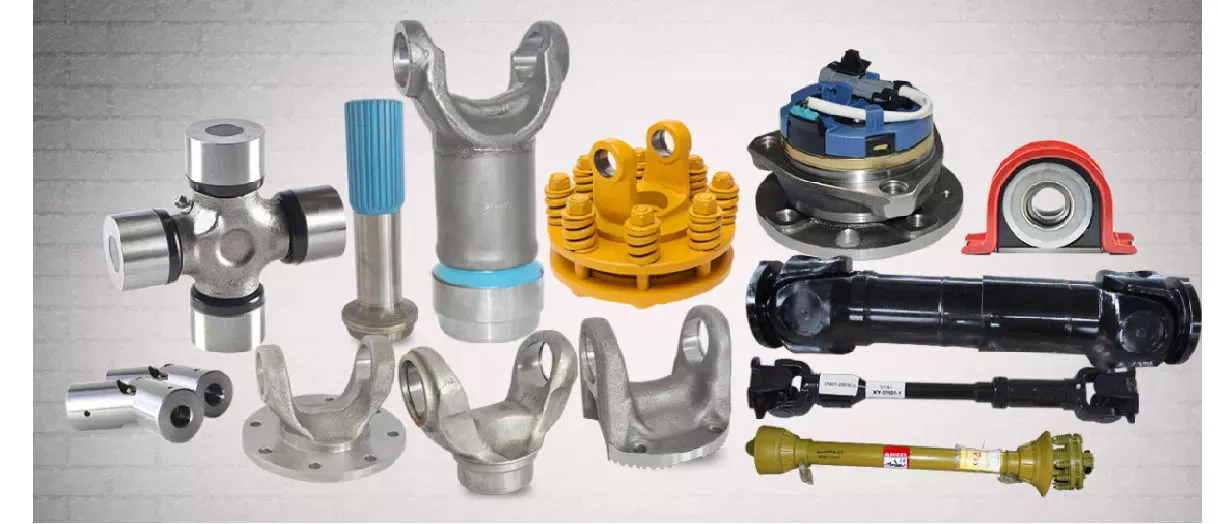
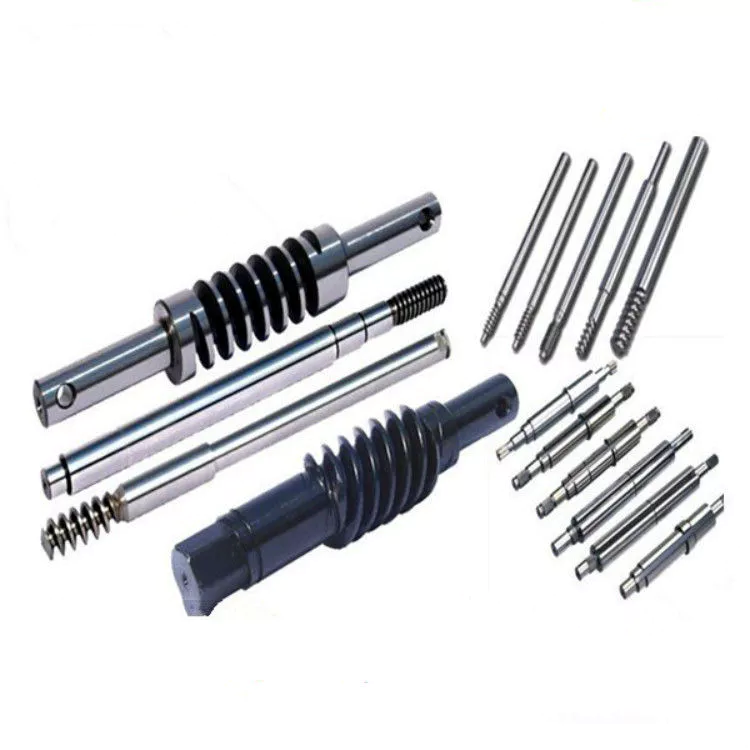
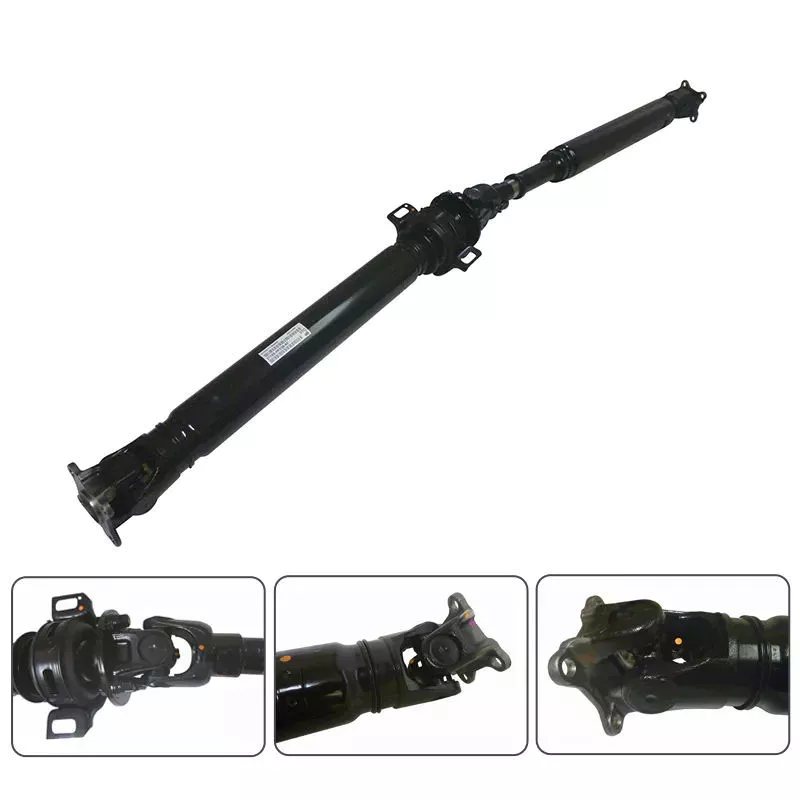
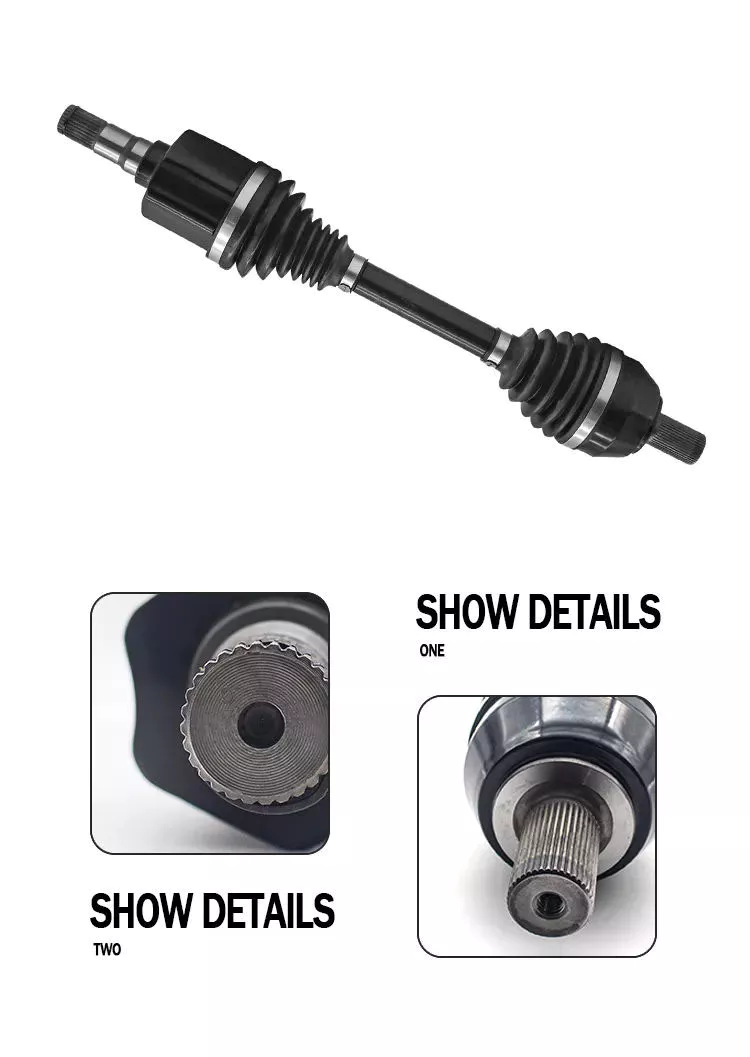
Product Description
Welcome to choose KORTON INDUSTRIAL LIMITED.; Please read the following information carefully.;
NO 1.; our adwantages
1.; 14 years bearing products manufacturing and exporting experiences.;
2.; OEM order and non-standard bearing order can be accepted.;
3.; Many sizes of bearing are available.; Large quantity bearing can be provided.;
4.; To respect customers,; you can choose the loading port.;
5.; A certain number of free sample can be provide to support our customer’s after-sale services and warranty.;
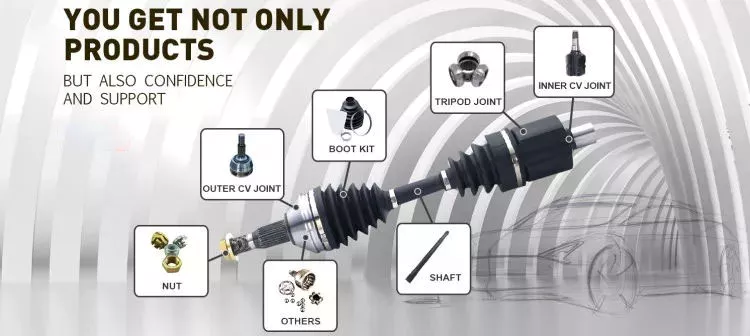
NO 2.; Description:; Auto wheel bearing
The main functions of wheel hub bearings are load and provide accurate guidance to the turn of hub bearings.; Hub bearings not only carry axial load but also carry radial load,; they are important components.; They can carry heavy radial load which include axial and radial load and torques load,; they can limit axial displacement both sides.; They are mainly used in components which limitation of bearings and shell axial displacement of both sides.; Hub bearings’ design are familiar to the 2 back to back order single row conntact ball bearings,; but the width are shorter than single row bearings.; Compare to the single row bearings hub bearings have better rigidity.;
NO 3.; OEM all brand bearing
NO 4.; Auto Wheel Bearing Specification:;
| Seals Types | ZZ,;2RS,;OPEN | ||||||||
| Vibration Level | Z1V1,;Z2V2,;Z3V3 | ||||||||
| Clearance | C2,;C0,;C3,;C4,;C5 | ||||||||
| Tolerance Codes | ABEC-1,;ABEC-3,;ABEC-5 | ||||||||
| Materral | GCr15-China/AISI521W | ||||||||
| DAC30600037 | 30 | 60 | 37 | 37 | 0.;42 | 529891AB | BA2B633313C | DAC3060W | |
| DAC30620038 | 30 | 62 | 38 | 38 | 0.;52 | 545312 | 418780 | 30BWD10 | |
| DAC30630042 | 30 | 63 | 42 | 42 | 0.;57 | 581736 | 45716A | 30BWD01A | |
| DAC30640042 | 30 | 64 | 42 | 42 | 0.;5 | 34BWD03ACA78 | DAC3064W2R | ||
| DAC32720045 | 32 | 72 | 45 | 45 | 0.;81 | 531910 | 32BWD05CA75 | ||
| DAC34620037 | 34 | 62 | 37 | 37 | 0.;41 | 561447 | BAHB311316B | 34BWD08/CA70 | |
| DAC34640037 | 34 | 64 | 37 | 37 | 0.;43 | 540466B | 3 0571 6DA | 34BWD11 | DAC3464G1 |
| DAC34660037 | 34 | 66 | 37 | 37 | 0.;5 | 580400CA | 636114A | 34BWD10B | |
| DAC34670037 | 34 | 67 | 37 | 37 | 0.;52 | 532066DB | |||
| DAC34680037 | 34 | 68 | 37 | 37 | 0.;55 | 567918B | DAC3468DW | ||
| DAC35620040 | 35 | 62 | 40 | 40 | 0.;43 | 430042C | |||
| DAC35640037 | 35 | 64 | 37 | 37 | 0.;41 | BT2B445620B | |||
| DAC35650035 | 35 | 65 | 35 | 35 | 0.;4 | 546238A | 443952 | DAC3565WCS30 | |
