typically produced using 3 steps. Screws are manufactured from large coils, wire, or round bar stock. After these are produced, the blanks are cut to the appropriate length and cold headed. This cold working process pressudes features into the screw head. More complicated screw shapes may require 2 heading processes to achieve the desired shape. The process is very precise and accurate, so it is an ideal choice for screw manufacturing.
The type of material used to manufacture a screw shaft is crucial for the function it will serve. The type of material chosen will depend on where the screw is being used. If the screw is for an indoor project, you can opt for a cheaper, low-tech screw. But if the screw is for an outdoor project, you’ll need to use a specific type of screw. This is because outdoor screws will be exposed to humidity and temperature changes. Some screws may even be coated with a protective coating to protect them from the elements.
Screws can also be self-threading and self-tapping. The self-threading or self-tapping screw creates a complementary helix within the material. Other screws are made with a thread which cuts into the material it fastens. Other types of screws create a helical groove on softer material to provide compression. The most common uses of a screw include holding 2 components together.
There are many types of bolts available. Some are more expensive than others, but they are generally more resistant to corrosion. They can also be made from stainless steel or aluminum. But they require high-strength materials. If you’re wondering what screws are, consider this article. There are tons of options available for screw shaft manufacturing. You’ll be surprised how versatile they can be! The choice is yours, and you can be confident that you’ll find the screw shaft that will best fit your application.


China Best Sales Wheel Hub Bearing Wholesale Axle Bearing Dac356535z with Free Design Custom
Product Description
Welcome to choose KORTON INDUSTRIAL LIMITED.; Please read the following information carefully.;
NO 1.; our adwantages
1.; 14 years bearing products manufacturing and exporting experiences.;
2.; OEM order and non-standard bearing order can be accepted.;
3.; Many sizes of bearing are available.; Large quantity bearing can be provided.;
4.; To respect customers,; you can choose the loading port.;
5.; A certain number of free sample can be provide to support our customer’s after-sale services and warranty.;
NO 2.; Description:; Auto wheel bearing
The main functions of wheel hub bearings are load and provide accurate guidance to the turn of hub bearings.; Hub bearings not only carry axial load but also carry radial load,; they are important components.; They can carry heavy radial load which include axial and radial load and torques load,; they can limit axial displacement both sides.; They are mainly used in components which limitation of bearings and shell axial displacement of both sides.; Hub bearings’ design are familiar to the 2 back to back order single row conntact ball bearings,; but the width are shorter than single row bearings.; Compare to the single row bearings hub bearings have better rigidity.;
NO 3.; OEM all brand bearing
NO 4.; Auto Wheel Bearing Specification:;
| Seals Types | ZZ,;2RS,;OPEN | ||||||||
| Vibration Level | Z1V1,;Z2V2,;Z3V3 | ||||||||
| Clearance | C2,;C0,;C3,;C4,;C5 | ||||||||
| Tolerance Codes | ABEC-1,;ABEC-3,;ABEC-5 | ||||||||
| Materral | GCr15-China/AISI521W | ||||||||
| DAC30600037 | 30 | 60 | 37 | 37 | 0.;42 | 529891AB | BA2B633313C | DAC3060W | |
| DAC30620038 | 30 | 62 | 38 | 38 | 0.;52 | 545312 | 418780 | 30BWD10 | |
| DAC30630042 | 30 | 63 | 42 | 42 | 0.;57 | 581736 | 45716A | 30BWD01A | |
| DAC30640042 | 30 | 64 | 42 | 42 | 0.;5 | 34BWD03ACA78 | DAC3064W2R | ||
| DAC32720045 | 32 | 72 | 45 | 45 | 0.;81 | 531910 | 32BWD05CA75 | ||
| DAC34620037 | 34 | 62 | 37 | 37 | 0.;41 | 561447 | BAHB311316B | 34BWD08/CA70 | |
| DAC34640037 | 34 | 64 | 37 | 37 | 0.;43 | 540466B | 3 0571 6DA | 34BWD11 | DAC3464G1 |
| DAC34660037 | 34 | 66 | 37 | 37 | 0.;5 | 580400CA | 636114A | 34BWD10B | |
| DAC34670037 | 34 | 67 | 37 | 37 | 0.;52 | 532066DB | |||
| DAC34680037 | 34 | 68 | 37 | 37 | 0.;55 | 567918B | DAC3468DW | ||
| DAC35620040 | 35 | 62 | 40 | 40 | 0.;43 | 430042C | |||
| DAC35640037 | 35 | 64 | 37 | 37 | 0.;41 | BT2B445620B | |||
| DAC35650035 | 35 | 65 | 35 | 35 | 0.;4 | 546238A | 443952 | DAC3565WCS30 | |
| DAC35660033 | 35 | 66 | 33 | 33 | 0.;43 | BAHB633676 | |||
| DAC35660037 | 35 | 66 | 37 | 37 | 0.;48 | 544307 | BAHB311309 | DAC35660037 | |
| DAC35680033/30 | 35 | 68 | 33 | 30 | 0.;47 | 546238 | BA2B445535AE | 35BWD07A | DAC3568W-6 |
| DAC35680037 | 35 | 68 | 37 | 37 | 0.;52 | 541153 | 633295 | DAC3568A2RS | |
| DAC35720033 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;58 | 548083 | BA2B446762B | ||
| DAC35725713/31 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 31 | 0.;56 | 562686 | FWB14 | 35BWD06ACA111 | DAC357233B-1W |
| DAC3572571 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;58 | 548083 | BAHB633669 | 35BWD08A | DAC357545CW2R |
| DAC35720034 | 35 | 72 | 34 | 34 | 0.;58 | 54 0571 | BAHB633967 | 35BWD01 | DAC357234A |
| DAC3572571 | 35 | 72 | 34 | 34 | 0.;58 | BAHB633528F | |||
| DAC36640042 | 36 | 64 | 42 | 42 | 0.;46 | CRI-0787 | |||
| DAC36680033 | 36 | 68 | 33 | 33 | 0.;47 | DAC3668AWCS36 | |||
| DAC37720033 | 37 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;5 | BAH-0051B |
NO 6.; Some Auto wheel bearing OEM number and Application:;
| OEM NUMBERS | DESCRIPTION | APPLICATION |
| B001-33-043 | WHEEL BEARINGS | SPORTAGE |
| 04495-0K120 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HILUX’07 |
| 42409-19015 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | COROLLA |
