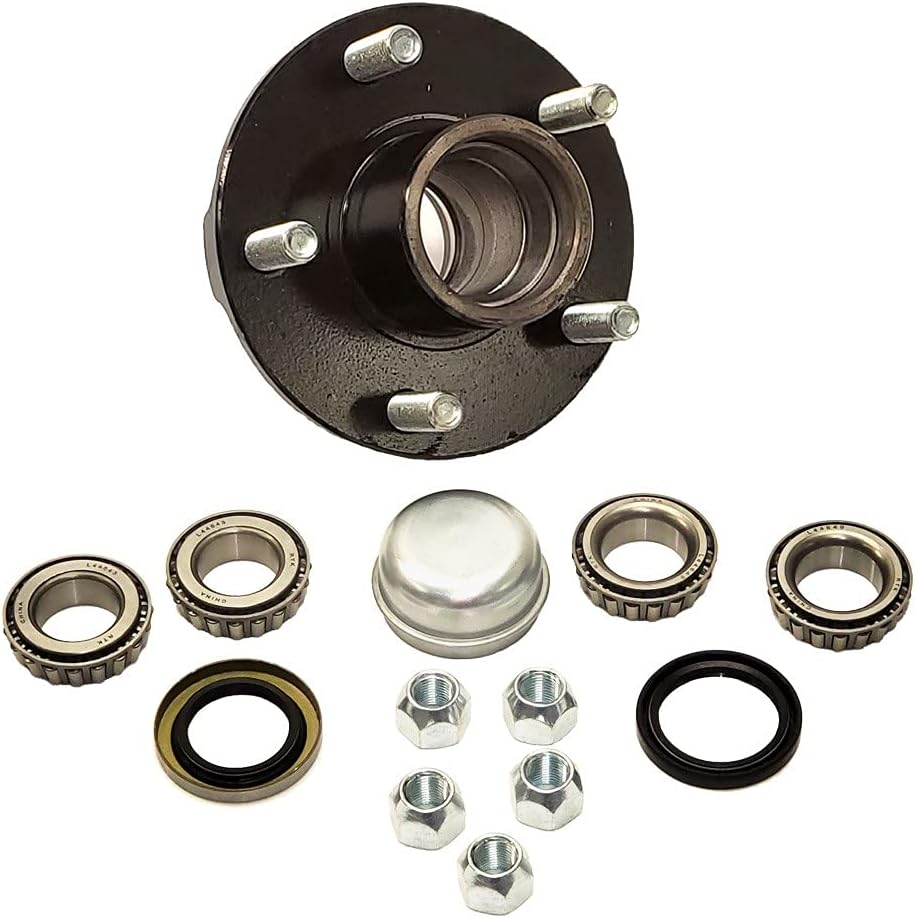
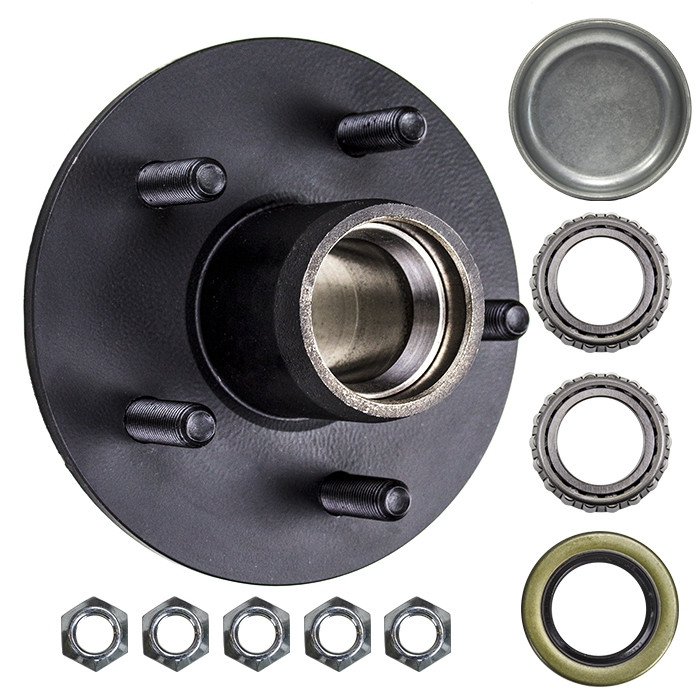
Product Description
| Name: | Wheel HUBS with BEARINGS for CHRYSLER OE 5 0571 06AA 5 0571 06AB 5 0571 06AC 51 0571 3AA 51 0571 3AB 51 0571 3AC 5154211AA KAC K5714211AA bearing hub |
| Type: | wheel bearing |
| Position: | Front/rear axle |
| Weight: | 2.5KG |
| Specifications: | OEM standard size |
| Material: | Chrome steel/GCR-15 |
| Technology: | Hot forging |
| CAGE: | TN Nylon |
| SEAL: | ZZ, 2RS |
| Rolling body: | Steel ball |
| ABS: | Without |
| Quality: | Top grade |
| Brands: | DHXB, OEM |
| Origin: | China |
DODGE : AA DODGE : AB DODGE : AC DODGE : 5715233AB
DODGE : 5715233AC DODGE : 5714211AA DODGE : 5 0571 06AA DODGE : 5 0571 06AB
DODGE : 5 0571 06AC DODGE : 51 0571 3AB DODGE : 51 0571 3AC DODGE : 5154211AA
Introduction to WHEEL HUB BEARING ASSEMBLY
Our wheel hub bearings assembly are characterised by:
- optimisation of internal geometry and sealing
- the use of steel with a very high level of cleanliness
- the use of greases specifically developed with our suppliers
Our third generation of wheel bearings integrate hub and flange functions for a streamlined and effective assembly and precise adjustment of the pre-load.
We can provide you with robust solutions, whatever your areas of application: passenger vehicles, utilities or heavy goods vehicles.
Related Catalogues You May Concern
| NTN number | KOYO number | NSK number | OE number |
| HUB002-6 | DACF01 | 27BWK02 | 51750-25000 |
| HUB005 | DACF09 | 27BWK03 | 52710-57100 |
| HUB008 | DACF1005C | 27BWK04 | 52710-02XXX |
| HUB030 | DACF1015D | 27BWK06 | 52710-22400 |
| HUB031 | DACF1018L | 28BWK06 | 52710-22600 |
| HUB033 | DACF1571 | 28BWK08 | 52710-25000 |
| HUB036 | DACF1033K | 28BWK09 | 52710-25001 |
| HUB042-32 | DACF1033K-1 | 28BWK12 | 52710-25100 |
| HUB053 | DACF1033K-2 | 28BWK15 | 52710-25101 |
| HUB059 | DACF1034C-3 | 28BWK16 | 52710-29400 |
| HUB065-15 | DACF1034AR-2 | 28BWK19 | 52710-29450 |
| HUB066-52 | DACF1041H | 30BWK06 | 52710-29460 |
| HUB066-53 | DACF1041JR | 30BWK10 | 52710-29500 |
| HUB081-45 | DACF1050B | 30BWK11 | 52710-29XXX |
| HUB082-6 | DACF1065A | 30BWK15 | 52710-29ZZZ |
| HUB083-64 | DACF1072B | 30BWK16 | 52710-34XXX |
| HUB083-65 | DACF1076D | 33BWK02 | 52710-34500 |
| HUB099 | DACF1082 | 36BWK02 | 52710-34501 |
| HUB132-2 | DACF1085 | 38BWK01 | 52710-2D000 |
| HUB144 | DACF1085-2 | 41BWK03 | 52710-2D100 |
| HUB145-7 | DACF1085-4-123 | 43BWK01 | 52710-3A101 |
| HUB147-20/L | DACF1085-5-140 | 43BWK03 | 52710-34700 |
| HUB147-22/R | DACF1086-2 | 51KWH01 | 52730-38002 |
| HUB150-5 | DACF1091 | 54KWH01 | 52730-38102 |
| HUB156-37 | DACF1092 | 54KWH02 | 52730-38103 |
| HUB156-39 | DACF1097 | 55BWKH01RHS | 52750-1G100 |
| HUB181-22 | DACF1091/G3 | 55BWKH01LHS | 45712-EL000 |
| HUB181-32 | DACF1092/G3 | 2DUF58BWK038 | 43202-EL00A |
| HUB184 | DACF1102A | 2DUF50KWH01EJB | 42410-06091 |
| HUB184A | DACF1172 | 2DUF053N | 42450-52060 |
| HUB188-6 | DACF1177 | DU5496-5 | 89544-12571 |
| HUB189-2/R | 3DACF026F-7 | DU4788-2LFT | 89544-57171 |
| HUB189-4/L | 3DACF026F-7S | 38BWD10 | 89544-32040 |
| HUB199 | 3DACF026F-1A | 40BWD12 | 42200-SAA-G51 |
| HUB226 | 3DACF026F-1AS | 40BWD16 | 43200-9F510 |
| HUB227 | DACF35711AC | 40BWD17 | 43200-9F510ABS |
| HUB230A | DACF35711A | 43200-WE205 | |
| HUB231 | DACF7001 | 89544-48571 | |
| HUB254 | DACF7002 | 52008208 | |
| HUB280-2 | 3DACF026-8S | 52009867AA | |
| HUB283-6 | 3DACF030N-1 | OK202-26-150 | |
| HUB294 | DACF2044M | OK9A5-26-150 | |
| HUB80-27 | DACF2126 PR | BN8B-26-15XD | |
| DACF805201 BA | 13207-01M00 | ||
| DAC4278A2RSC53 | MR223284 | ||
| 3C0498621 | |||
| 46T080705CCZ | |||
| 6X0501477 | |||
| 1T0498621 | |||
| 1T571611B | |||
| 6D20A |
ZheJiang Huaxu Bearing Co.,Ltd
Our factory specialize wheel hub bearing, wheel bearing kit, clutch bearing, taper roller bearing, truck bearing, wheel hub bearing in high quality.