| DAC35660033 | 35 | 66 | 33 | 33 | 0.;43 | BAHB633676 | |||
| DAC35660037 | 35 | 66 | 37 | 37 | 0.;48 | 544307 | BAHB311309 | DAC35660037 | |
| DAC35680033/30 | 35 | 68 | 33 | 30 | 0.;47 | 546238 | BA2B445535AE | 35BWD07A | DAC3568W-6 |
| DAC35680037 | 35 | 68 | 37 | 37 | 0.;52 | 541153 | 633295 | DAC3568A2RS | |
| DAC35720033 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;58 | 548083 | BA2B446762B | ||
| DAC35725713/31 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 31 | 0.;56 | 562686 | FWB14 | 35BWD06ACA111 | DAC357233B-1W |
| DAC3572571 | 35 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;58 | 548083 | BAHB633669 | 35BWD08A | DAC357545CW2R |
| DAC35720034 | 35 | 72 | 34 | 34 | 0.;58 | 54 0571 | BAHB633967 | 35BWD01 | DAC357234A |
| DAC3572571 | 35 | 72 | 34 | 34 | 0.;58 | BAHB633528F | |||
| DAC36640042 | 36 | 64 | 42 | 42 | 0.;46 | CRI-0787 | |||
| DAC36680033 | 36 | 68 | 33 | 33 | 0.;47 | DAC3668AWCS36 | |||
| DAC37720033 | 37 | 72 | 33 | 33 | 0.;5 | BAH-0051B |
NO 6.; Some Auto wheel bearing OEM number and Application:;
| OEM NUMBERS | DESCRIPTION | APPLICATION |
| B001-33-043 | WHEEL BEARINGS | SPORTAGE |
| 04495-0K120 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HILUX’07 |
| 42409-19015 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | COROLLA |
| 42409-33571 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | CAMRY 1 |
| 90369-38011 | WHEEL BEARING FRONT | COROLLA 3872 |
| 43504-12090 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | COROLLA |
| 42409-2571 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | AVENSIS,; CARINA |
| 43502-20131 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | CARINA |
| 44300-S3V-AO1 | WHEEL BEARINGS FRONT | TRUCK / LAND CRUISE |
| 42409-42571 | WHEEL BEARINGS REAR | RAV 4 |
| 518506 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | CAMRY |
| 175407615 | WHEEL HUB FRONT | GOLF 1 |
| 331598625 | WHEEL BEARING REAR | GOLF II |
| 3871 | WHEEL BEARING FRONT | TOY STARLET |
| 4382 | WHEEL BEARING | CAMRY |
| 90368-50008 | WHEEL BEARING | DYNA |
| 90369-32003 | WHEEL BEARING | RX80 FRONT |
| 45710-C6000 | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN PATROL FRONT |
| 45710-50Y00-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN SUNNY |
| 45710-71L00-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN |
| 42200-SH3-970-D | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA CIVIC |
| 42300-SD4-004 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA BALLADE |
| 43210-C9300-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISSAN PATROL |
| 43210-D5710-D | WHEEL BEARING | NISS-B/BIRD REAR |
