Product Description
Fine original genuine mechanical dump truck parts shaft-axle 15017032 for terex
Elephant Fluid Power specializes in the production of: all parts of mining trucks such as Caterpilla, Terex, Komatsu, Belaz, Volvo, etc.
Elephant Fluid Power accepts custom parts products!
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 15571636 | rear axle differential assembly | ||
| 15034034 | case/housing | ||
| 3152818 | bolt | ||
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | ||
| 8172961 | Bearing | ||
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 20366534 | Nuts | ||
| 2571865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | ||
| 8172966 | O-ring | ||
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | ||
| 2 0571 385 | seal | ||
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing | ||
| 8171088 | Adjusting ring | ||
| 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN | ||
| 1522099 | Combined flange | ||
| 1522102 | washer | ||
| 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 155716 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly | ||
| 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET | ||
| 1522293 | Nuts | ||
| 914484 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 1523319 | Lock washer | ||
| Part No. | Product name | Part No. | Product name |
| 15571636 | rear axle differential assembly | 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing |
| 15034034 | case/housing | 8171088 | Adjusting ring |
| 3152818 | bolt | 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN |
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | 1522099 | Combined flange |
| 8172961 | Bearing | 1522102 | washer |
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 20366534 | Nuts | 155716 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly |
| 2571865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET |
| 8172966 | O-ring | 1522293 | Nuts |
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | 914484 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 2 0571 385 | seal | 1523319 | Lock washer |
| 8171086 | bolt | 11036504 | Combination flange |
| 15042302 | Flange, flange | 1523124 | Sealing ring |
| 8172958 | Differential housing | 948642 | Sealing ring |
| 8172959 | Differential housing | 1557130 | Gland/Cover/Cap |
| 8171089 | bolt | 1557192 | Gasket |
| 8172910 | Cross shaft/Spider/Unversal joint cross/joint cross/CRoss Axle | 1557179 | Gasket |
| 15046285 | Gear-shaft/Pinion-shaft | 965715 | O-ring |
| Pinion | 1557120 | axle/shaft/pin | |
| 155713 | pad/GASKET | 4880126 | Needle bearing/Bearing |
| 1557101 | Thrust washer | 1557158 | bolt |
| 20582548 | Roller bearing/Bearing | 8172922 | Nuts |
Elephant Fluid Power’s products are 100% compatible with original accessories, and we are at your technical service 24 hours a day.
| To Be Negotiated | 1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Offering Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Condition: | New |
| Transport Package: | Carton Box or Wooden Case |
| Specification: | 15017032 |
| Trademark: | Elephant Fluid Power |
###
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 15020636 | rear axle differential assembly | ||
| 15034034 | case/housing | ||
| 3152818 | bolt | ||
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | ||
| 8172961 | Bearing | ||
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 20366534 | Nuts | ||
| 20512865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | ||
| 8172966 | O-ring | ||
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | ||
| 20832385 | seal | ||
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing | ||
| 8171088 | Adjusting ring | ||
| 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN | ||
| 1522099 | Combined flange | ||
| 1522102 | washer | ||
| 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 15080546 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly | ||
| 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET | ||
| 1522293 | Nuts | ||
| 914484 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 1523319 | Lock washer | ||
###
| Part No. | Product name | Part No. | Product name |
| 15020636 | rear axle differential assembly | 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing |
| 15034034 | case/housing | 8171088 | Adjusting ring |
| 3152818 | bolt | 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN |
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | 1522099 | Combined flange |
| 8172961 | Bearing | 1522102 | washer |
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 20366534 | Nuts | 15080546 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly |
| 20512865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET |
| 8172966 | O-ring | 1522293 | Nuts |
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | 914484 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 20832385 | seal | 1523319 | Lock washer |
| 8171086 | bolt | 11036504 | Combination flange |
| 15042302 | Flange, flange | 1523124 | Sealing ring |
| 8172958 | Differential housing | 948642 | Sealing ring |
| 8172959 | Differential housing | 15037130 | Gland/Cover/Cap |
| 8171089 | bolt | 15037292 | Gasket |
| 8172910 | Cross shaft/Spider/Unversal joint cross/joint cross/CRoss Axle | 15037279 | Gasket |
| 15046285 | Gear-shaft/Pinion-shaft | 960255 | O-ring |