Our bearings have large loading capacity and long lifetime, and widely fit in different vehicles.
wheel bearings and kits to vehicles like LADA, TOYOTA, HONDA, RENAULT, AUDI,Chevrolet, HYUNDAI,FIAT, FORD and so on.
Truck bearings applied to VOLVO, MAN, BENZ, DAF, SAF and so on.
And we can produce bearings which can meet your multifarious demands.
For example, wheel bearing, taper roller bearing, clutch release bearing, ball bearing, truck bearing ect.
We can provide brands likeTIMKEN, NSK, KOYO, NTN,, NACHI, GMB, BW, GM, HYUNDAI ect.
Q:What’s your after-sales service and warranty?
A: We promise to bear the following responsibilities when defective products were found:
1.12 months warranty from the first day of receiving goods;
2. Replacements would be sent with goods of your next order;
3. Refund for defective products if customers require.
Q:Do you accept ODM&OEM orders?
A: Yes, we provide ODM&OEM services to worldwide customers, we also customize OEM box and packing as your requirements.
Q:What’s the MOQ?
A: MOQ is 10pcs for standardized products; for customized products, MOQ should be negotiated in advance. There is no MOQ for sample orders.
Q:How long is the lead time?
A: The lead time for sample orders is 3-5 days, for bulk orders is 5-15 days.
Q:Do you offer free samples?
A: Yes we offer free samples to distributors and wholesalers, however customers should bear freight. We DO NOT offer free samples to end users.
Q:How to place order?
A: 1. Email us the model, brand and quantity,shipping way of bearings and we will quote our best price for you;
2. Proforma Invoice made and sent to you as the price agreed by both parts;
3. Deposit Payment after confirming the PI and we arrange production;
4. Balance paid before shipment or after copy of Bill of Loading.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | After Market Service |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 50000km |
| Type: | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Material: | Chrome Steel |
| Tolerance: | P0.P6.P5 |
| Certification: | TS16949, IATF16949 |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Set
1 Set(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

Can you recommend reliable brands for purchasing replacement axle hubs?
When it comes to purchasing replacement axle hubs, there are several reliable brands known for their quality and durability. Here are some recommended brands:
- Timken: Timken is a well-known brand that specializes in manufacturing high-quality bearings and hub assemblies. They have a reputation for producing reliable and long-lasting products. Timken axle hubs are widely used in the automotive industry and are trusted by both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
- Moog: Moog is another reputable brand that offers a wide range of suspension and steering components, including axle hubs. Moog axle hubs are known for their precision engineering, excellent build quality, and reliable performance. They are designed to meet or exceed OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) specifications and are a popular choice among car owners.
- ACDelco: ACDelco is a trusted brand that provides a comprehensive range of automotive replacement parts. Their axle hubs are designed to deliver reliable performance and durability. ACDelco axle hubs are often recommended for their compatibility with various vehicle makes and models, making them a reliable choice for replacement.
- SKF: SKF is a well-established brand with a strong reputation in the automotive industry. They are known for their high-quality bearings and hub assemblies, including axle hubs. SKF axle hubs are engineered to provide excellent performance and longevity. They are often regarded as a premium option for those seeking reliable replacement parts.
- NTN: NTN is a trusted manufacturer of bearings and hub assemblies. They offer a range of axle hubs that are designed to meet stringent quality standards. NTN axle hubs are known for their durability and precise fitment, making them a reliable choice for replacement in various vehicles.
It’s important to note that the availability of specific brands may vary depending on your location and the make and model of your vehicle. Additionally, it’s always a good idea to consult with a trusted mechanic or do thorough research to ensure the compatibility of the axle hubs with your vehicle before making a purchase.
In summary, some reliable brands for purchasing replacement axle hubs include Timken, Moog, ACDelco, SKF, and NTN. These brands have a solid reputation for producing high-quality and durable axle hubs, making them trusted choices for maintaining and repairing your vehicle’s axle system.

Are there specific tools required for DIY axle hub replacement, and where can I find them?
When undertaking a DIY axle hub replacement, certain tools are needed to ensure a smooth and successful process. Here are some specific tools that are commonly required for DIY axle hub replacement and where you can find them:
- Jack and jack stands: These tools are essential for raising the vehicle off the ground and providing a stable support system. You can find jacks and jack stands at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Lug wrench or socket set: A lug wrench or a socket set with the appropriate size socket is necessary to loosen and tighten the lug nuts on the wheel. These tools are commonly available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Torque wrench: A torque wrench is required to tighten the lug nuts on the wheel and other fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. Torque wrenches can be found at automotive supply stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Pry bar: A pry bar is useful for gently separating the axle hub assembly from the mounting point, especially if it is tightly secured. Pry bars are available at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, and online retailers.
- Hammer: A hammer can be used to tap or lightly strike the axle hub assembly or its components for removal or installation. Hammers are commonly available at hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers.
- Wheel bearing grease: High-quality wheel bearing grease is necessary for lubricating the axle hub assembly and ensuring smooth operation. Wheel bearing grease can be purchased at automotive supply stores, lubricant suppliers, and online retailers.
- Additional tools: Depending on the specific vehicle and axle hub assembly, you may require additional tools such as a socket set, wrenches, pliers, or specific specialty tools. Consult the vehicle’s service manual or online resources for the specific tools needed for your vehicle model.
To find these tools, you can visit local automotive supply stores, hardware stores, or tool stores in your area. They typically carry a wide range of automotive tools and equipment. Alternatively, you can explore online retailers that specialize in automotive tools and equipment, where you can conveniently browse and purchase the tools you need.
It’s important to ensure that the tools you acquire are of good quality and suitable for the task at hand. Investing in quality tools can make the DIY axle hub replacement process more efficient and help achieve better results. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety guidelines when using tools and equipment.
In summary, specific tools are required for DIY axle hub replacement, such as a jack and jack stands, lug wrench or socket set, torque wrench, pry bar, hammer, and wheel bearing grease. These tools can be found at automotive supply stores, hardware stores, tool stores, and online retailers. Acquiring quality tools and following proper safety guidelines will contribute to a successful DIY axle hub replacement.