| 42409-33571 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | CAMRY 1 |
| 90369-38011 | WHEEL BEARING FRONT | COROLLA 3872 |
| 43504-12090 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | COROLLA |
| 42409-2571 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | AVENSIS,; CARINA |
| 43502-20131 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | CARINA |
| 44300-S3V-AO1 | WHEEL BEARINGS FRONT | TRUCK / LAND CRUISE |
| 42409-42571 | WHEEL BEARINGS REAR | RAV 4 |
| 518506 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | CAMRY |
| 175407615 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | GOLF 1 |
| 331598625 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | GOLF II |
| 3871 | WHEEL BEARING FRONT | TOY STARLET |
| 4382 | WHEEL BEARING | CAMRY |
| 90368-50008 | WHEEL BEARING | DYNA |
| 90369-32003 | WHEEL BEARING | RX80 FRONT |
| 45710-C6000 | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN PATROL FRONT |
| 45710-50Y00-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN SUNNY |
| 45710-71L00-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN |
| 42200-SH3-970-D | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA CIVIC |
| 42300-SD4-004 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA BALLADE |
| 43210-C9300-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN PATROL |
| 43210-D5710-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISS-B/BIRD REAR |
| 44200-SM4-0131 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA-CIVIC |
| 44300-SB2-965 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA |
| 44300-S04-0040 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA-CIVIC |
| MB584761 | WHEEL BEARING | MITS-LANCER |
| MB664447 | WHEEL BEARING | MITS-PAJERO |
| 46T080604 | WHEEL BEARING | COROLLA-REAR |
| DG4 0571 6WRS/DG4094W | WHEEL BEARING REAR | HIACE 4X4 |
| 3874 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CORONA |
| 157148/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 104948/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 48548/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HIACE 2Y |
| 12649/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HIACE 2Y |
| 30303D | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 4T-CR1-0881 | WHEEL BEARINGS | BLUEBIRD |
| 11162/ | WHEEL BEARINGS | LAND ROVER |
| 69345/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA 323 |
| 11749/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 35715 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA B1800 |
| 35714 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 67048/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CRESSIDA |
| 44649/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 45449/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | COROLLA DX |
| 30849/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA |
| 6308 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOY HIACE |
| U399 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOY HILUX |
| 11949/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 30304 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 4080 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI |
| 603049/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA |
| 6306CNXL330 | GEAR BOX BEARINGS | NISSAN TD27 |
| TR080702J | GEAR BOX BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA |
| 3314598 | WHEEL BEARINGS | FORD RANGER |
| DAC38640036 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA REAR |
| TR070904-J-N | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| R30-13 | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| TR100802-I-N | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 42BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN BLUEBIRD |
| 46T 0571 05 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA LUCIDA |
| HM801310-22-N | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| LM603049/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | FORD/L/ROVER |
| 17831/17887 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| 2788 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 26882 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 28985/28920 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| HM801349-N | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| 50KW8019 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| 45289 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA |
| 43BWD03 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA MARK11 |
| 35BWD16 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN MARCH |
| LM300811 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1TONNER |
| LM60571 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1TONNER |
| 35712 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER FRONT |
| 35718j/57307 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200 REAR |
| ST2749 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA STARLET FRONT |
| 55KW02 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| 55KW01 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| 25KC802 | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 35BW08 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOWNACE REAR |
| 32207 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER FRONT |
| DAC4380A | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA 626 |
| 46T 0571 04A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA CONDOR FRONT |
| TR0708030 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| 32012X | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200/CANTER REAR |
| 4276 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200/CANTER REAR |
| 28580 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 3579R/25 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA FRONT |