| 44200-SM4-0131 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA-CIVIC |
| 44300-SB2-965 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA |
| 44300-S04-0040 | WHEEL BEARING | HONDA-CIVIC |
| MB584761 | WHEEL BEARING | MITS-LANCER |
| MB664447 | WHEEL BEARING | MITS-PAJERO |
| 46T080604 | WHEEL BEARING | COROLLA-REAR |
| DG4 0571 6WRS/DG4094W | WHEEL BEARING REAR | HIACE 4X4 |
| 3874 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CORONA |
| 157148/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 104948/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 48548/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HIACE 2Y |
| 12649/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | HIACE 2Y |
| 30303D | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 4T-CR1-0881 | WHEEL BEARINGS | BLUEBIRD |
| 11162/ | WHEEL BEARINGS | LAND ROVER |
| 69345/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA 323 |
| 11749/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 35715 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA B1800 |
| 35714 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 67048/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CRESSIDA |
| 44649/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 45449/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | COROLLA DX |
| 30849/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA |
| 6308 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOY HIACE |
| U399 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOY HILUX |
| 11949/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1400 |
| 30304 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 4080 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI |
| 603049/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA |
| 6306CNXL330 | GEAR BOX BEARINGS | NISSAN TD27 |
| TR080702J | GEAR BOX BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA |
| 3314598 | WHEEL BEARINGS | FORD RANGER |
| DAC38640036 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA REAR |
| TR070904-J-N | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| R30-13 | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| TR100802-I-N | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 42BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN BLUEBIRD |
| 46T 0571 05 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA LUCIDA |
| HM801310-22-N | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| LM603049/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | FORD/L/ROVER |