Are there any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models?
Recalls and common issues can occur with specific axle hub models due to manufacturing defects, design flaws, or other factors. Here’s a detailed explanation:
It’s important to note that specific recalls and common issues can vary depending on the make, model, and year of the vehicle, as well as the specific axle hub manufacturer. Manufacturers and regulatory bodies such as the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) monitor and address safety concerns related to axle hubs through recalls and investigations.
Recalls are typically initiated by the vehicle manufacturer or the axle hub manufacturer in response to identified safety defects or non-compliance with safety standards. Recalls aim to address the issues and rectify any potential safety risks associated with the axle hub models. They may involve inspections, repairs, or replacements of the affected components.
To determine if there are any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models, it is recommended to check the following sources:
- Manufacturer’s Website: Visit the official website of the vehicle manufacturer or the axle hub manufacturer. They often provide information on recalls, technical service bulletins (TSBs), and common issues related to their products. Look for any relevant information specific to the axle hub models in question.
- NHTSA Website: The NHTSA maintains a comprehensive database of recalls and investigations related to vehicle components, including axle hubs. Their website allows users to search for recalls and investigations by specific make, model, and component. You can use their search tool to check if there are any recalls or investigations associated with the axle hub models of interest.
- Owner Forums and Online Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to specific vehicle makes and models can be a valuable source of information. Owners often share their experiences, including common issues they have encountered with axle hub models. It’s important to consider multiple sources and exercise caution when relying on anecdotal information.
- Service Centers and Mechanics: Local service centers and mechanics who specialize in the specific vehicle make or have experience with the axle hub models in question may be aware of any recalls or common issues. They can provide insights based on their firsthand knowledge and experience.
By consulting these sources, you can gather information about any recalls or common issues associated with specific axle hub models. If any recalls or safety concerns are identified, it is recommended to contact the vehicle manufacturer or a certified dealership to inquire about the necessary actions, such as inspections or repairs, to address the issues.
In summary, recalls and common issues can occur with specific axle hub models. Checking the manufacturer’s website, the NHTSA website, owner forums, and consulting with service centers and mechanics can provide valuable information regarding any recalls or common issues associated with the axle hub models of interest. It’s important to stay informed and take appropriate actions to address any identified safety concerns.


editor by CX 2024-05-13
China factory Auto Automotive Car Unit Front Axle Wheel Bearing Hub Tapered Thrust Cylindrical Deep Groove Pillow Block Roller Ball Hub Bearings for (43550-26010) with Hot selling
Product Description
Applications
1. machine tools,metallurgical machinery,
2. textile machinery,printing machinery,
3.other machinery,equipment,Can make the mechanical
4. system design very compact and nimble
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are you a trading company or a manufacturer?
A: We are factory.
Q: How long is your delivery time?
A: Generally it is 5-10 days if the goods are in stock. or it is 15-20 days if the goods are not in stock, it is according to quantity.
Q: Do you provide samples ? is it free or extra ?
A: Yes, we could offer the sample for free charge but do not pay the cost of freight.
Q: What is your terms of payment ?
A: Payment=1000USD, 30% T/T in advance ,balance before shippment.
How to Calculate the Diameter of a Worm Gear

In this article, we will discuss the characteristics of the Duplex, Single-throated, and Undercut worm gears and the analysis of worm shaft deflection. Besides that, we will explore how the diameter of a worm gear is calculated. If you have any doubt about the function of a worm gear, you can refer to the table below. Also, keep in mind that a worm gear has several important parameters which determine its working.
Duplex worm gear
A duplex worm gear set is distinguished by its ability to maintain precise angles and high gear ratios. The backlash of the gearing can be readjusted several times. The axial position of the worm shaft can be determined by adjusting screws on the housing cover. This feature allows for low backlash engagement of the worm tooth pitch with the worm gear. This feature is especially beneficial when backlash is a critical factor when selecting gears.
The standard worm gear shaft requires less lubrication than its dual counterpart. Worm gears are difficult to lubricate because they are sliding rather than rotating. They also have fewer moving parts and fewer points of failure. The disadvantage of a worm gear is that you cannot reverse the direction of power due to friction between the worm and the wheel. Because of this, they are best used in machines that operate at low speeds.
Worm wheels have teeth that form a helix. This helix produces axial thrust forces, depending on the hand of the helix and the direction of rotation. To handle these forces, the worms should be mounted securely using dowel pins, step shafts, and dowel pins. To prevent the worm from shifting, the worm wheel axis must be aligned with the center of the worm wheel’s face width.
The backlash of the CZPT duplex worm gear is adjustable. By shifting the worm axially, the section of the worm with the desired tooth thickness is in contact with the wheel. As a result, the backlash is adjustable. Worm gears are an excellent choice for rotary tables, high-precision reversing applications, and ultra-low-backlash gearboxes. Axial shift backlash is a major advantage of duplex worm gears, and this feature translates into a simple and fast assembly process.
When choosing a gear set, the size and lubrication process will be crucial. If you’re not careful, you might end up with a damaged gear or 1 with improper backlash. Luckily, there are some simple ways to maintain the proper tooth contact and backlash of your worm gears, ensuring long-term reliability and performance. As with any gear set, proper lubrication will ensure your worm gears last for years to come.
Single-throated worm gear
Worm gears mesh by sliding and rolling motions, but sliding contact dominates at high reduction ratios. Worm gears’ efficiency is limited by the friction and heat generated during sliding, so lubrication is necessary to maintain optimal efficiency. The worm and gear are usually made of dissimilar metals, such as phosphor-bronze or hardened steel. MC nylon, a synthetic engineering plastic, is often used for the shaft.
Worm gears are highly efficient in transmission of power and are adaptable to various types of machinery and devices. Their low output speed and high torque make them a popular choice for power transmission. A single-throated worm gear is easy to assemble and lock. A double-throated worm gear requires 2 shafts, 1 for each worm gear. Both styles are efficient in high-torque applications.
Worm gears are widely used in power transmission applications because of their low speed and compact design. A numerical model was developed to calculate the quasi-static load sharing between gears and mating surfaces. The influence coefficient method allows fast computing of the deformation of the gear surface and local contact of the mating surfaces. The resultant analysis shows that a single-throated worm gear can reduce the amount of energy required to drive an electric motor.
In addition to the wear caused by friction, a worm wheel can experience additional wear. Because the worm wheel is softer than the worm, most of the wear occurs on the wheel. In fact, the number of teeth on a worm wheel should not match its thread count. A single-throated worm gear shaft can increase the efficiency of a machine by as much as 35%. In addition, it can lower the cost of running.
A worm gear is used when the diametrical pitch of the worm wheel and worm gear are the same. If the diametrical pitch of both gears is the same, the 2 worms will mesh properly. In addition, the worm wheel and worm will be attached to each other with a set screw. This screw is inserted into the hub and then secured with a locknut.
Undercut worm gear
Undercut worm gears have a cylindrical shaft, and their teeth are shaped in an evolution-like pattern. Worms are made of a hardened cemented metal, 16MnCr5. The number of gear teeth is determined by the pressure angle at the zero gearing correction. The teeth are convex in normal and centre-line sections. The diameter of the worm is determined by the worm’s tangential profile, d1. Undercut worm gears are used when the number of teeth in the cylinder is large, and when the shaft is rigid enough to resist excessive load.
The center-line distance of the worm gears is the distance from the worm centre to the outer diameter. This distance affects the worm’s deflection and its safety. Enter a specific value for the bearing distance. Then, the software proposes a range of suitable solutions based on the number of teeth and the module. The table of solutions contains various options, and the selected variant is transferred to the main calculation.
A pressure-angle-angle-compensated worm can be manufactured using single-pointed lathe tools or end mills. The worm’s diameter and depth are influenced by the cutter used. In addition, the diameter of the grinding wheel determines the profile of the worm. If the worm is cut too deep, it will result in undercutting. Despite the undercutting risk, the design of worm gearing is flexible and allows considerable freedom.