| 15045393 | Pinion | 15037120 | axle/shaft/pin |
| 15048143 | pad/GASKET | 4880126 | Needle bearing/Bearing |
| 15037001 | Thrust washer | 15037958 | bolt |
| 20582548 | Roller bearing/Bearing | 8172922 | Nuts |
| To Be Negotiated | 1 Piece (Min. Order) |
###
| After-sales Service: | Offering Technical Support |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 6 Months |
| Condition: | New |
| Transport Package: | Carton Box or Wooden Case |
| Specification: | 15017032 |
| Trademark: | Elephant Fluid Power |
###
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 15020636 | rear axle differential assembly | ||
| 15034034 | case/housing | ||
| 3152818 | bolt | ||
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | ||
| 8172961 | Bearing | ||
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 20366534 | Nuts | ||
| 20512865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | ||
| 8172966 | O-ring | ||
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | ||
| 20832385 | seal | ||
| Part No. | Product name | ||
| 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing | ||
| 8171088 | Adjusting ring | ||
| 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN | ||
| 1522099 | Combined flange | ||
| 1522102 | washer | ||
| 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 15080546 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly | ||
| 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET | ||
| 1522293 | Nuts | ||
| 914484 | Circlip/snap ring | ||
| 1523319 | Lock washer | ||
###
| Part No. | Product name | Part No. | Product name |
| 15020636 | rear axle differential assembly | 20582549 | Roller bearing/Bearing |
| 15034034 | case/housing | 8171088 | Adjusting ring |
| 3152818 | bolt | 8171090 | Cotter pin/PIN-COTTER/PIN-SPLIT/COTTER-PIN/COTTER PIN |
| 20508641 | Transmission gear set | 1522099 | Combined flange |
| 8172961 | Bearing | 1522102 | washer |
| 8172962 | Circlip/snap ring | 8172159 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 20366534 | Nuts | 15080546 | Middle axle main reducer assembly/Middle axle differential assembly |
| 20512865 | Adjustment mats/SEAL GASKET | 15036900 | Frame-head/Frame-end/BRACKET |
| 8172966 | O-ring | 1522293 | Nuts |
| 8172960 | Gland/Cover/Cap | 914484 | Circlip/snap ring |
| 20832385 | seal | 1523319 | Lock washer |
| 8171086 | bolt | 11036504 | Combination flange |
| 15042302 | Flange, flange | 1523124 | Sealing ring |
| 8172958 | Differential housing | 948642 | Sealing ring |
| 8172959 | Differential housing | 15037130 | Gland/Cover/Cap |
| 8171089 | bolt | 15037292 | Gasket |
| 8172910 | Cross shaft/Spider/Unversal joint cross/joint cross/CRoss Axle | 15037279 | Gasket |
| 15046285 | Gear-shaft/Pinion-shaft | 960255 | O-ring |
| 15045393 | Pinion | 15037120 | axle/shaft/pin |
| 15048143 | pad/GASKET | 4880126 | Needle bearing/Bearing |
| 15037001 | Thrust washer | 15037958 | bolt |
| 20582548 | Roller bearing/Bearing | 8172922 | Nuts |
How to Repair an Axle
An axle is the central shaft of a gear or wheel. The axle can be fixed to the wheels or the vehicle itself and rotates along with them. The axle may include bearings. This article discusses the different types and their functions. It also covers how to repair an axle. In addition to its function, an axle may include mounting points and bearings.
Structure
An axle is a part of railway machinery that helps move trains. It is made up of a cylinder and a system of springs. The axle is positioned near the center of the train’s wheels and is connected to the frame and wagon. Axle box bogies are used in economic trains.
Axles can be integral or detached, depending on the type of vehicle. An integral axle is the central part of the suspension system and supports the weight of the vehicle. A disengaged axle has two wheels on opposite sides. In a vehicle with independent suspension, the axles are matched together with independent suspension. Different types of axles are designed for different purposes, so it’s important to understand which type of axle is used for the vehicle you’re driving.
A conventional axle assembly consists of the hub assembly 10, brake disk 20, wheel bearing assembly 30, and knuckle 40. It also has a hub bolt 14. The wheel bearing assembly 30 is made up of the bearing 32, outer ring 36, and bearing connecting bolt 38. The wheel bearing assembly is connected to the hub using a hub.
The type of axle used in a vehicle is determined by the type of driving force that the axle is expected to deliver. Some vehicles use standard axles while others have custom-made axles to meet their specifications. This allows for better control over the wheels’ speed and torque. These differences can greatly affect the performance of your vehicle.
Full-floating axles are most common in light, medium, and heavy-duty trucks. These axles can handle more weight than their semi-floating counterparts. They also prevent the wheel from coming off in case of axle failure. Full-floating axles are used in some Land-Rover vehicles and are used in American stock car racing. In addition, full-floating axles help maintain wheel alignment and handle side thrust and driving torque.
The structure of an axle assembly comprises an input shaft, a brake disk, and the hub. The input shaft is connected to the drive pulley.