| 17831/17887 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| 2788 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 26882 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 28985/28920 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| HM801349-N | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| 50KW8019 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| 45289 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA |
| 43BWD03 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA MARK11 |
| 35BWD16 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN MARCH |
| LM300811 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1TONNER |
| LM60571 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN 1TONNER |
| 35712 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER FRONT |
| 35718j/57307 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200 REAR |
| ST2749 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA STARLET FRONT |
| 55KW02 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| 55KW01 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| 25KC802 | DIFF BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 35BW08 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOWNACE REAR |
| 32207 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER FRONT |
| DAC4380A | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA 626 |
| 46T 0571 04A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA CONDOR FRONT |
| TR0708030 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| 32012X | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200/CANTER REAR |
| 4276 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI L200/CANTER REAR |
| 28580 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 3579R/25 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA FRONT |
| HR32210J | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI CANTER |
| HR32206J | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN SUNNY |
| HR35717J | DIFF BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| DU5496-5 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA HILUX |
| 40KW019 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO FRONT |
| TR0607R | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HIACE |
| TR57326 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 2474 | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 33013A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| HR32307CN | DIFF BEARINGS | TOYOTA HILUX |
| 32310 | WHEEL BEARINGS | ISUZU LIGHT TRUCK |
| 40BWD12 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA VISTA |
| 33205JR | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA VISTA |
| LM300849 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN-DATSUN |
| 50KWH01 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI SPORTERO |