The reduction ratio of a worm gear is massive. With only a little effort, the worm gear can significantly reduce speed and torque. In contrast, conventional gear sets need to make multiple reductions to get the same reduction level. Worm gears also have several disadvantages. Worm gears can’t reverse the direction of power because the friction between the worm and the wheel makes this impossible. The worm gear can’t reverse the direction of power, but the worm moves from 1 direction to another.
The process of undercutting is closely related to the profile of the worm. The worm’s profile will vary depending on the worm diameter, lead angle, and grinding wheel diameter. The worm’s profile will change if the generating process has removed material from the tooth base. A small undercut reduces tooth strength and reduces contact. For smaller gears, a minimum of 14-1/2degPA gears should be used.
Analysis of worm shaft deflection
To analyze the worm shaft deflection, we first derived its maximum deflection value. The deflection is calculated using the Euler-Bernoulli method and Timoshenko shear deformation. Then, we calculated the moment of inertia and the area of the transverse section using CAD software. In our analysis, we used the results of the test to compare the resulting parameters with the theoretical ones.
We can use the resulting centre-line distance and worm gear tooth profiles to calculate the required worm deflection. Using these values, we can use the worm gear deflection analysis to ensure the correct bearing size and worm gear teeth. Once we have these values, we can transfer them to the main calculation. Then, we can calculate the worm deflection and its safety. Then, we enter the values into the appropriate tables, and the resulting solutions are automatically transferred into the main calculation. However, we have to keep in mind that the deflection value will not be considered safe if it is larger than the worm gear’s outer diameter.
We use a four-stage process for investigating worm shaft deflection. We first apply the finite element method to compute the deflection and compare the simulation results with the experimentally tested worm shafts. Finally, we perform parameter studies with 15 worm gear toothings without considering the shaft geometry. This step is the first of 4 stages of the investigation. Once we have calculated the deflection, we can use the simulation results to determine the parameters needed to optimize the design.
Using a calculation system to calculate worm shaft deflection, we can determine the efficiency of worm gears. There are several parameters to optimize gearing efficiency, including material and geometry, and lubricant. In addition, we can reduce the bearing losses, which are caused by bearing failures. We can also identify the supporting method for the worm shafts in the options menu. The theoretical section provides further information.


China supplier CZPT Dac256200206 Zz Car Wheel Bearings Rear Axle Auto Hub Bearing with Hot selling
Product Description
Product Description
KOYO DAC25625716 ZZ Car Wheel Bearings Rear Axle Auto Hub Bearing
Bearings used in automobile, including wheel hub bearing, gearbox bearing, air conditioning compressor bearing, separation bearing, etc
The main function of hub bearing is to bear load and provide accurate guidance for the rotation of hub. It bears both axial load and radial load, so it is a very important part. The traditional bearings for automobile wheels are composed of 2 sets of tapered roller bearings or ball bearings. The installation, oiling, sealing and clearance adjustment of bearings are carried out on the automobile production line. This kind of structure makes it difficult to assemble, high cost and poor reliability in the automobile factory, and when the automobile is in the maintenance point, it also needs to clean, oil and adjust the bearing. Hub bearing unit is developed on the basis of standard angular contact ball bearing and tapered roller bearing. It integrates 2 sets of bearings. It has the advantages of good assembly performance, omitting clearance adjustment, light weight, compact structure, large load capacity, pre loading grease for sealed bearings, omitting external hub sealing and avoiding maintenance. It has been widely used in cars, There is also a trend to gradually expand the application in trucks.
| Product nameWheel | Wheel Hub Bearing |
| Material | Bearing Steel |
| Standard | DIN GB ISO JIS |
| Bearing Package | Barreled, bagged, boxed, palletized or as customers’ requirement. |
| Service | OEM service provided |
| Delivery time | 3-10 days depends on quantity needed |
Detailed Photos
Product Parameters
| BDL.NO | Automotive type |
|||||||||||
| SKF | KOYO | NTN | SNR | NSK | BCA | IRB | OEM | |||||
| 1 | DAC124 | DAC3568A2RS | GB10840 S02 | B-33 | IR-8026 | Fiat Volvo | ||||||
| 76 | 633,967,633,967 | LaDa Chrysrle | ||||||||||
| 77 | DAC3568 | M8-808442 | DAC4074CWCS73 | AU0803 | 40BWD016 | Proton | ||||||
| 136 | DAC4074 | Chrysler Peugeot | ||||||||||
| 202 | DAC45800045 2RS | 0.80 | 564725AB | 510051 | 700-498-630- | |||||||
| 203 | DAC45800048 ZZ | 0.83 | GB 40096 | |||||||||
| 204 | DAC45830044 2RS | 0.88 | 615645 | |||||||||
| 205 | DAC45840039 2RS | 0.88 | BAHB 35717 | 547103E | GB12398S02 | 45BWD03 | 513130 | IR-8529 | 2571810127 | |||
| 206 | DAC45840039 ZZ | 0.88 | GB40264 | |||||||||
| 207 | DAC45840041/39 2RS | 0.89 | DAC4584DW | 43BWD113 | Citroen Peugeot Volvo | |||||||
| 208 | DAC45840041/39 ZZ | 0.89 | 510034 | |||||||||
| 209 | DAC45840042/40 ZZ | 0.90 | DE571 | 45BWD07B | 510039 | Mitsubish,2.3 | ||||||
| 210 | DAC4585571 | 0.70 | 4209ATN9 | 4209BTVH | IR-8566 | |||||||
| 211 | DAC458500302 2RS | 0.86 | DAC2004 | |||||||||
| 212 | DAC45850041 ZZ | 0.88 | 580191 | 33411090505 | Ford | |||||||
| 213 | DAC45850051 ZZ | 0.88 | DAC4585 | |||||||||
| 214 | DAC45880039 | 0.95 | GB40300 S03 | |||||||||
| 215 | DAC47810053 ZZ | 0.88 | DAC4781WSH2 | 51571 | ||||||||
| 216 | DAC47850045 ZZ | 0.90 | K559431 | 516008 | ||||||||
| 217 | DAC48860042/40 | 48BWD01 | ||||||||||
| 218 | DAC49840048 2RS | 0.98 | BAHB35717C | 547103 | DAC458439BW | IR-8572 | ||||||
| 219 | DAC49840048 ZZ | 0.98 | ||||||||||
| 220 | DAC49880046 ZZ | 0.92 | 572506 | GB45719S02 | 49BWD01B | Toyota Lexus | ||||||
| BDL.NO | Automotive type | |||||||||||
| Kg | SKF | KOYO | NTN | SNR | NSK | BCA | IRB | OEM | ||||
| 221 | DAC50900034 | 0.84 | 633007C | 528514 | ||||||||
| 222 | DAC55900040 | |||||||||||
| 223 | DAC50820033/28 ZZ | 0.78 | ||||||||||
| 224 | DAC55900060 | |||||||||||
| 225 | DAC35720033 ABS | 0.56 | BAH00583ADX | |||||||||
| 226 | DAC37720033 ABS | 0.56 | BAH0072 | |||||||||
| 227 | DAC37720037 ABS | 0.58 | BAH0055 | |||||||||
| 228 | DAC38730040 ABS | 0.65 | 38BWD26 | |||||||||
| 229 | DAC38740040 ABS | 38BWD27 | ||||||||||
| 230 | DAC39720037 ABS | 0.58 | BAH5716 | |||||||||
| 231 | DAC39740039 ABS | 0.66 | BAH 0043 C | |||||||||
| 232 | DAC4571037 ABS | 0.62 | BAH 0068 D | |||||||||
| 233 | DAC4571039 ABS | 0.67 | 40BWD17 | |||||||||
| 234 | DAC40840040 ABS | 0.90 | XGB40492 | |||||||||
| 235 | DAC42780045 ABS | 0.90 | BAH0069 | |||||||||
| 236 | DAC42820036 ABS | 0.78 | BAH0178 | |||||||||
| 237 | DAC43800040 ABS | 0.88 | ||||||||||
| 238 | DAC43780044 ABS | 0.85 | DAC4378W-1 | AU571-4 | 510089 | |||||||
| 239 | DAC45870041/39 ABS | 0.98 | ||||||||||
Packaging & Shipping
Company Profile
Our Advantages
Our Advantages:
1. World-Class Bearing: We provide our customers with all types of indigenous bearing with world-class quality.
2. OEM or Non-Stand Bearings: Any requirement for Nonstandard bearings is Easily Fulfilled by us due to its vast knowledge and links in the industry.