| HR32210J | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| HR32206J | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN SUNNY |
| HR35717J | DIFF BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| DU5496-5 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA HILUX |
| 40KW019 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| TR0607R | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| TR57326 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 2474 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 33013A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| HR32307CN | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HILUX |
| 32310 | WHEEL BEARINGS | ISUZU LIGHT TRUCK |
| 40BWD12 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA VISTA |
| 33205JR | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA VISTA |
| LM300849 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN-DATSUN |
| 50KWH01 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI SPORTERO |
| 40KW01 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO |
| 30305 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 32571XJ | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 35718 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 32304 | WHEEL BEARINGS | ISUZU |
| DAC43792RS | WHEEL BEARINGS | HONDA CRV |
| 40KWD02 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI SPORTERO |
| 38BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA MARK11 FRONT |
| 43KWD04 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN PRIMERA |
| 427638 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA REGUS FRONT |
| LM68149/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CROWN FRONT |
| LM12749/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CROWN FRONT |
| 32005JR | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA FRONT |
| 35BCD08 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA NOAH REAR |
| LM506810 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| ET33011 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN CABSTER |
| RNU0727 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 46T08805 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI PAJERO |
| 1220 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA |
| 28584 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 469-N | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER REAR |
| 28BWD01A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA REAR |
| 57305 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA TOWNACE |
| 40BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA FRONT |
| AU 0571 -2 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN X-TRAIL |
| ME6 0571 4 | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D30 |
| 30502-28E20 | THRUST BEARING | TD27 |
| 30502-53J00 | THRUST BEARING | GA16 |
| 31230-12140 | THRUST BEARING | EE90 |
| 31230-35070 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-3L |
| 31250-35050 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-2L |
| 31230-35090 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-5L |
| 31230-36160 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-1HZ |
| 31230-60130 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-1FZ |
| MD703270 | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D55 |
| ME657110-D | THRUST BEARING | MITS-CANTER |
| 5712-16-222-D | THRUST BEARING | MAZ-HA |
| 31230-60120 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-2H |
| 31230-60150 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-FJ80 |
| 31230-32571 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-3S |
| 1304-16-510B | THRUST BEARING | MAZ-TITAN |
| MD719469-D | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D56 |
| 31230-36150 | THRUST BEARING | COASTER |
| 31230-32060 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-4AF |
| 58SCRN37P | THRUST BEARINGS | TOYOTA 1KZ |
Why Choose Us:;
We are an industrial company.;We have our own brand:; SFNB .;If you interested in our product,;I can take you to visit our factory.;
Our factory have advanced testing equipment,;before the every product leave the factory,;we will be testing.;We can send samples to you,;you can test the quality,;and if you accept the sample quality,;we can promise:; the follow-up orders’ quality will be the same as samples.;
About ordinary standard type of bearing ,;We have rich inventory,;not have MOQ,;if your need a product is Non-standard size,;need customize,;we will according the product size to determine the MOQ.;
Our company can accept OEM,;you can send sample to me,;we can manufacturing products the same as sample.;Meanwhile,;we also can accept some well-known brands of OEM,;
If the amount of money is less,;you can pay it by Paypal or Alipay.;Of course you can payment by TT or Western Union etc.;
Lead Screws and Clamp Style Collars
If you have a lead screw, you’re probably interested in learning about the Acme thread on this type of shaft. You might also be interested in finding out about the Clamp style collars and Ball screw nut. But before you buy a new screw, make sure you understand what the terminology means. Here are some examples of screw shafts:
Acme thread
The standard ACME thread on a screw shaft is made of a metal that is resistant to corrosion and wear. It is used in a variety of applications. An Acme thread is available in a variety of sizes and styles. General purpose Acme threads are not designed to handle external radial loads and are supported by a shaft bearing and linear guide. Their design is intended to minimize the risk of flank wedging, which can cause friction forces and wear. The Centralizing Acme thread standard caters to applications without radial support and allows the thread to come into contact before its flanks are exposed to radial loads.