| 40KW01 | DIFF BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI FUSO |
| 30305 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 32571XJ | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 35718 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN |
| 32304 | WHEEL BEARINGS | ISUZU |
| DAC43792RS | WHEEL BEARINGS | HONDA CRV |
| 40KWD02 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI SPORTERO |
| 38BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA MARK11 FRONT |
| 43KWD04 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN PRIMERA |
| 427638 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA REGUS FRONT |
| LM68149/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CROWN FRONT |
| LM12749/10 | WHEEL BEARINGS | CROWN FRONT |
| 32005JR | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA FRONT |
| 35BCD08 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA NOAH REAR |
| LM506810 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| ET33011 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN CABSTER |
| RNU0727 | WHEEL BEARINGS | L/CRUISER |
| 46T08805 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MITSUBISHI PAJERO |
| 1220 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA DYNA |
| 28584 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER |
| 469-N | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COASTER REAR |
| 28BWD01A | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA COROLLA REAR |
| 57305 | WHEEL BEARINGS | TOYOTA TOWNACE |
| 40BWD06 | WHEEL BEARINGS | MAZDA FRONT |
| AU 0571 -2 | WHEEL BEARINGS | NISSAN X-TRAIL |
| ME6 0571 4 | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D30 |
| 30502-28E20 | THRUST BEARING | TD27 |
| 30502-53J00 | THRUST BEARING | GA16 |
| 31230-12140 | THRUST BEARING | EE90 |
| 31230-35070 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-3L |
| 31250-35050 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-2L |
| 31230-35090 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-5L |
| 31230-36160 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-1HZ |
| 31230-60130 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-1FZ |
| MD703270 | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D55 |
| ME657110-D | THRUST BEARING | MITS-CANTER |
| 5712-16-222-D | THRUST BEARING | MAZ-HA |
| 31230-60120 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-2H |
| 31230-60150 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-FJ80 |
| 31230-32571 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-3S |
| 1304-16-510B | THRUST BEARING | MAZ-TITAN |
| MD719469-D | THRUST BEARING | MITS-4D56 |
| 31230-36150 | THRUST BEARING | COASTER |