Function
Axle springs are used to support the axle. The spring rate depends on the amount of load applied to the axle. The position of the axle can be determined by detecting signals produced by a position sensor. The sensor detects a change in distance between the axle body and the chassis. The spring rate is then adjusted to provide the required level of deflection.
The differential between the spring supported and unsprung axle suspension can lead to dangerous operating conditions. An operator may not always be aware of the occurrence of a switch from spring-supported to unsprung condition, and may overtax the vehicle as a result. Thus, the proper operation of axles depends on a thorough understanding of axle functions.
The Michigan DOT study used mechanistic models and laboratory studies to develop axle factors. These factors describe the relative damage caused by a single distress to a standard axle. They were used to adjust the AASHTO-based LEFs for single axle weights and to derive new LEFs independent of ESALs.
Models for estimating service lives are based on the work of Timm et al. for the FHWA. These models assume accurate axle loading spectra and a small number of tightly defined scenarios. This greatly simplifies the task of estimating LEFs and improves the accuracy of results.
The MEPDG version of the model supports the NAPCOM and PaveDAT models. They show a considerable variation in the effects of different axle weights on various metrics of pavement condition. This is because different axle weights can cause different results in different sections, if they are associated with two failure mechanisms.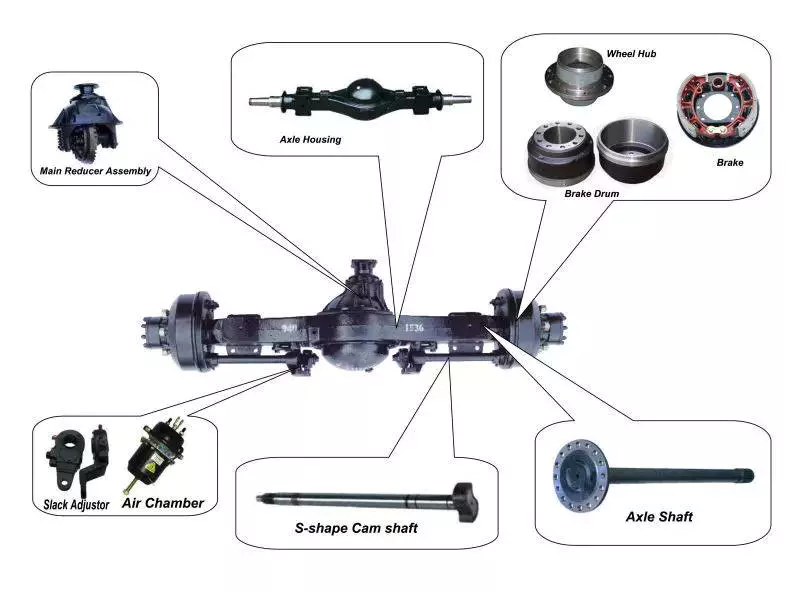
Types
There are many different types of axles, each with their own characteristics. The most common of these is the Ford 9-inch axle, which is found in most Blue Oval muscle cars and trucks. It is so popular that aftermarket companies even make versions for Chevy applications. This particular type of axle features a 3/8-inch square-drive fill plug and is reinforced with a Daytona-style pinion cartridge, which accommodates a stronger pinion head bearing and thicker inner ribbing.
Another type of axle is the rigid front axle, which uses leaf springs to provide suspension. These springs are fixed to spring seats on the axle beam. The axle beam and track rod are connected to each other using screws. The length and thickness of the axle tubes are important for the strength and performance of the axle.
The rear axle is responsible for transferring power to the driving wheels. The front axle, on the other hand, is responsible for processing road shocks and steering. The driving torque produces thrust in the wheels. This force must be transmitted to the chassis frame and body to move the vehicle. These are the most affordable types of axles, but they can also lead to problems.
While many axles are manufactured in standard formats, many of them are custom-made for a particular car, allowing for a more individualized look and performance. In addition to being custom-made for the vehicle, axle housing cases can be either a single unit or split like a banjo. The front opening of the axle housing is closed by a differential carrier, while the rear opening is covered by a spherical cover plate.
Different types of axles have different strengths and weaknesses. Typically, the weight of an axle should be proportionate to the vehicle’s weight and the pressure it will exert on the road. When the axle weight is higher, a vehicle will not be as efficient, as it will use more fuel to move at the same speed. This can cut into profit margins.