3. Genuine products With Excellent Quality: The company has always proved the 100% quality products it provides with genuine intent.
4. After Sales Service and Technical Assistance: The company provides after-sales service and technical assistance as per the customer’s requirements and needs.
5. Quick Delivery: The company provides just-in-time delivery with its streamlined supply chain.
SAMPLES
1. Samples quantity: 1-10 PCS are available.
2. Free samples: It depends on the Model No., material and quantity. Some of the bearings samples need client to pay samples charge and shipping cost.
3. It’s better to start your order with Trade Assurance to get full protection for your samples order.
CUSTOMIZED
The customized LOGO or drawing is acceptable for us.
MOQ
1. MOQ: 10 PCS standard bearings.
2. MOQ: 1000 PCS customized your brand bearings.
OEM POLICY
1. We can printing your brand (logo, artwork)on the shield or laser engraving your brand on the shield.
2. We can custom your packaging according to your design
3. All copyright own by clients and we promised don’t disclose any info.
FAQ
1.What is the minimum order quantity for this product?
Can be negotiated, we will try our best to meet customer needs.Our company is mainly based on wholesale sales, most customers’orders are more than 1 ton.
2.What is your latest delivery time?
Most orders will be shipped within 7-15 days of payment being received.
3.Does your company have quality assurance?
Yes, for 1 years.
4.What is the competitiveness of your company’s products compared to other companies?
High precision, high speed, low noise.
5.What are the advantages of your company’s services compared to other companies?
Answer questions online 24 hours a day, reply in a timely manner, and provide various documents required by customers for customs clearance or sales. 100% after-sales service.
6.Which payment method does your company support?
Do our best to meet customer needs, negotiable.
7.How to contact us quickly?
Please send us an inquiry or message and leave your other contact information, such as phone number, account or account, we will contact you as soon as possible and provide the detailed information you need.
Please feel free to contact us, if you have any other question
What is a drive shaft?
If you notice a clicking noise while driving, it is most likely the driveshaft. An experienced auto mechanic will be able to tell you if the noise is coming from both sides or from 1 side. If it only happens on 1 side, you should check it. If you notice noise on both sides, you should contact a mechanic. In either case, a replacement driveshaft should be easy to find.
The drive shaft is a mechanical part
A driveshaft is a mechanical device that transmits rotation and torque from the engine to the wheels of the vehicle. This component is essential to the operation of any driveline, as the mechanical power from the engine is transmitted to the PTO (power take-off) shaft, which hydraulically transmits that power to connected equipment. Different drive shafts contain different combinations of joints to compensate for changes in shaft length and angle. Some types of drive shafts include connecting shafts, internal constant velocity joints, and external fixed joints. They also contain anti-lock system rings and torsional dampers to prevent overloading the axle or causing the wheels to lock.
Although driveshafts are relatively light, they need to handle a lot of torque. Torque applied to the drive shaft produces torsional and shear stresses. Because they have to withstand torque, these shafts are designed to be lightweight and have little inertia or weight. Therefore, they usually have a joint, coupling or rod between the 2 parts. Components can also be bent to accommodate changes in the distance between them.
The drive shaft can be made from a variety of materials. The most common material for these components is steel, although alloy steels are often used for high-strength applications. Alloy steel, chromium or vanadium are other materials that can be used. The type of material used depends on the application and size of the component. In many cases, metal driveshafts are the most durable and cheapest option. Plastic shafts are used for light duty applications and have different torque levels than metal shafts.
It transfers power from the engine to the wheels
A car’s powertrain consists of an electric motor, transmission, and differential. Each section performs a specific job. In a rear-wheel drive vehicle, the power generated by the engine is transmitted to the rear tires. This arrangement improves braking and handling. The differential controls how much power each wheel receives. The torque of the engine is transferred to the wheels according to its speed.
The transmission transfers power from the engine to the wheels. It is also called “transgender”. Its job is to ensure power is delivered to the wheels. Electric cars cannot drive themselves and require a gearbox to drive forward. It also controls how much power reaches the wheels at any given moment. The transmission is the last part of the power transmission chain. Despite its many names, the transmission is the most complex component of a car’s powertrain.
The driveshaft is a long steel tube that transmits mechanical power from the transmission to the wheels. Cardan joints connect to the drive shaft and provide flexible pivot points. The differential assembly is mounted on the drive shaft, allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. The differential allows the wheels to turn at different speeds and is very important when cornering. Axles are also important to the performance of the car.
It has a rubber boot that protects it from dust and moisture
To keep this boot in good condition, you should clean it with cold water and a rag. Never place it in the dryer or in direct sunlight. Heat can deteriorate the rubber and cause it to shrink or crack. To prolong the life of your rubber boots, apply rubber conditioner to them regularly. Indigenous peoples in the Amazon region collect latex sap from the bark of rubber trees. Then they put their feet on the fire to solidify the sap.
it has a U-shaped connector
The drive shaft has a U-joint that transfers rotational energy from the engine to the axle. Defective gimbal joints can cause vibrations when the vehicle is in motion. This vibration is often mistaken for a wheel balance problem. Wheel balance problems can cause the vehicle to vibrate while driving, while a U-joint failure can cause the vehicle to vibrate when decelerating and accelerating, and stop when the vehicle is stopped.
The drive shaft is connected to the transmission and differential using a U-joint. It allows for small changes in position between the 2 components. This prevents the differential and transmission from remaining perfectly aligned. The U-joint also allows the drive shaft to be connected unconstrained, allowing the vehicle to move. Its main purpose is to transmit electricity. Of all types of elastic couplings, U-joints are the oldest.
Your vehicle’s U-joints should be inspected at least twice a year, and the joints should be greased. When checking the U-joint, you should hear a dull sound when changing gears. A clicking sound indicates insufficient grease in the bearing. If you hear or feel vibrations when shifting gears, you may need to service the bearings to prolong their life.
it has a slide-in tube
The telescopic design is a modern alternative to traditional driveshaft designs. This innovative design is based on an unconventional design philosophy that combines advances in material science and manufacturing processes. Therefore, they are more efficient and lighter than conventional designs. Slide-in tubes are a simple and efficient design solution for any vehicle application. Here are some of its benefits. Read on to learn why this type of shaft is ideal for many applications.
The telescopic drive shaft is an important part of the traditional automobile transmission system. These driveshafts allow linear motion of the 2 components, transmitting torque and rotation throughout the vehicle’s driveline. They also absorb energy if the vehicle collides. Often referred to as foldable driveshafts, their popularity is directly dependent on the evolution of the automotive industry.
It uses a bearing press to replace worn or damaged U-joints
A bearing press is a device that uses a rotary press mechanism to install or remove worn or damaged U-joints from a drive shaft. With this tool, you can replace worn or damaged U-joints in your car with relative ease. The first step involves placing the drive shaft in the vise. Then, use the 11/16″ socket to press the other cup in far enough to install the clips. If the cups don’t fit, you can use a bearing press to remove them and repeat the process. After removing the U-joint, use a grease nipple Make sure the new grease nipple is installed correctly.
Worn or damaged U-joints are a major source of driveshaft failure. If 1 of them were damaged or damaged, the entire driveshaft could dislocate and the car would lose power. Unless you have a professional mechanic doing the repairs, you will have to replace the entire driveshaft. Fortunately, there are many ways to do this yourself.