| 31230-32060 | THRUST BEARING | TOY-4AF |
| 58SCRN37P | THRUST BEARINGS | TOYOTA 1KZ |
Why Choose Us:;
We are an industrial company.;We have our own brand:; SFNB .;If you interested in our product,;I can take you to visit our factory.;
Our factory have advanced testing equipment,;before the every product leave the factory,;we will be testing.;We can send samples to you,;you can test the quality,;and if you accept the sample quality,;we can promise:; the follow-up orders’ quality will be the same as samples.;
About ordinary standard type of bearing ,;We have rich inventory,;not have MOQ,;if your need a product is Non-standard size,;need customize,;we will according the product size to determine the MOQ.;
Our company can accept OEM,;you can send sample to me,;we can manufacturing products the same as sample.;Meanwhile,;we also can accept some well-known brands of OEM,;
If the amount of money is less,;you can pay it by Paypal or Alipay.;Of course you can payment by TT or Western Union etc.;
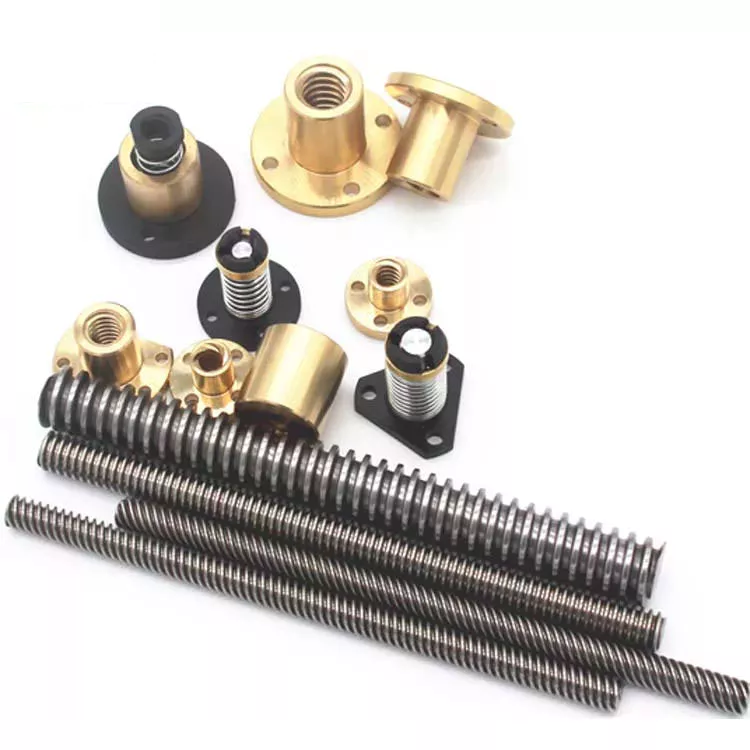
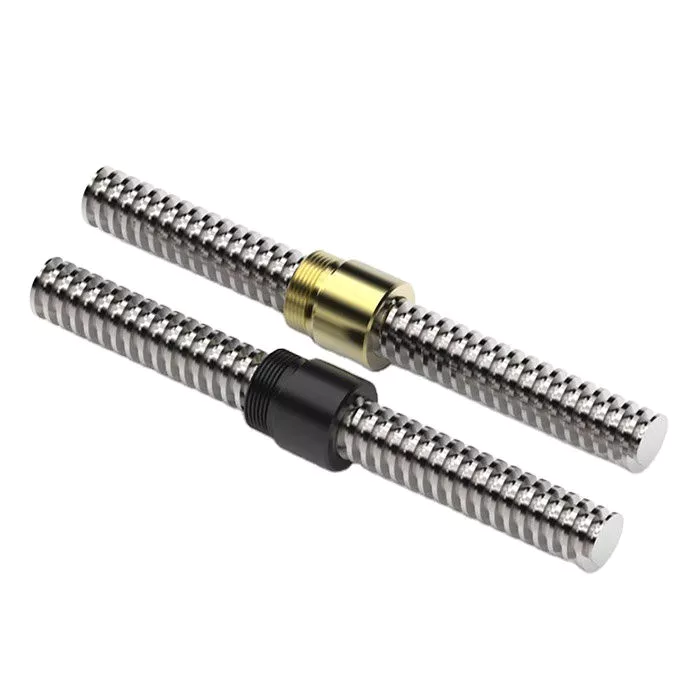
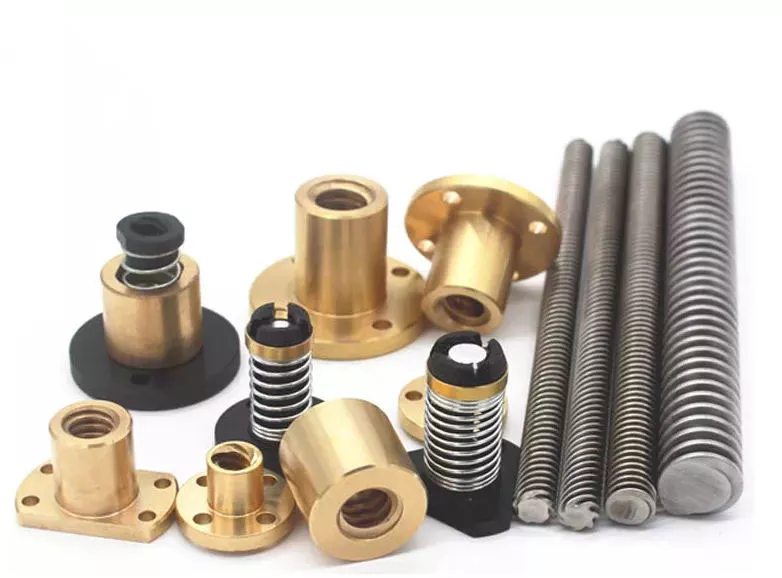
Lead Screws and Clamp Style Collars
If you have a lead screw, you’re probably interested in learning about the Acme thread on this type of shaft. You might also be interested in finding out about the Clamp style collars and Ball screw nut. But before you buy a new screw, make sure you understand what the terminology means. Here are some examples of screw shafts:
Acme thread
The standard ACME thread on a screw shaft is made of a metal that is resistant to corrosion and wear. It is used in a variety of applications. An Acme thread is available in a variety of sizes and styles. General purpose Acme threads are not designed to handle external radial loads and are supported by a shaft bearing and linear guide. Their design is intended to minimize the risk of flank wedging, which can cause friction forces and wear. The Centralizing Acme thread standard caters to applications without radial support and allows the thread to come into contact before its flanks are exposed to radial loads.
The ACME thread was first developed in 1894 for machine tools. While the acme lead screw is still the most popular screw in the US, European machines use the Trapezoidal Thread (Metric Acme). The acme thread is a stronger and more resilient alternative to square threads. It is also easier to cut than square threads and can be cut by using a single-point threading die.