The ACME thread was first developed in 1894 for machine tools. While the acme lead screw is still the most popular screw in the US, European machines use the Trapezoidal Thread (Metric Acme). The acme thread is a stronger and more resilient alternative to square threads. It is also easier to cut than square threads and can be cut by using a single-point threading die.
Similarly to the internal threads, the metric versions of Acme are similar to their American counterparts. The only difference is that the metric threads are generally wider and are used more frequently in industrial settings. However, the metric-based screw threads are more common than their American counterparts worldwide. In addition, the Acme thread on screw shafts is used most often on external gears. But there is still a small minority of screw shafts that are made with a metric thread.
ACME screws provide a variety of advantages to users, including self-lubrication and reduced wear and tear. They are also ideal for vertical applications, where a reduced frictional force is required. In addition, ACME screws are highly resistant to back-drive and minimize the risk of backlash. Furthermore, they can be easily checked with readily available thread gauges. So, if you’re looking for a quality ACME screw for your next industrial project, look no further than ACME.
Lead screw coatings
The properties of lead screw materials affect their efficiency. These materials have high anti-corrosion, thermal resistance, and self-lubrication properties, which eliminates the need for lubrication. These coating materials include polytetrafluoroethylene (PFE), polyether ether ketone (PEK), and Vespel. Other desirable properties include high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and rigidity.
The most common materials for lead screws are carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Lead screw coatings can be PTFE-based to withstand harsh environments and remove oil and grease. In addition to preventing corrosion, lead screw coatings improve the life of polymer parts. Lead screw assembly manufacturers offer a variety of customization options for their lead screw, including custom-molded nuts, thread forms, and nut bodies.
Lead screws are typically measured in rpm, or revolutions per minute. The PV curve represents the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. This value is affected by the material used in the construction of the screw, lubrication conditions, and end fixity. The critical speed of lead screws is determined by their length and minor diameter. End fixity refers to the support for the screw and affects its rigidity and critical speed.
The primary purpose of lead screws is to enable smooth movement. To achieve this, lead screws are usually preloaded with axial load, enabling consistent contact between a screw’s filets and nuts. Lead screws are often used in linear motion control systems and feature a large area of sliding contact between male and female threads. Lead screws can be manually operated or mortised and are available in a variety of sizes and materials. The materials used for lead screws include stainless steel and bronze, which are often protected by a PTFE type coating.
These screws are made of various materials, including stainless steel, bronze, and various plastics. They are also made to meet specific requirements for environmental conditions. In addition to lead screws, they can be made of stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Surface coatings can improve the screw’s corrosion resistance, while making it more wear resistant in tough environments. A screw that is coated with PTFE will maintain its anti-corrosion properties even in tough environments.
Clamp style collars
The screw shaft clamp style collar is a basic machine component, which is attached to the shaft via multiple screws. These collars act as mechanical stops, load bearing faces, or load transfer points. Their simple design makes them easy to install. This article will discuss the pros and cons of this style of collar. Let’s look at what you need to know before choosing a screw shaft clamp style collar. Here are some things to keep in mind.
Clamp-style shaft collars are a versatile mounting option for shafts. They have a recessed screw that fully engages the thread for secure locking. Screw shaft clamp collars come in different styles and can be used in both drive and power transmission applications. Listed below are the main differences between these 2 styles of collars. They are compatible with all types of shafts and are able to handle axial loads of up to 5500 pounds.