If any of these warning signs appear on your vehicle, you should consider replacing the damaged or worn U-joint. Common symptoms of damaged U-joints include rattling or periodic squeaking when moving, rattling when shifting, wobbling when turning, or rusted oil seals. If you notice any of these symptoms, take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic for a full inspection. Neglecting to replace a worn or damaged u-joint on the driveshaft can result in expensive and dangerous repairs and can cause significant damage to your vehicle.


China Custom Railway Vehicle Axle Roller Bearing 23060/W33 Spherical Roller Bearings near me shop
Product Description
Product Description:
Types of Spherical Roller Bearings:
| For Spherical Roller Bearings, the dimensional series are: | |
| 21300 Series | ISO Dimension Series 13 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 22200 Series | ISO Dimension Series 22 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 22300 Series | ISO Dimension Series 23 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 23000 Series | ISO Dimension Series 30 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 23100 Series | ISO Dimension Series 31 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 23200 Series | ISO Dimension Series 32 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 232/ Series | Extra Large ISO 32 Series Spherical Roller Bearing |
| 23900 Series | ISO Dimension Series 39 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 24000 Series | ISO Dimension Series 40 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 24100 Series | ISO Dimension Series 41 Spherical Roller Bearings |
| 29000 Series | ISO Dimension Series 90 Spherical Thrust Roller Bearings |
| Dimensions | Chamfer | Basic Load Ratings | Designation | Weight | Speed limited | |||||
| mm | r/min | |||||||||
| d | D | B | rmin | Cr | Cor | Current | Original | Kgs | Grease | Oil |
| 300 | 460 | 118 | 4 | 1260 | 3070 | 23060 | 30 0571 0 | 75.2 | 800 | 1000 |
| 300 | 460 | 118 | 4 | 1260 | 3070 | 23060/W33 | 30 0571 0Y | 74.6 | 800 | 1000 |
| 300 | 460 | 160 | 4 | 2360 | 5571 | 24060C/W33 | 457160Y | 101 | 600 | 750 |
| 300 | 500 | 160 | 5 | 2670 | 4800 | 23160 | 30 0571 0 | 134 | 670 | 850 |
| 300 | 500 | 160 | 5 | 2670 | 4800 | 23160/W33 | 30 0571 0Y | 133 | 670 | 850 |
| 300 | 500 | 200 | 5 | 3100 | 5800 | 24160C | 457160 | 160 | 530 | 670 |
| 300 | 500 | 200 | 5 | 3100 | 580 | 24160C/W33 | 457160Y | 159 | 530 | 670 |
| 300 | 540 | 140 | 5 | 2610 | 4250 | 22260 | 3560 | 143 | 750 | 950 |
Why choose us:
1.With more than 25 years experiences of producing and R&D bearings.
2. All of ours roller bearing and ball bearings with CE ISO TUV certificate
3. Our products have been exported to about 30 country/areas, and enjoyed a high reputation on the domestic and overseas market.
4. The OEM and ODM are available.
5. Professional after-sales team
6. Offering most reasonable price
Package:
Payment & Delivery:
Application :
FAQ:
Q: Can you provide us sample, is it free or need to pay?
A: If you don’t need to print your Logo or other artwork on the products, we will not charge any cost, just tell us your freight collect account like Fedex Dhl TNT, if you don’t have We need to charge Express fee properly.
Q: How to deliver?
A: By sea or by air or by courier like DHL,UPS, Fedex
Q: What’s your Payment term?
A: T/T or L/C or Western union 30% deposit,the 70% balance before shipping!
Q:Where is your factory located, is it convenient to visit?
A:Our factory located in Yandian town, HangZhou city, ZheJiang Province, China.
very close to the high-way train station and the high-way entrance, only 40 minutes to HangZhou Yaoqiang Airport, we can provide business vehicle to take you coming and departure.
Contact us:
Screw Sizes and Their Uses
Screws have different sizes and features. This article will discuss screw sizes and their uses. There are 2 main types: right-handed and left-handed screw shafts. Each screw features a point that drills into the object. Flat tipped screws, on the other hand, need a pre-drilled hole. These screw sizes are determined by the major and minor diameters. To determine which size of screw you need, measure the diameter of the hole and the screw bolt’s thread depth.
The major diameter of a screw shaft
The major diameter of a screw shaft is the distance from the outer edge of the thread on 1 side to the tip of the other. The minor diameter is the inner smooth part of the screw shaft. The major diameter of a screw is typically between 2 and 16 inches. A screw with a pointy tip has a smaller major diameter than 1 without. In addition, a screw with a larger major diameter will have a wider head and drive.
The thread of a screw is usually characterized by its pitch and angle of engagement. The pitch is the angle formed by the helix of a thread, while the crest forms the surface of the thread corresponding to the major diameter of the screw. The pitch angle is the angle between the gear axis and the pitch surface. Screws without self-locking threads have multiple starts, or helical threads.
The pitch is a crucial component of a screw’s threading system. Pitch is the distance from a given thread point to the corresponding point of the next thread on the same shaft. The pitch line is 1 element of pitch diameter. The pitch line, or lead, is a crucial dimension for the thread of a screw, as it controls the amount of thread that will advance during a single turn.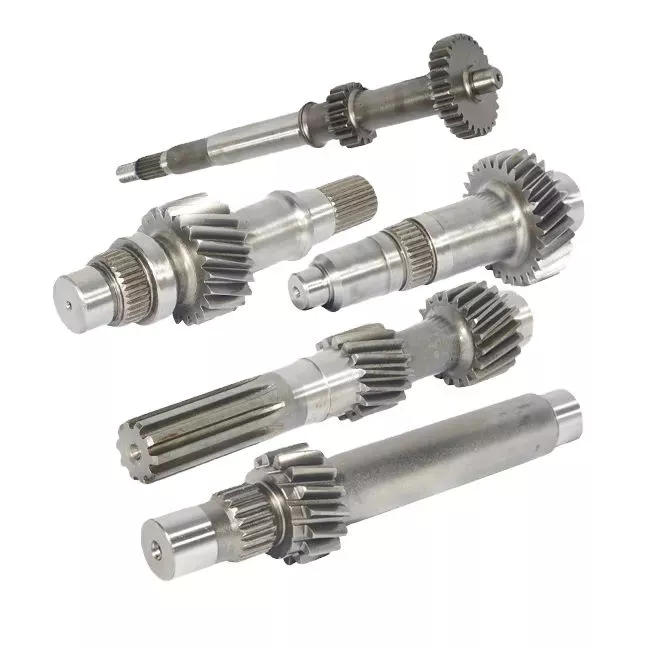
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft
When choosing the appropriate screw, it is important to know its pitch diameter and pitch line. The pitch line designates the distance between adjacent thread sides. The pitch diameter is also known as the mean area of the screw shaft. Both of these dimensions are important when choosing the correct screw. A screw with a pitch of 1/8 will have a mechanical advantage of 6.3. For more information, consult an application engineer at Roton.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured as the distance between the crest and the root of the thread. Threads that are too long or too short will not fit together in an assembly. To measure pitch, use a measuring tool with a metric scale. If the pitch is too small, it will cause the screw to loosen or get stuck. Increasing the pitch will prevent this problem. As a result, screw diameter is critical.
The pitch diameter of a screw shaft is measured from the crest of 1 thread to the corresponding point on the next thread. Measurement is made from 1 thread to another, which is then measured using the pitch. Alternatively, the pitch diameter can be approximated by averaging the major and minor diameters. In most cases, the pitch diameter of a screw shaft is equal to the difference between the two.
The thread depth of a screw shaft
Often referred to as the major diameter, the thread depth is the outermost diameter of the screw. To measure the thread depth of a screw, use a steel rule, micrometer, or caliper. In general, the first number in the thread designation indicates the major diameter of the thread. If a section of the screw is worn, the thread depth will be smaller, and vice versa. Therefore, it is good practice to measure the section of the screw that receives the least amount of use.