Similarly to the internal threads, the metric versions of Acme are similar to their American counterparts. The only difference is that the metric threads are generally wider and are used more frequently in industrial settings. However, the metric-based screw threads are more common than their American counterparts worldwide. In addition, the Acme thread on screw shafts is used most often on external gears. But there is still a small minority of screw shafts that are made with a metric thread.
ACME screws provide a variety of advantages to users, including self-lubrication and reduced wear and tear. They are also ideal for vertical applications, where a reduced frictional force is required. In addition, ACME screws are highly resistant to back-drive and minimize the risk of backlash. Furthermore, they can be easily checked with readily available thread gauges. So, if you’re looking for a quality ACME screw for your next industrial project, look no further than ACME.
Lead screw coatings
The properties of lead screw materials affect their efficiency. These materials have high anti-corrosion, thermal resistance, and self-lubrication properties, which eliminates the need for lubrication. These coating materials include polytetrafluoroethylene (PFE), polyether ether ketone (PEK), and Vespel. Other desirable properties include high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and rigidity.
The most common materials for lead screws are carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Lead screw coatings can be PTFE-based to withstand harsh environments and remove oil and grease. In addition to preventing corrosion, lead screw coatings improve the life of polymer parts. Lead screw assembly manufacturers offer a variety of customization options for their lead screw, including custom-molded nuts, thread forms, and nut bodies.
Lead screws are typically measured in rpm, or revolutions per minute. The PV curve represents the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. This value is affected by the material used in the construction of the screw, lubrication conditions, and end fixity. The critical speed of lead screws is determined by their length and minor diameter. End fixity refers to the support for the screw and affects its rigidity and critical speed.
The primary purpose of lead screws is to enable smooth movement. To achieve this, lead screws are usually preloaded with axial load, enabling consistent contact between a screw’s filets and nuts. Lead screws are often used in linear motion control systems and feature a large area of sliding contact between male and female threads. Lead screws can be manually operated or mortised and are available in a variety of sizes and materials. The materials used for lead screws include stainless steel and bronze, which are often protected by a PTFE type coating.