Clamp-style shaft collars are designed to prevent the screw from accidentally damaging the shaft when tightened. They can be tightened with a set screw to counteract the initial clamping force and prevent the shaft from coming loose. However, when tightening the screw, you should use a torque wrench. Using a set screw to tighten a screw shaft collar can cause it to warp and reduce the surface area that contacts the shaft.
Another key advantage to Clamp-style shaft collars is that they are easy to install. Clamp-style collars are available in one-piece and two-piece designs. These collars lock around the shaft and are easy to remove and install. They are ideal for virtually any shaft and can be installed without removing any components. This type of collar is also recommended for those who work on machines with sensitive components. However, be aware that the higher the OD, the more difficult it is to install and remove the collar.
Screw shaft clamp style collars are usually one-piece. A two-piece collar is easier to install than a one-piece one. The two-piece collars provide a more effective clamping force, as they use the full seating torque. Two-piece collars have the added benefit of being easy to install because they require no tools to install. You can disassemble one-piece collars before installing a two-piece collar.
Ball screw nut
The proper installation of a ball screw nut requires that the nut be installed on the center of the screw shaft. The return tubes of the ball nut must be oriented upward so that the ball nut will not overtravel. The adjusting nut must be tightened against a spacer or spring washer, then the nut is placed on the screw shaft. The nut should be rotated several times in both directions to ensure that it is centered.
Ball screw nuts are typically manufactured with a wide range of preloads. Large preloads are used to increase the rigidity of a ball screw assembly and prevent backlash, the lost motion caused by a clearance between the ball and nut. Using a large amount of preload can lead to excessive heat generation. The most common preload for ball screw nuts is 1 to 3%. This is usually more than enough to prevent backlash, but a higher preload will increase torque requirements.
The diameter of a ball screw is measured from its center, called the ball circle diameter. This diameter represents the distance a ball will travel during 1 rotation of the screw shaft. A smaller diameter means that there are fewer balls to carry the load. Larger leads mean longer travels per revolution and higher speeds. However, this type of screw cannot carry a greater load capacity. Increasing the length of the ball nut is not practical, due to manufacturing constraints.
The most important component of a ball screw is a ball bearing. This prevents excessive friction between the ball and the nut, which is common in lead-screw and nut combinations. Some ball screws feature preloaded balls, which avoid “wiggle” between the nut and the ball. This is particularly desirable in applications with rapidly changing loads. When this is not possible, the ball screw will experience significant backlash.
A ball screw nut can be either single or multiple circuits. Single or multiple-circuit ball nuts can be configured with 1 or 2 independent closed paths. Multi-circuit ball nuts have 2 or more circuits, making them more suitable for heavier loads. Depending on the application, a ball screw nut can be used for small clearance assemblies and compact sizes. In some cases, end caps and deflectors may be used to feed the balls back to their original position.


China Best Sales Axle Wheel Hub Unit Bearing Whole Complete 54kwh02 with Free Design Custom
Product Description
Axle WHEEL HUB UNIT Bearing whole complete 54KWH02
Quick Details
Usage: Auto
Car Make: CZPT CITROEN HYUNDAI Chevrolet
532066dB
Precision Rating: P0, P6, P5
Seals Type: Open, sealed
Place of Origin: China (Mainland)
Wheel bearings for truck bearing
Bearing type: Double-row tapered roller bearing
Application: Wheel bearing for Volvo, Man truckBearing size: 68/68.2*125*115mmBearing material: High quality chrome steel
Precision Rating: P0, P6, P5, P4, P2
Number of Row: Double Row
Port: Any Port
Usage: FIAT, Ford, LXIHU (WEST LAKE) DIS.A. Renault19-21, Chrysler
Car Make: Renault, peugeot. Citroen, Renault
We can promise 3 Years Working Life for this Auto Wheel Bearings. We use high temperature and high speed grease.
Vibration Level: V4, V3, V2, V1
Clearance: C2, C3, C4, C5T
Olerance: ABEC-1, ABEC-3, ABEC-5, ABEC-7
Quality level:
Material: : Carbon steel; Chrome steelGreese:
As your requirement, asSRL, PS2, Alvania R12
Application:
Auto, tractor, machine tool, electric machine and water pump, ect.