In screw manufacturing, the thread depth is measured from the crest of the screw to the root. The pitch diameter is halfway between the major and minor diameters. The lead diameter represents the amount of linear distance traveled in 1 revolution. As the lead increases, the load capacity decreases. This measurement is primarily used in the construction of screws. However, it should not be used for precision machines. The thread depth of a screw shaft is essential for achieving accurate screw installation.
To measure the thread depth of a screw shaft, the manufacturer must first determine how much material the thread is exposed to. If the thread is exposed to side loads, it can cause the nut to wedge. Because the nut will be side loaded, its thread flanks will contact the nut. The less clearance between the nut and the screw, the lower the clearance between the nut and the screw. However, if the thread is centralized, there is no risk of the nut wedgeing.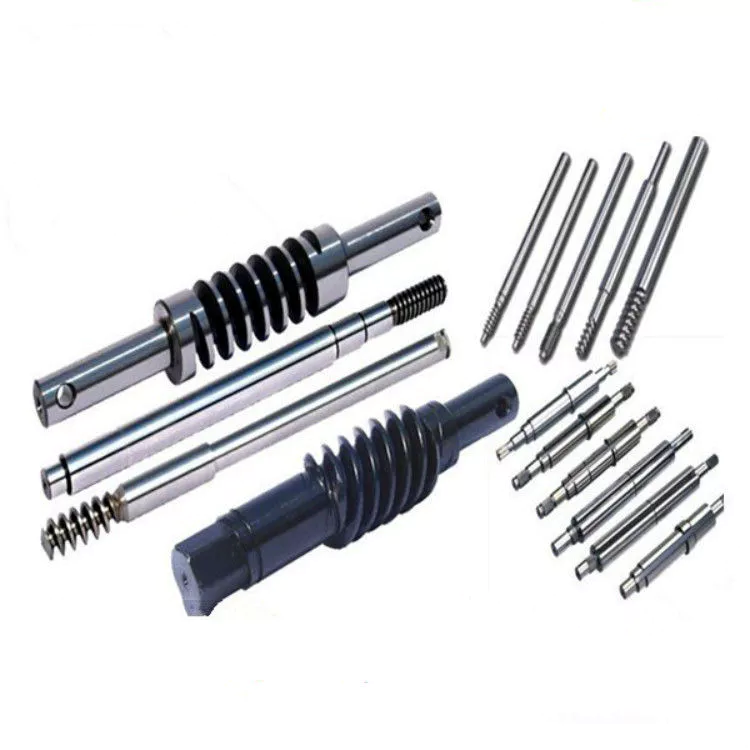
The lead of a screw shaft
Pitch and lead are 2 measurements of a screw’s linear distance per turn. They’re often used interchangeably, but their definitions are not the same. The difference between them lies in the axial distance between adjacent threads. For single-start screws, the pitch is equal to the lead, while the lead of a multi-start screw is greater than the pitch. This difference is often referred to as backlash.
There are 2 ways to calculate the pitch and lead of a screw. For single-start screws, the lead and pitch are equal. Multiple-start screws, on the other hand, have multiple starts. The pitch of a multiple-start screw is the same as its lead, but with 2 or more threads running the length of the screw shaft. A square-thread screw is a better choice in applications requiring high load-bearing capacity and minimal friction losses.
The PV curve defines the safe operating limits of lead screw assemblies. It describes the inverse relationship between contact surface pressure and sliding velocity. As the load increases, the lead screw assembly must slow down in order to prevent irreversible damage from frictional heat. Furthermore, a lead screw assembly with a polymer nut must reduce rpm as the load increases. The more speed, the lower the load capacity. But, the PV factor must be below the maximum allowed value of the material used to make the screw shaft.
The thread angle of a screw shaft
The angle between the axes of a thread and the helix of a thread is called the thread angle. A unified thread has a 60-degree angle in all directions. Screws can have either a tapped hole or a captive screw. The screw pitch is measured in millimeters (mm) and is usually equal to the screw major diameter. In most cases, the thread angle will be equal to 60-degrees.
Screws with different angles have various degrees of thread. Originally, this was a problem because of the inconsistency in the threading. However, Sellers’s thread was easier to manufacture and was soon adopted as a standard throughout the United States. The United States government began to adopt this thread standard in the mid-1800s, and several influential corporations in the railroad industry endorsed it. The resulting standard is called the United States Standard thread, and it became part of the ASA’s Vol. 1 publication.
There are 2 types of screw threads: coarse and fine. The latter is easier to tighten and achieves tension at lower torques. On the other hand, the coarse thread is deeper than the fine one, making it easier to apply torque to the screw. The thread angle of a screw shaft will vary from bolt to bolt, but they will both fit in the same screw. This makes it easier to select the correct screw.
The tapped hole (or nut) into which the screw fits
A screw can be re-threaded without having to replace it altogether. The process is different than that of a standard bolt, because it requires threading and tapping. The size of a screw is typically specified by its major and minor diameters, which is the inside distance between threads. The thread pitch, which is the distance between each thread, is also specified. Thread pitch is often expressed in threads per inch.
Screws and bolts have different thread pitches. A coarse thread has fewer threads per inch and a longer distance between threads. It is therefore larger in diameter and longer than the material it is screwed into. A coarse thread is often designated with an “A” or “B” letter. The latter is generally used in smaller-scale metalworking applications. The class of threading is called a “threaded hole” and is designated by a letter.
A tapped hole is often a complication. There is a wide range of variations between the sizes of threaded holes and nut threads, so the tapped hole is a critical dimension in many applications. However, even if you choose a threaded screw that meets the requisite tolerance, there may be a mismatch in the thread pitch. This can prevent the screw from freely rotating.


China Professional Axle Bearing 518445 518410 Truck Bearings Hm518445/410 Tapered Roller Bearing with Free Design Custom
Product Description
|
Type |
BALL |
|
Structure |
Deep Groove |
|
Applicable Industries |
Industrial machinery |
|
Model Number |
518445 518410 |
|
Precision Rating |
P0 P6 P5 |
|
Seals Type |
OPEN ZZ 2RS |
|
Number of Row |
Single Row |
|
Place of Origin |
ZheJiang ,China |
|
Material |
Chrome Steel |
|
Cage |
Steel Cage |
|
Service |
OEM Customized Services |
|
Feature |
Low Noise |
|
Package |
One Plastic Tube |
|
Lubrication |
Oil Grease |
FAQ:
CAN YOU PROVIDE FREE SAMPLE?
ONCE YOU CONIRM THE PRICE, IT IS NO PROBLEM FOR US TO PROVIDE THE FREE SAMPLE FOR CHECKING QUALITY.
HOW TO CONTROL YOUR QUALITY?
FROM MATERIAL TO FINISHED GOODS, EACH STEP WE HAVE SPECIAL PERSON TO CHECK TO GURANTEE THE GOOD QUALITY.
WHAT IS YOUR MOQ?
100PCS OR AS PER CONSULTED
IS IT OK TO SHOW CUSTOMER’S LOGO?
OK, NO PROBLEM.
WHAT ABOUT THE DELIVERY TIME?
FOR A SAMPLE, USUALLY, IT NEED 3-5 DAYS. FOR THE MASS PRODUCTION, IT NEED ABOUT 35-40 DAYS.
Different parts of the drive shaft
The driveshaft is the flexible rod that transmits torque between the transmission and the differential. The term drive shaft may also refer to a cardan shaft, a transmission shaft or a propeller shaft. Parts of the drive shaft are varied and include:
The driveshaft is a flexible rod that transmits torque from the transmission to the differential
When the driveshaft in your car starts to fail, you should seek professional help as soon as possible to fix the problem. A damaged driveshaft can often be heard. This noise sounds like “tak tak” and is usually more pronounced during sharp turns. However, if you can’t hear the noise while driving, you can check the condition of the car yourself.
The drive shaft is an important part of the automobile transmission system. It transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which then transfers it to the wheels. The system is complex, but still critical to the proper functioning of the car. It is the flexible rod that connects all other parts of the drivetrain. The driveshaft is the most important part of the drivetrain, and understanding its function will make it easier for you to properly maintain your car.