Different types of axles can have various purposes, but one main function is to transfer power from the engine to the wheels. These axles need to be durable and able to withstand the weight of a vehicle, as well as withstand accelerated forces.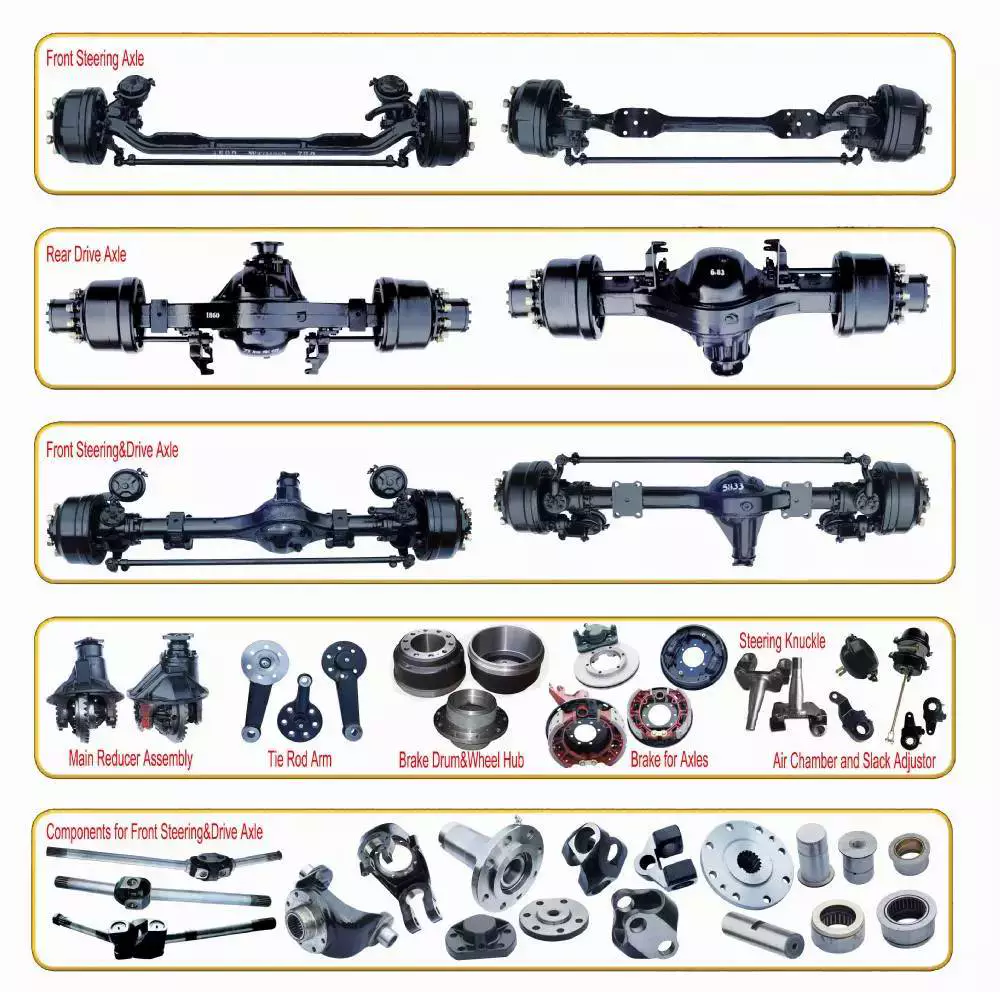
Repair
If you notice any signs of wear or damage to the axle on your vehicle, you may need to repair it. This type of repair will not only protect the wheels, but will also increase the overall performance of your car. A good repair job can help you enjoy smoother driving and better control of your tires. However, there are certain precautions you must take before starting the repair.
To fix an axle, a mechanic must first determine the cause of the problem. This can involve replacing worn or broken parts, replacing them with new ones, and adjusting the car’s alignment. The mechanic will then tighten the fasteners and tires according to manufacturer specifications. Finally, the car will be road tested to ensure that everything is working properly.
A CV joint is also a common item to be replaced. The lubrication in these joints can become dirty, which causes them to wear out. A failing joint will make a clicking sound when it turns sharply. A failed joint may also affect the differential. This part of the car’s drivetrain contains a set of gears that transfer the rotational power of the engine to the wheels. Over time, the gears can wear out, resulting in high labour and replacement costs.
If your car has bent axles, it is important to repair them as soon as possible. Even if the damage is slight, the problem can lead to additional damage to your car’s wheels, CV joints, or other powertrain components. Thankfully, some insurance policies cover the cost of axle repair after an accident.
The average cost to repair an axle varies from about $450 to $900 before taxes. The cost depends on the size of the vehicle and the type of labor required. A rear axle repair can cost up to $700. In addition to labor fees, parts can cost as little as $50 to 70. The cost of the repair can also vary depending on the type of vehicle and the parts used.
If you notice bad vibrations in your vehicle, it’s likely that the axle has been damaged. These vibrations can cause problems with the handling of your vehicle and your comfort while driving.

editor by czh 2022-11-28