Specifications
Wheel hub Bearings
1. High quality and competitive price
2. Excellent in craftsmanship
3. Low noise and long life
The bearings supplied to the original equipment market are also available for aftermarket repair The bearings can be found in, and are available, for applications such as Wheel, Clutch, Belt Tensioners and Transmissions, as well as other common automotive repair applications. Bearings are available for most domestic and import applications.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Automotive Hub Units
Other Enhanced Tapered Roller Bearings
Long Life Tapered Roller/KE, SH, HR & HRS
High Performance Series/LFT Bearings
Ball Bearings
Automotive Hub Units
DAC Automotive Wheel bearings
Double Row Ball Bearings
Tension/Idler Pulley Bearings
Water Pump Bearings
Clutch Release Bearings
Ceramic Ball Bearings
Roller Bearings
Needle Roller Bearings
Cylindrical Roller
Packaging & Delivery:
Packaging Detail: Neutral Packing: White Plastic bag / Outer Carton / Pallet, yws Brand packing: Yws Plastic bag/yws outer carton / Pallet, Outer Carton Size: 39.5cm*26cm*21.5cm or 39.5cm*26cm*17cm, Pallet Size: 80cm*120cm*80cmor 120cm*80cm*1
45712-JG01B
43401-65D00
513266
515571
515081
28063-AA000
45712-ZX00A
43401-65D10
513268
515013
515086
45712-0009R
45713-JP01A
43401-65J02
513270
515571
515090
45712-0M571
45710-VW000
43402-54G10
513272
515571
515091
45712-1AA0A
42200-S5A-J01
43402-60G20
513273
515571
515093
45712-1LA0A
42450-42030
43402-64B01
513275
515571
515100
Driveshaft structure and vibrations associated with it
The structure of the drive shaft is critical to its efficiency and reliability. Drive shafts typically contain claw couplings, rag joints and universal joints. Other drive shafts have prismatic or splined joints. Learn about the different types of drive shafts and how they work. If you want to know the vibrations associated with them, read on. But first, let’s define what a driveshaft is.
transmission shaft
As the demand on our vehicles continues to increase, so does the demand on our drive systems. Higher CO2 emission standards and stricter emission standards increase the stress on the drive system while improving comfort and shortening the turning radius. These and other negative effects can place significant stress and wear on components, which can lead to driveshaft failure and increase vehicle safety risks. Therefore, the drive shaft must be inspected and replaced regularly.
Depending on your model, you may only need to replace 1 driveshaft. However, the cost to replace both driveshafts ranges from $650 to $1850. Additionally, you may incur labor costs ranging from $140 to $250. The labor price will depend on your car model and its drivetrain type. In general, however, the cost of replacing a driveshaft ranges from $470 to $1850.
Regionally, the automotive driveshaft market can be divided into 4 major markets: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and Rest of the World. North America is expected to dominate the market, while Europe and Asia Pacific are expected to grow the fastest. Furthermore, the market is expected to grow at the highest rate in the future, driven by economic growth in the Asia Pacific region. Furthermore, most of the vehicles sold globally are produced in these regions.
The most important feature of the driveshaft is to transfer the power of the engine to useful work. Drive shafts are also known as propeller shafts and cardan shafts. In a vehicle, a propshaft transfers torque from the engine, transmission, and differential to the front or rear wheels, or both. Due to the complexity of driveshaft assemblies, they are critical to vehicle safety. In addition to transmitting torque from the engine, they must also compensate for deflection, angular changes and length changes.
type
Different types of drive shafts include helical shafts, gear shafts, worm shafts, planetary shafts and synchronous shafts. Radial protruding pins on the head provide a rotationally secure connection. At least 1 bearing has a groove extending along its circumferential length that allows the pin to pass through the bearing. There can also be 2 flanges on each end of the shaft. Depending on the application, the shaft can be installed in the most convenient location to function.
Propeller shafts are usually made of high-quality steel with high specific strength and modulus. However, they can also be made from advanced composite materials such as carbon fiber, Kevlar and fiberglass. Another type of propeller shaft is made of thermoplastic polyamide, which is stiff and has a high strength-to-weight ratio. Both drive shafts and screw shafts are used to drive cars, ships and motorcycles.
Sliding and tubular yokes are common components of drive shafts. By design, their angles must be equal or intersect to provide the correct angle of operation. Unless the working angles are equal, the shaft vibrates twice per revolution, causing torsional vibrations. The best way to avoid this is to make sure the 2 yokes are properly aligned. Crucially, these components have the same working angle to ensure smooth power flow.