Driveshafts are used in different vehicles, including front-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, and front-engine rear-wheel drive. Drive shafts are also used in motorcycles, locomotives and ships. Common front-engine, rear-wheel drive vehicle configurations are shown below. The type of tube used depends on the size, speed and strength of the drive shaft.
The output shaft is also supported by the output link, which has 2 identical supports. The upper part of the drive module supports a large tapered roller bearing, while the opposite flange end is supported by a parallel roller bearing. This ensures that the torque transfer between the differentials is efficient. If you want to learn more about car differentials, read this article.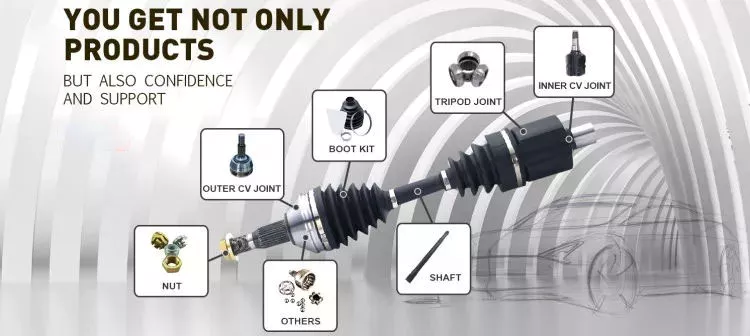
It is also known as cardan shaft, propeller shaft or drive shaft
A propshaft or propshaft is a mechanical component that transmits rotation or torque from an engine or transmission to the front or rear wheels of a vehicle. Because the axes are not directly connected to each other, it must allow relative motion. Because of its role in propelling the vehicle, it is important to understand the components of the driveshaft. Here are some common types.
Isokinetic Joint: This type of joint guarantees that the output speed is the same as the input speed. To achieve this, it must be mounted back-to-back on a plane that bisects the drive angle. Then mount the 2 gimbal joints back-to-back and adjust their relative positions so that the velocity changes at 1 joint are offset by the other joint.
Driveshaft: The driveshaft is the transverse shaft that transmits power to the front wheels. Driveshaft: The driveshaft connects the rear differential to the transmission. The shaft is part of a drive shaft assembly that includes a drive shaft, a slip joint, and a universal joint. This shaft provides rotational torque to the drive shaft.
Dual Cardan Joints: This type of driveshaft uses 2 cardan joints mounted back-to-back. The center yoke replaces the intermediate shaft. For the duplex universal joint to work properly, the angle between the input shaft and the output shaft must be equal. Once aligned, the 2 axes will operate as CV joints. An improved version of the dual gimbal is the Thompson coupling, which offers slightly more efficiency at the cost of added complexity.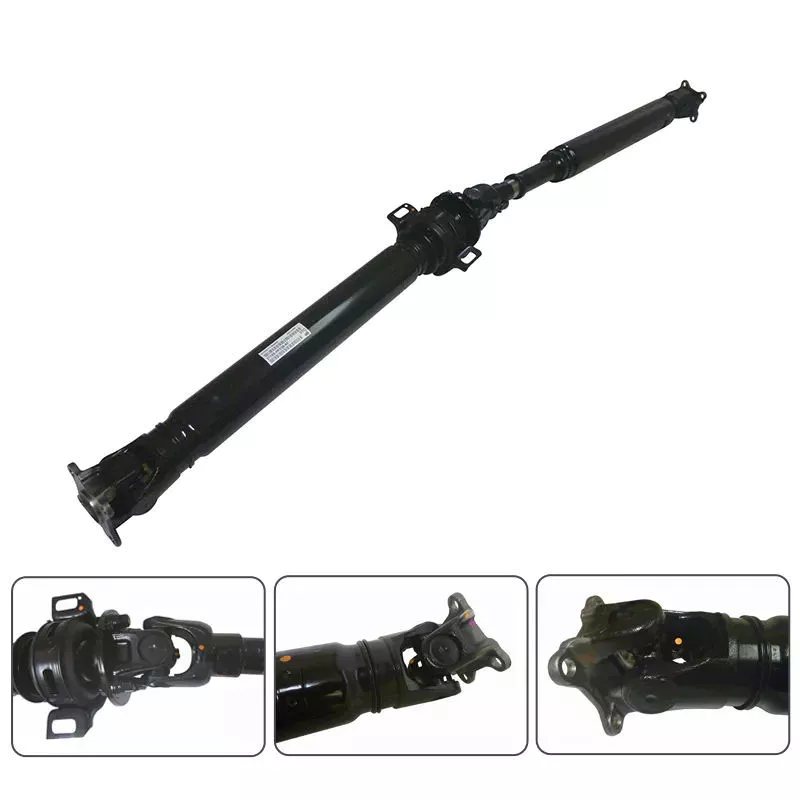
It transmits torque at different angles between driveline components
A vehicle’s driveline consists of various components that transmit power from the engine to the wheels. This includes axles, propshafts, CV joints and differentials. Together, these components transmit torque at different angles between driveline components. A car’s powertrain can only function properly if all its components work in harmony. Without these components, power from the engine would stop at the transmission, which is not the case with a car.
The CV driveshaft design provides smoother operation at higher operating angles and extends differential and transfer case life. The assembly’s central pivot point intersects the joint angle and transmits smooth rotational power and surface speed through the drivetrain. In some cases, the C.V. “U” connector. Drive shafts are not the best choice because the joint angles of the “U” joints are often substantially unequal and can cause torsional vibration.
Driveshafts also have different names, including driveshafts. A car’s driveshaft transfers torque from the transmission to the differential, which is then distributed to other driveline components. A power take-off (PTO) shaft is similar to a prop shaft. They transmit mechanical power to connected components. They are critical to the performance of any car. If any of these components are damaged, the entire drivetrain will not function properly.
A car’s powertrain can be complex and difficult to maintain. Adding vibration to the drivetrain can cause premature wear and shorten overall life. This driveshaft tip focuses on driveshaft assembly, operation, and maintenance, and how to troubleshoot any problems that may arise. Adding proper solutions to pain points can extend the life of the driveshaft. If you’re in the market for a new or used car, be sure to read this article.
it consists of several parts
“It consists of several parts” is 1 of 7 small prints. This word consists of 10 letters and is 1 of the hardest words to say. However, it can be explained simply by comparing it to a cow’s kidney. The cocoa bean has several parts, and the inside of the cocoa bean before bursting has distinct lines. This article will discuss the different parts of the cocoa bean and provide a fun way to learn more about the word.
Replacement is expensive
Replacing a car’s driveshaft can be an expensive affair, and it’s not the only part that needs servicing. A damaged drive shaft can also cause other problems. This is why getting estimates from different repair shops is essential. Often, a simple repair is cheaper than replacing the entire unit. Listed below are some tips for saving money when replacing a driveshaft. Listed below are some of the costs associated with repairs:
First, learn how to determine if your vehicle needs a driveshaft replacement. Damaged driveshaft components can cause intermittent or lack of power. Additionally, improperly installed or assembled driveshaft components can cause problems with the daily operation of the car. Whenever you suspect that your car needs a driveshaft repair, seek professional advice. A professional mechanic will have the knowledge and experience needed to properly solve the problem.
Second, know which parts need servicing. Check the u-joint bushing. They should be free of crumbs and not cracked. Also, check the center support bearing. If this part is damaged, the entire drive shaft needs to be replaced. Finally, know which parts to replace. The maintenance cost of the drive shaft is significantly lower than the maintenance cost. Finally, determine if the repaired driveshaft is suitable for your vehicle.
If you suspect your driveshaft needs service, make an appointment with a repair shop as soon as possible. If you are experiencing vibration and rough riding, driveshaft repairs may be the best way to prevent costly repairs in the future. Also, if your car is experiencing unusual noise and vibration, a driveshaft repair may be a quick and easy solution. If you don’t know how to diagnose a problem with your car, you can take it to a mechanic for an appointment and a quote.