These screws are made of various materials, including stainless steel, bronze, and various plastics. They are also made to meet specific requirements for environmental conditions. In addition to lead screws, they can be made of stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. Surface coatings can improve the screw’s corrosion resistance, while making it more wear resistant in tough environments. A screw that is coated with PTFE will maintain its anti-corrosion properties even in tough environments.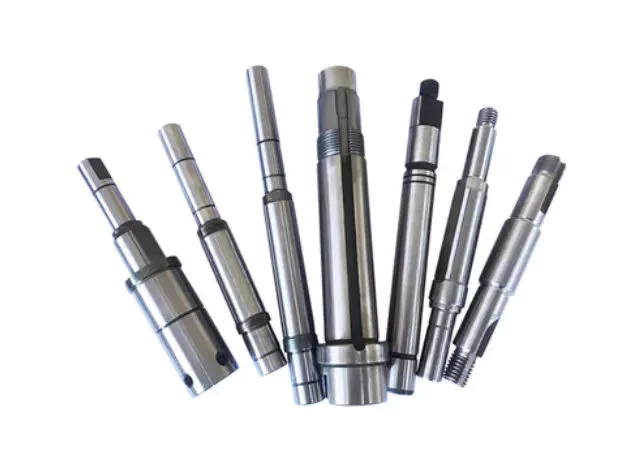
Clamp style collars
The screw shaft clamp style collar is a basic machine component, which is attached to the shaft via multiple screws. These collars act as mechanical stops, load bearing faces, or load transfer points. Their simple design makes them easy to install. This article will discuss the pros and cons of this style of collar. Let’s look at what you need to know before choosing a screw shaft clamp style collar. Here are some things to keep in mind.
Clamp-style shaft collars are a versatile mounting option for shafts. They have a recessed screw that fully engages the thread for secure locking. Screw shaft clamp collars come in different styles and can be used in both drive and power transmission applications. Listed below are the main differences between these 2 styles of collars. They are compatible with all types of shafts and are able to handle axial loads of up to 5500 pounds.
Clamp-style shaft collars are designed to prevent the screw from accidentally damaging the shaft when tightened. They can be tightened with a set screw to counteract the initial clamping force and prevent the shaft from coming loose. However, when tightening the screw, you should use a torque wrench. Using a set screw to tighten a screw shaft collar can cause it to warp and reduce the surface area that contacts the shaft.
Another key advantage to Clamp-style shaft collars is that they are easy to install. Clamp-style collars are available in one-piece and two-piece designs. These collars lock around the shaft and are easy to remove and install. They are ideal for virtually any shaft and can be installed without removing any components. This type of collar is also recommended for those who work on machines with sensitive components. However, be aware that the higher the OD, the more difficult it is to install and remove the collar.
Screw shaft clamp style collars are usually one-piece. A two-piece collar is easier to install than a one-piece one. The two-piece collars provide a more effective clamping force, as they use the full seating torque. Two-piece collars have the added benefit of being easy to install because they require no tools to install. You can disassemble one-piece collars before installing a two-piece collar.
Ball screw nut
The proper installation of a ball screw nut requires that the nut be installed on the center of the screw shaft. The return tubes of the ball nut must be oriented upward so that the ball nut will not overtravel. The adjusting nut must be tightened against a spacer or spring washer, then the nut is placed on the screw shaft. The nut should be rotated several times in both directions to ensure that it is centered.
Ball screw nuts are typically manufactured with a wide range of preloads. Large preloads are used to increase the rigidity of a ball screw assembly and prevent backlash, the lost motion caused by a clearance between the ball and nut. Using a large amount of preload can lead to excessive heat generation. The most common preload for ball screw nuts is 1 to 3%. This is usually more than enough to prevent backlash, but a higher preload will increase torque requirements.
The diameter of a ball screw is measured from its center, called the ball circle diameter. This diameter represents the distance a ball will travel during 1 rotation of the screw shaft. A smaller diameter means that there are fewer balls to carry the load. Larger leads mean longer travels per revolution and higher speeds. However, this type of screw cannot carry a greater load capacity. Increasing the length of the ball nut is not practical, due to manufacturing constraints.
The most important component of a ball screw is a ball bearing. This prevents excessive friction between the ball and the nut, which is common in lead-screw and nut combinations. Some ball screws feature preloaded balls, which avoid “wiggle” between the nut and the ball. This is particularly desirable in applications with rapidly changing loads. When this is not possible, the ball screw will experience significant backlash.
A ball screw nut can be either single or multiple circuits. Single or multiple-circuit ball nuts can be configured with 1 or 2 independent closed paths. Multi-circuit ball nuts have 2 or more circuits, making them more suitable for heavier loads. Depending on the application, a ball screw nut can be used for small clearance assemblies and compact sizes. In some cases, end caps and deflectors may be used to feed the balls back to their original position.