The type of drive shaft varies according to the type of motor. Some are geared, while others are non-geared. In some cases, the drive shaft is fixed and the motor can rotate and steer. Alternatively, a flexible shaft can be used to control the speed and direction of the drive. In some applications where linear power transmission is not possible, flexible shafts are a useful option. For example, flexible shafts can be used in portable devices.
put up
The construction of the drive shaft has many advantages over bare metal. A shaft that is flexible in multiple directions is easier to maintain than a shaft that is rigid in other directions. The shaft body and coupling flange can be made of different materials, and the flange can be made of a different material than the main shaft body. For example, the coupling flange can be made of steel. The main shaft body is preferably flared on at least 1 end, and the at least 1 coupling flange includes a first generally frustoconical projection extending into the flared end of the main shaft body.
The normal stiffness of fiber-based shafts is achieved by the orientation of parallel fibers along the length of the shaft. However, the bending stiffness of this shaft is reduced due to the change in fiber orientation. Since the fibers continue to travel in the same direction from the first end to the second end, the reinforcement that increases the torsional stiffness of the shaft is not affected. In contrast, a fiber-based shaft is also flexible because it uses ribs that are approximately 90 degrees from the centerline of the shaft.
In addition to the helical ribs, the drive shaft 100 may also contain reinforcing elements. These reinforcing elements maintain the structural integrity of the shaft. These reinforcing elements are called helical ribs. They have ribs on both the outer and inner surfaces. This is to prevent shaft breakage. These elements can also be shaped to be flexible enough to accommodate some of the forces generated by the drive. Shafts can be designed using these methods and made into worm-like drive shafts.
vibration
The most common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper installation. There are 5 common types of driveshaft vibration, each related to installation parameters. To prevent this from happening, you should understand what causes these vibrations and how to fix them. The most common types of vibration are listed below. This article describes some common drive shaft vibration solutions. It may also be beneficial to consider the advice of a professional vibration technician for drive shaft vibration control.
If you’re not sure if the problem is the driveshaft or the engine, try turning on the stereo. Thicker carpet kits can also mask vibrations. Nonetheless, you should contact an expert as soon as possible. If vibration persists after vibration-related repairs, the driveshaft needs to be replaced. If the driveshaft is still under warranty, you can repair it yourself.
CV joints are the most common cause of third-order driveshaft vibration. If they are binding or fail, they need to be replaced. Alternatively, your CV joints may just be misaligned. If it is loose, you can check the CV connector. Another common cause of drive shaft vibration is improper assembly. Improper alignment of the yokes on both ends of the shaft can cause them to vibrate.
Incorrect trim height can also cause driveshaft vibration. Correct trim height is necessary to prevent drive shaft wobble. Whether your vehicle is new or old, you can perform some basic fixes to minimize problems. One of these solutions involves balancing the drive shaft. First, use the hose clamps to attach the weights to it. Next, attach an ounce of weight to it and spin it. By doing this, you minimize the frequency of vibration.
cost
The global driveshaft market is expected to exceed (xxx) million USD by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of XX%. Its soaring growth can be attributed to several factors, including increasing urbanization and R&D investments by leading market players. The report also includes an in-depth analysis of key market trends and their impact on the industry. Additionally, the report provides a comprehensive regional analysis of the Driveshaft Market.
The cost of replacing the drive shaft depends on the type of repair required and the cause of the failure. Typical repair costs range from $300 to $750. Rear-wheel drive cars usually cost more. But front-wheel drive vehicles cost less than four-wheel drive vehicles. You may also choose to try repairing the driveshaft yourself. However, it is important to do your research and make sure you have the necessary tools and equipment to perform the job properly.
The report also covers the competitive landscape of the Drive Shafts market. It includes graphical representations, detailed statistics, management policies, and governance components. Additionally, it includes a detailed cost analysis. Additionally, the report presents views on the COVID-19 market and future trends. The report also provides valuable information to help you decide how to compete in your industry. When you buy a report like this, you are adding credibility to your work.
A quality driveshaft can improve your game by ensuring distance from the tee and improving responsiveness. The new material in the shaft construction is lighter, stronger and more responsive than ever before, so it is becoming a key part of the driver. And there are a variety of options to suit any budget. The main factor to consider when buying a shaft is its quality. However, it’s important to note that quality doesn’t come cheap and you should always choose an axle based on what your budget can handle.

